Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and edge retention compared to carbon steel, making it ideal for chisel blades. Carbon steel is easier to sharpen and more cost-effective but may dull faster and require more frequent maintenance.
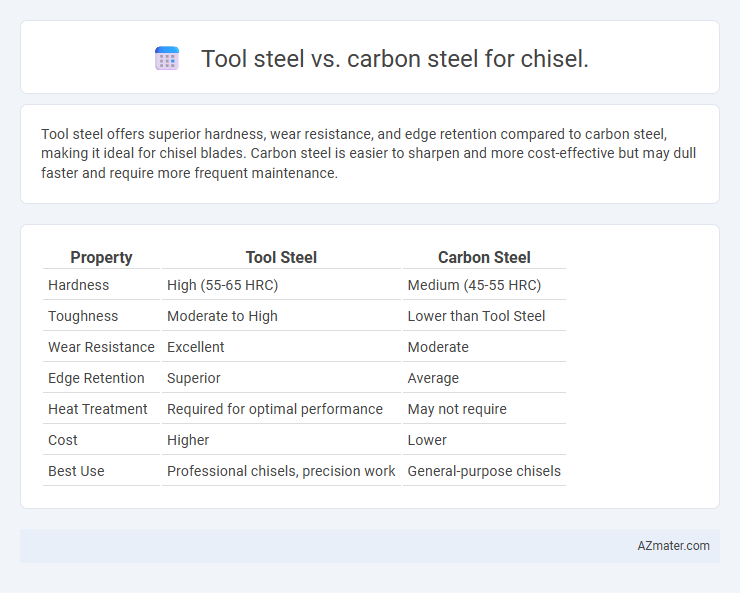
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (55-65 HRC) | Medium (45-55 HRC) |
| Toughness | Moderate to High | Lower than Tool Steel |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Edge Retention | Superior | Average |
| Heat Treatment | Required for optimal performance | May not require |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Best Use | Professional chisels, precision work | General-purpose chisels |
Introduction: Tool Steel vs Carbon Steel for Chisels
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and edge retention compared to carbon steel, making it ideal for chisels subjected to heavy-duty tasks and prolonged use. Carbon steel, while easier to sharpen and more affordable, tends to lose its edge more quickly under repeated impact and requires frequent maintenance. Selecting tool steel enhances chisel durability and performance, especially in professional woodworking and metalworking applications.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Tool steel contains higher amounts of alloying elements such as chromium, vanadium, and molybdenum compared to carbon steel, which primarily consists of iron and carbon. The increased alloy content in tool steel enhances hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain a sharp edge, making it suitable for chisels subjected to heavy impact. In contrast, carbon steel offers greater toughness but lower hardness, limiting its performance in high-stress applications where edge retention is critical.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
Tool steel exhibits significantly higher hardness and superior wear resistance compared to carbon steel, making it ideal for chisels subjected to heavy-duty use and prolonged impact. High alloy content in tool steel, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium, enhances its ability to maintain a sharp edge and resist deformation under stress. In contrast, carbon steel offers moderate hardness and wear resistance suitable for general-purpose chisels but dulls more quickly during intensive applications.
Edge Retention and Sharpening
Tool steel offers superior edge retention compared to carbon steel, making it ideal for chisels requiring prolonged sharpness during intensive woodworking tasks. Its alloy composition enhances hardness and wear resistance, reducing the frequency of sharpening needed in demanding applications. Carbon steel chisels are easier to sharpen but tend to lose their edge faster, requiring more regular maintenance to maintain peak performance.
Toughness and Durability
Tool steel exhibits superior toughness and durability compared to carbon steel, making it ideal for chisels subjected to heavy impact and repeated stress. Its alloy composition enhances resistance to wear, deformation, and heat, ensuring the tool maintains sharpness and structural integrity over extended use. Carbon steel chisels, while harder and easier to sharpen, are more prone to chipping and wear under rigorous conditions.
Rust Resistance and Maintenance
Tool steel exhibits superior rust resistance compared to carbon steel due to its higher alloy content, including chromium and vanadium, which form a protective oxide layer. Carbon steel chisels require more frequent maintenance, such as oiling and drying, to prevent corrosion, whereas tool steel chisels maintain sharpness and durability with less intensive care. Selecting tool steel for chisels reduces the risk of rust and extends tool life, making it ideal for professional use.
Performance in Woodworking Applications
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance compared to carbon steel, making it ideal for chisels used in demanding woodworking tasks. Its enhanced ability to retain a sharp edge under high-impact and high-friction conditions results in precise cuts and longer tool life. Carbon steel chisels, while easier to sharpen, may dull faster and require more frequent maintenance, impacting overall performance in detailed woodworking applications.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Tool steel chisels typically cost more than carbon steel due to their enhanced hardness and wear resistance, which justify the higher price in professional or heavy-duty applications. Carbon steel chisels are more widely available and offer a budget-friendly option, making them ideal for general-purpose use or hobbyists. Availability of tool steel can be limited to specialized suppliers, whereas carbon steel is commonly stocked by most hardware stores, impacting overall cost and accessibility.
User Preferences and Professional Recommendations
Tool steel is preferred by professionals for chisels due to its superior hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain a sharp edge over extended use, making it ideal for heavy-duty woodworking and metalworking tasks. Carbon steel chisels are favored by users seeking easier sharpening and a more cost-effective option, but they require more frequent maintenance and may lose sharpness faster. Professional recommendations emphasize tool steel for longevity and performance, while hobbyists might choose carbon steel for affordability and ease of use.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Steel for Your Chisel
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and edge retention compared to carbon steel, making it ideal for chisels requiring long-lasting sharpness and durability. Carbon steel is easier to sharpen and more cost-effective but may require frequent maintenance and re-sharpening due to lower wear resistance. Selecting tool steel for heavy-duty chisels ensures enhanced performance, while carbon steel suits lighter, budget-friendly applications.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Carbon steel for Chisel
 azmater.com
azmater.com