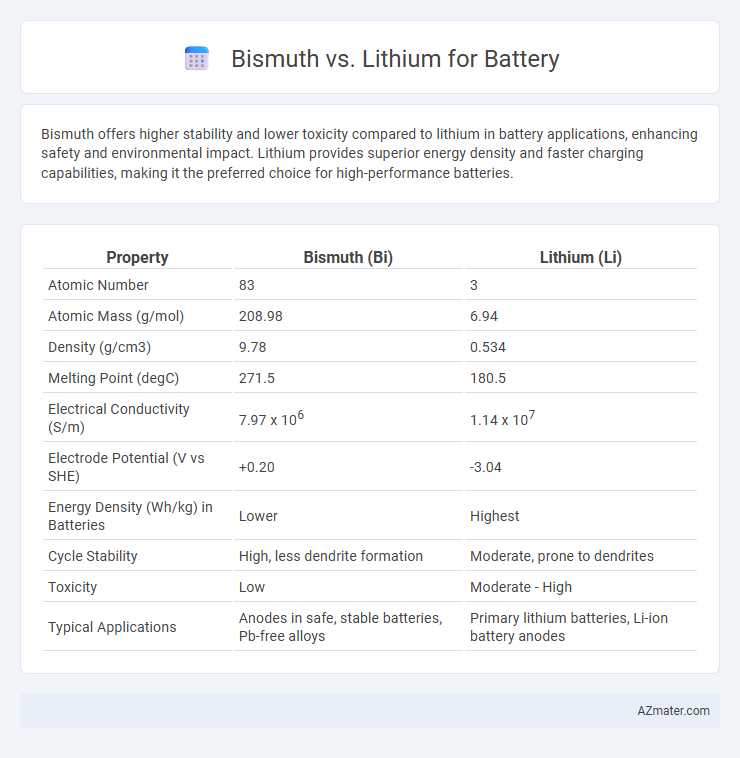
Bismuth offers higher stability and lower toxicity compared to lithium in battery applications, enhancing safety and environmental impact. Lithium provides superior energy density and faster charging capabilities, making it the preferred choice for high-performance batteries.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bismuth (Bi) | Lithium (Li) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 83 | 3 |
| Atomic Mass (g/mol) | 208.98 | 6.94 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 9.78 | 0.534 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 271.5 | 180.5 |
| Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | 7.97 x 106 | 1.14 x 107 |
| Electrode Potential (V vs SHE) | +0.20 | -3.04 |
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) in Batteries | Lower | Highest |
| Cycle Stability | High, less dendrite formation | Moderate, prone to dendrites |
| Toxicity | Low | Moderate - High |
| Typical Applications | Anodes in safe, stable batteries, Pb-free alloys | Primary lithium batteries, Li-ion battery anodes |
Introduction to Bismuth and Lithium in Battery Technology
Bismuth and lithium are key materials in battery technology, each offering unique electrochemical properties. Lithium, widely used in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, provides high energy density and lightweight characteristics essential for portable electronics and electric vehicles. Bismuth, emerging as a promising alternative anode material, offers environmental benefits with low toxicity and excellent cycling stability, making it suitable for next-generation energy storage systems.
Chemical Properties: Bismuth vs Lithium
Bismuth exhibits higher atomic weight and lower electrochemical potential compared to lithium, resulting in greater stability but reduced energy density in battery applications. Lithium's low atomic mass and high electrochemical potential enable superior charge capacity and faster ion mobility, making it ideal for high-performance rechargeable batteries. Chemical inertness of bismuth provides enhanced safety and corrosion resistance, whereas lithium's high reactivity necessitates stringent handling precautions.
Energy Density Comparison
Bismuth-based batteries generally exhibit lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries, which typically achieve energy densities of 150-250 Wh/kg. Lithium batteries benefit from lithium's light atomic weight and high electrochemical potential, enabling greater energy storage per unit mass. Although bismuth offers advantages in terms of environmental friendliness and safety, its heavier atomic mass limits the overall energy density in practical battery applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bismuth batteries offer lower environmental toxicity and greater sustainability compared to lithium batteries, as bismuth is more abundant and less harmful to ecosystems during extraction and disposal. Lithium mining often causes habitat destruction, water depletion, and pollution, raising significant ecological concerns. Utilizing bismuth-based batteries can enhance green energy storage solutions by reducing the carbon footprint and promoting resource renewability in battery manufacturing.
Battery Lifespan and Cycle Stability
Bismuth-based batteries demonstrate superior cycle stability and longer battery lifespan compared to lithium-ion counterparts due to their low volume expansion and robust electrode integrity during charge-discharge cycles. Lithium-ion batteries typically experience capacity degradation caused by electrolyte decomposition and structural changes in electrode materials, limiting cycle life. The enhanced durability of bismuth electrodes contributes to extended battery longevity, making them ideal for applications requiring high cycle stability and long-term energy storage.
Safety and Thermal Management
Bismuth-based batteries exhibit superior safety compared to lithium-ion counterparts due to their lower reactivity and reduced risk of thermal runaway, minimizing fire hazards in energy storage applications. Their high thermal conductivity enhances heat dissipation, improving thermal management and maintaining stable operating temperatures during charge-discharge cycles. In contrast, lithium batteries require complex cooling systems to prevent overheating and potential thermal failures, making bismuth an attractive alternative for safer, more reliable battery technologies.
Cost Analysis: Bismuth vs Lithium Batteries
Bismuth batteries offer a cost advantage over lithium batteries due to the lower raw material expenses and greater abundance of bismuth, which reduces overall production costs. Lithium batteries, while benefiting from high energy density and widespread use, face price volatility linked to lithium resource scarcity and geopolitical factors. Evaluating total cost of ownership, bismuth-based batteries provide a more stable and potentially lower-cost alternative for large-scale and long-term energy storage applications.
Current Applications in Energy Storage
Bismuth-based batteries have gained attention for grid-scale energy storage due to their low toxicity, abundance, and stable cycling performance, making them suitable for large, stationary applications. Lithium-ion batteries dominate portable electronics and electric vehicles thanks to their high energy density, long cycle life, and fast charge capabilities. While lithium remains the preferred choice for mobile applications, bismuth offers a promising alternative for safer, cost-effective grid storage solutions.
Research Developments and Innovations
Research developments in battery technology highlight Bismuth as a promising alternative to Lithium due to its higher safety profile, abundant availability, and environmental friendliness. Innovations in Bismuth-based anodes have demonstrated improved cycle stability and capacity retention, addressing challenges of volume expansion and dendrite formation found in Lithium-ion batteries. Recent studies also emphasize the integration of Bismuth with novel electrolytes and nanostructured materials, enhancing energy density and charging speed in next-generation energy storage systems.
Future Prospects and Market Trends
Bismuth-based batteries are gaining attention for their enhanced safety, environmental friendliness, and potential for stable cycling performance compared to lithium-ion counterparts, which dominate current markets due to high energy density and established infrastructure. Emerging research focuses on bismuth's application in sodium-ion and lead-acid battery technologies, targeting grid storage and environmentally sustainable energy solutions amid rising lithium supply constraints and cost volatility. Market trends indicate growing investment in alternative battery chemistries like bismuth to diversify supply chains and meet increasing demand for safer, longer-lasting energy storage in electric vehicles and renewable integration.
Infographic: Bismuth vs Lithium for Battery
 azmater.com
azmater.com