Ruthenium offers superior wear resistance and corrosion stability compared to platinum, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts. Platinum provides excellent conductivity but is softer, leading to faster degradation under repeated mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
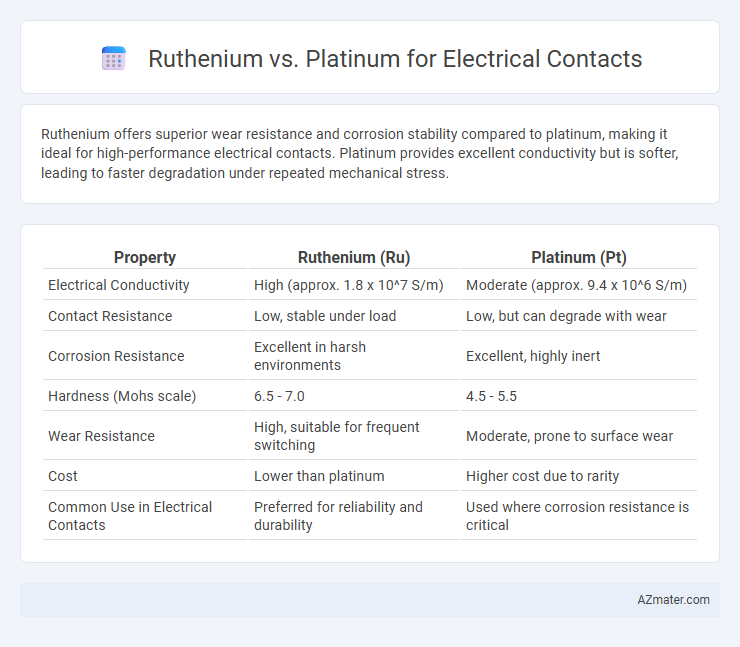
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Platinum (Pt) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High (approx. 1.8 x 10^7 S/m) | Moderate (approx. 9.4 x 10^6 S/m) |
| Contact Resistance | Low, stable under load | Low, but can degrade with wear |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in harsh environments | Excellent, highly inert |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 6.5 - 7.0 | 4.5 - 5.5 |
| Wear Resistance | High, suitable for frequent switching | Moderate, prone to surface wear |
| Cost | Lower than platinum | Higher cost due to rarity |
| Common Use in Electrical Contacts | Preferred for reliability and durability | Used where corrosion resistance is critical |
Introduction to Ruthenium and Platinum in Electrical Contacts
Ruthenium and platinum are precious metals widely used in electrical contacts due to their excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Ruthenium offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-load contacts and applications requiring long-term durability. Platinum provides exceptional chemical stability and conductivity, ensuring reliable performance in low-voltage switching and harsh environments.
Key Properties of Ruthenium and Platinum
Ruthenium exhibits exceptional hardness, excellent corrosion resistance, and high melting point, making it ideal for durable and reliable electrical contacts. Platinum offers superior electrical conductivity, outstanding resistance to oxidation, and excellent stability under high temperatures. While ruthenium provides enhanced wear resistance and cost efficiency, platinum ensures better consistent conductivity and longevity in harsh environments.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Ruthenium and platinum differ notably in electrical conductivity, with platinum exhibiting higher electrical conductivity typically around 9.4 x 10^6 S/m compared to ruthenium's approximately 2.1 x 10^7 S/m; however, ruthenium offers superior resistance to oxidation and wear. Platinum's conductivity ensures efficient current flow in electrical contacts, but ruthenium's durability under harsh conditions enhances long-term performance and reliability. The choice between these metals depends on balancing conductivity requirements with environmental and mechanical stress factors in electrical contact applications.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Ruthenium exhibits superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to platinum, making it highly effective for electrical contacts operating in harsh environments. Its ability to maintain conductivity and structural integrity under high-temperature conditions reduces contact degradation and extends service life. Platinum, while corrosion-resistant, is more susceptible to surface oxidation under extreme conditions, leading to decreased performance in long-term electrical applications.
Wear and Durability Performance
Ruthenium offers superior wear resistance and durability in electrical contacts due to its hardness and excellent corrosion resistance, which reduces material degradation under repeated switching cycles. Platinum, while highly conductive and corrosion-resistant, tends to exhibit greater wear and material transfer in high-load applications, leading to decreased contact performance over time. The combination of ruthenium's mechanical strength and stable electrical properties makes it more suitable for demanding electrical contacts requiring long-term reliability.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Ruthenium offers a cost-effective alternative to platinum for electrical contacts due to its lower price per gram and greater availability in commercial markets. Platinum's higher market price and limited supply increase the overall cost of manufacturing electrical components. Ruthenium's abundance in industrial mining and better price stability make it a preferred choice for cost-sensitive electrical contact applications.
Application Suitability in Electrical Contacts
Ruthenium offers superior wear resistance and stable electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical contacts in harsh environments and low current applications. Platinum provides excellent corrosion resistance and thermal stability, suitable for contacts exposed to extreme temperatures and chemically aggressive conditions. The choice between ruthenium and platinum depends on specific application demands such as electrical load, environmental exposure, and longevity requirements in electrical switches, relays, and connectors.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Ruthenium offers superior resistance to oxidation and corrosion compared to platinum, enhancing electrical contact durability in harsh environments while minimizing environmental degradation. Ruthenium's higher melting point and hardness contribute to reduced material wear and lower risk of hazardous particle release during use or disposal. Platinum, although highly stable and non-toxic, allows for greater resource extraction impacts due to its extensive mining requirements and lower recyclability in contact applications.
Industry Standards and Recommendations
Ruthenium and platinum are both valued in electrical contacts for their corrosion resistance and conductivity, yet industry standards like IEC 60512 recommend platinum for high-reliability applications due to its superior oxidation resistance. Ruthenium offers enhanced hardness and wear resistance, making it suitable for contacts subjected to frequent mechanical operations, which aligns with IPC standards focusing on durability. Electrical component manufacturers often follow guidelines that suggest using platinum in environments requiring stable performance under high temperatures, while ruthenium is preferred in lower-load circuits where cost efficiency and durability are prioritized.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Ruthenium and Platinum
Ruthenium offers superior hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical contacts subjected to harsh environments and high wear. Platinum provides excellent conductivity and stability but is softer, which may lead to quicker degradation in high-friction applications. For durable electrical contacts with long service life, ruthenium is generally the preferred choice, while platinum suits applications prioritizing conductivity and chemical stability.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Platinum for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com