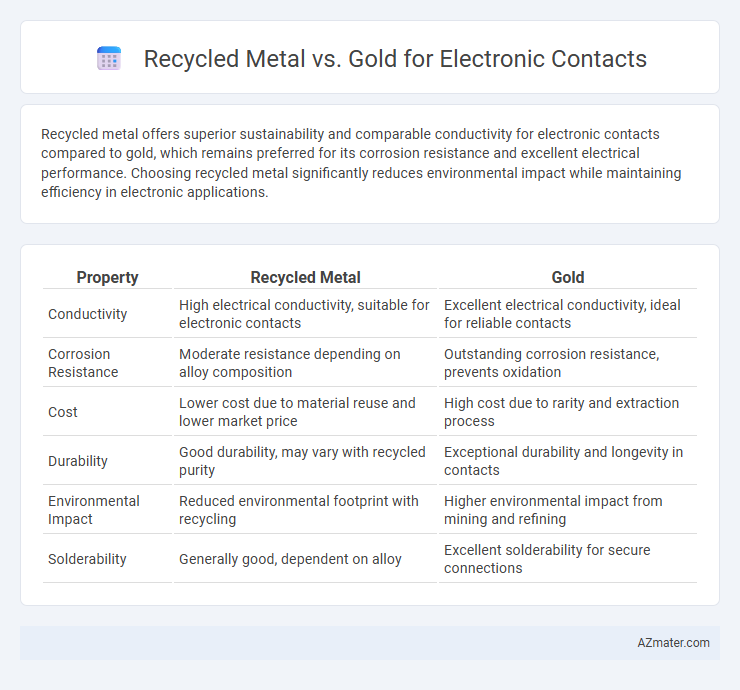
Recycled metal offers superior sustainability and comparable conductivity for electronic contacts compared to gold, which remains preferred for its corrosion resistance and excellent electrical performance. Choosing recycled metal significantly reduces environmental impact while maintaining efficiency in electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Metal | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity, suitable for electronic contacts | Excellent electrical conductivity, ideal for reliable contacts |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate resistance depending on alloy composition | Outstanding corrosion resistance, prevents oxidation |
| Cost | Lower cost due to material reuse and lower market price | High cost due to rarity and extraction process |
| Durability | Good durability, may vary with recycled purity | Exceptional durability and longevity in contacts |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced environmental footprint with recycling | Higher environmental impact from mining and refining |
| Solderability | Generally good, dependent on alloy | Excellent solderability for secure connections |
Introduction: Importance of Material Choice in Electronic Contacts
Material choice in electronic contacts directly influences device reliability, conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Recycled metal offers sustainability advantages and cost efficiency while maintaining essential electrical properties. Gold remains preferred for its superior conductivity, oxidation resistance, and long-term performance in critical electronic applications.
Overview of Recycled Metal in Electronics
Recycled metal plays a crucial role in electronics by providing a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to gold for electronic contacts. Metals such as copper, silver, and nickel reclaimed from electronic waste retain excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for connectors and circuit pathways. The use of recycled metals reduces environmental impact, lowers dependency on mining, and supports circular economy practices in the electronics industry.
Gold in Electronic Contacts: Key Properties
Gold is preferred in electronic contacts due to its excellent corrosion resistance and superior electrical conductivity, ensuring reliable signal transmission and long-term durability. Its non-tarnishing nature prevents the formation of oxides that can degrade contact performance, which is critical in high-reliability applications. Recycled metals often lack the purity and stability of gold, making gold indispensable for maintaining consistent contact quality in sensitive electronic components.
Electrical Conductivity: Gold vs Recycled Metal
Gold exhibits exceptional electrical conductivity, maintaining stable performance and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for electronic contacts. Recycled metals often contain impurities or varying compositions that can reduce conductivity and increase susceptibility to corrosion. Choosing gold ensures consistent low electrical resistance and reliable signal transmission compared to recycled metals with unpredictable conductive properties.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Recycled metal used in electronic contacts often exhibits enhanced corrosion resistance due to advanced purification and alloying processes that reduce impurities, whereas gold remains the industry benchmark for its exceptional oxidation resistance and stable conductivity over time. Gold's inert surface prevents tarnish and corrosion, ensuring reliable long-term performance even in harsh environments, while recycled metals may require protective coatings to achieve similar durability. The longevity of gold contacts typically surpasses that of recycled metals, making gold the preferred choice for critical applications demanding consistent electrical integrity and minimal maintenance.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Resource Use
Recycled metal significantly reduces environmental impact compared to gold in electronic contacts by minimizing mining activities that deplete natural resources and generate toxic waste. Utilizing recycled metals lowers greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption, promoting sustainability through circular economy practices. Conversely, gold mining is resource-intensive, causing habitat destruction and water pollution, making recycled metals a more eco-friendly and sustainable choice for electronic applications.
Cost Comparison: Economic Implications
Recycled metal offers a significantly lower cost alternative to gold for electronic contacts, reducing raw material expenses by up to 70%. Gold maintains superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, but its high market price and volatility drive up production costs. Economic implications favor recycled metals in large-scale manufacturing, balancing performance with cost-efficiency for sustainable electronics.
Performance Reliability in High-Demand Applications
Recycled metal, particularly recycled copper and silver alloys, offers comparable electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance to gold in electronic contacts, making it a cost-effective alternative for high-demand applications. Gold remains the benchmark for performance reliability due to its exceptional resistance to oxidation and stable conductivity under extreme environmental conditions such as high temperature and humidity. While recycled metals can meet many operational standards, gold's superior long-term stability ensures consistent signal integrity and minimal contact degradation in critical electronics.
Trends in Industry Adoption and Innovation
Recycled metals are increasingly preferred over gold for electronic contacts due to their cost-effectiveness and sustainability, driving a significant shift in industry adoption. Innovations in metallurgical processing enhance the conductivity and corrosion resistance of recycled metals, making them competitive alternatives to traditional gold contacts. Major electronics manufacturers are investing in circular economy practices, integrating recycled metal contacts to reduce environmental impact while maintaining performance standards.
Future Outlook: Advancements and Alternatives
Recycled metal offers a sustainable and cost-effective approach for electronic contacts by utilizing existing materials and reducing environmental impact, while gold remains preferred for its exceptional conductivity and corrosion resistance. Future advancements focus on improving the purity and performance of recycled metals through innovative refining techniques and the integration of alternative conductive materials like graphene and silver nanowires. Emerging technologies may shift industry reliance toward hybrid composites combining recycled metals with advanced coatings to enhance durability and conductivity in next-generation electronic devices.
Infographic: Recycled metal vs Gold for Electronic contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com