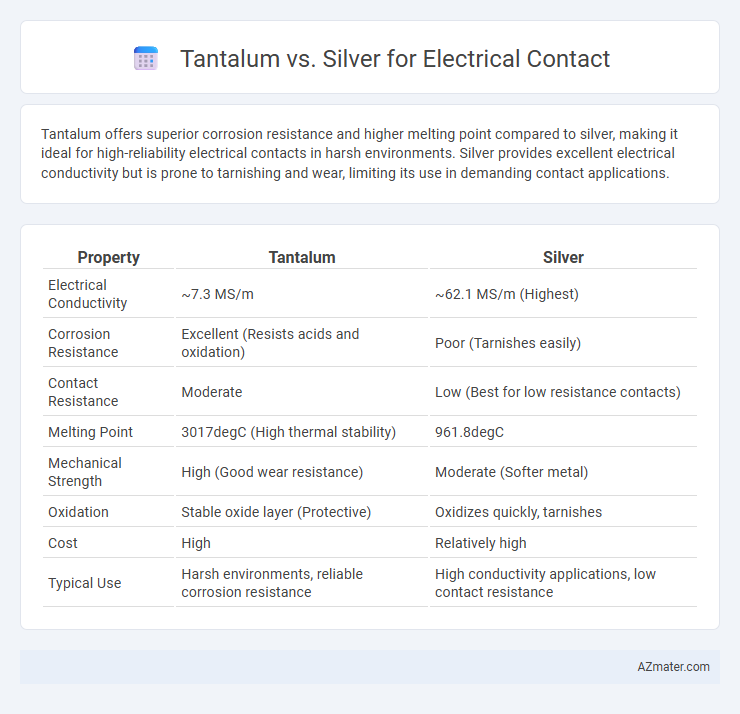
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and higher melting point compared to silver, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical contacts in harsh environments. Silver provides excellent electrical conductivity but is prone to tarnishing and wear, limiting its use in demanding contact applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tantalum | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | ~7.3 MS/m | ~62.1 MS/m (Highest) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Resists acids and oxidation) | Poor (Tarnishes easily) |
| Contact Resistance | Moderate | Low (Best for low resistance contacts) |
| Melting Point | 3017degC (High thermal stability) | 961.8degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High (Good wear resistance) | Moderate (Softer metal) |
| Oxidation | Stable oxide layer (Protective) | Oxidizes quickly, tarnishes |
| Cost | High | Relatively high |
| Typical Use | Harsh environments, reliable corrosion resistance | High conductivity applications, low contact resistance |
Introduction to Tantalum and Silver in Electrical Contacts
Tantalum and silver are prominent materials used in electrical contacts due to their distinctive conductive and corrosion-resistant properties. Tantalum offers excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point, and stable conductivity, making it suitable for harsh environments and high-reliability applications. Silver provides superior electrical and thermal conductivity, ensuring minimal contact resistance and efficient current flow in low-corrosion settings.
Electrical Conductivity: Tantalum vs Silver
Silver exhibits the highest electrical conductivity among metals, with a conductivity of approximately 63 x 10^6 S/m, making it ideal for electrical contacts requiring minimal resistance and efficient current flow. Tantalum, while corrosion-resistant and mechanically robust, has significantly lower electrical conductivity at around 7.4 x 10^6 S/m, resulting in higher contact resistance and reduced efficiency compared to silver. In applications prioritizing maximum electrical conductivity, silver outperforms tantalum despite tantalum's superior durability and resistance to oxidation.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Tantalum exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to silver in electrical contacts, especially in harsh environments with exposure to acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents. Its stable oxide film prevents degradation and ensures long-term electrical performance, while silver tends to tarnish and corrode more readily under similar conditions. This makes tantalum a preferred material for applications requiring durable, reliable conductivity with minimal maintenance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Tantalum exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to silver, making it highly resistant to deformation under mechanical stress in electrical contacts. Its exceptional durability enables longer service life and better performance in harsh environments, minimizing wear and erosion. While silver offers excellent electrical conductivity, tantalum's enhanced hardness and corrosion resistance ensure more reliable and stable contact performance over time.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan for electrical contacts but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to silver, which remains more affordable and widely available. Silver's excellent conductivity and abundant supply make it the preferred choice in cost-sensitive applications despite its susceptibility to tarnishing. The analysis of cost and availability favors silver for large-scale production, while tantalum suits specialized, high-performance electrical contacts where durability justifies the premium.
Thermal Conductivity Considerations
Tantalum offers moderate thermal conductivity around 57 W/m*K, ensuring reliable heat dissipation in high-temperature electrical contacts without significant performance loss. Silver outperforms with thermal conductivity approximately 429 W/m*K, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid heat transfer to prevent overheating and maintain contact stability. Selecting between tantalum and silver depends on balancing thermal management needs with factors like corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity in electrical contact design.
Wear Resistance in Electrical Applications
Tantalum exhibits superior wear resistance compared to silver in electrical contact applications, making it ideal for environments with frequent mechanical operations. Its oxide layer enhances durability and prevents material degradation, ensuring prolonged electrical conductivity under stress. Silver, while highly conductive, tends to wear faster due to softer mechanical properties and susceptibility to surface oxidation, reducing its lifespan in high-wear conditions.
Suitability for High-Frequency Circuits
Tantalum exhibits superior corrosion resistance and stable electrical properties, making it highly suitable for high-frequency circuits requiring consistent conductivity and minimal signal loss. Silver, known for the highest electrical conductivity among metals, provides excellent performance in low-frequency applications but can suffer from tarnishing and increased contact resistance at high frequencies. For high-frequency circuits, tantalum's capacity to maintain reliable contacts under thermal and electrical stress offers a significant advantage over silver.
Environmental and Safety Aspects
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and is highly stable, reducing the risk of environmental contamination and ensuring long-term safety in electrical contacts. Silver, while providing excellent electrical conductivity, is prone to tarnishing and can release harmful silver compounds upon corrosion, posing environmental and health hazards. The sustainable mining and recycling processes for tantalum further enhance its environmental profile compared to silver, which often involves more intensive extraction methods with greater ecological impact.
Choosing the Right Material: Tantalum or Silver
Tantalum offers excellent corrosion resistance and stability under high temperatures, making it ideal for electrical contacts in harsh environments, while silver excels in conductivity and low contact resistance for high-performance applications. The choice between tantalum and silver depends on factors such as operating temperature, exposure to corrosive elements, and required electrical conductivity. Silver is preferable for low-voltage, high-current scenarios demanding superior electrical performance, whereas tantalum suits applications requiring durability and reliability under extreme conditions.
Infographic: Tantalum vs Silver for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com