Niobium enhances alloy strength and corrosion resistance, outperforming traditional steel in high-performance applications. Its lightweight properties improve durability and thermal stability compared to standard steel alloys.
Table of Comparison
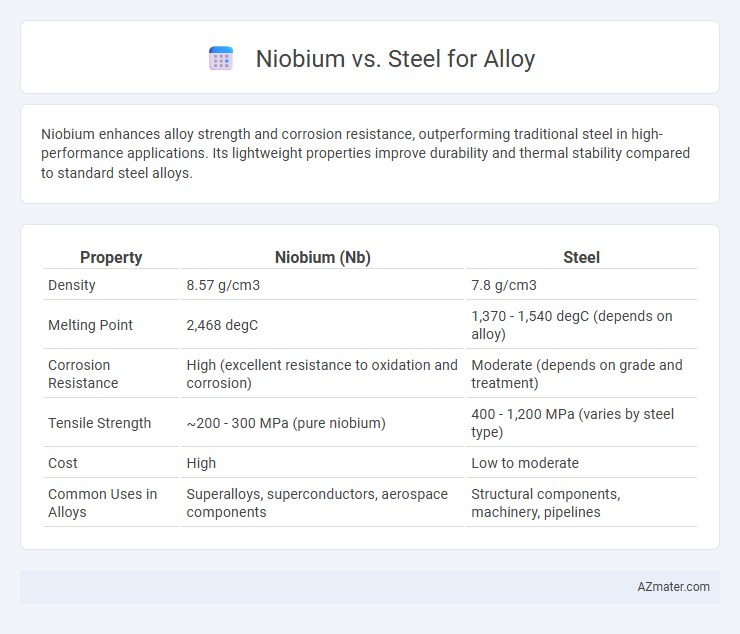
| Property | Niobium (Nb) | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.57 g/cm3 | 7.8 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2,468 degC | 1,370 - 1,540 degC (depends on alloy) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion) | Moderate (depends on grade and treatment) |
| Tensile Strength | ~200 - 300 MPa (pure niobium) | 400 - 1,200 MPa (varies by steel type) |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
| Common Uses in Alloys | Superalloys, superconductors, aerospace components | Structural components, machinery, pipelines |
Introduction to Niobium and Steel Alloys
Niobium is a rare, corrosion-resistant metal primarily used to enhance the strength and ductility of steel alloys, especially in high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels. Steel alloys, composed mainly of iron and carbon, rely on niobium additions to improve weldability, tensile strength, and resistance to wear and fatigue. The integration of niobium in steel alloys significantly optimizes mechanical properties and performance in critical applications such as aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Chemical Composition: Niobium vs Steel
Niobium is a transition metal with a chemical composition characterized by a high melting point and excellent corrosion resistance, typically containing 93.3% niobium and trace amounts of carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen. Steel is primarily an iron-carbon alloy, with carbon content varying from 0.02% to 2.14%, alongside elements such as manganese, silicon, and occasionally chromium or nickel for enhanced strength and corrosion resistance. The addition of niobium to steel alloys refines grain structure and increases strength by forming stable carbides and nitrides, significantly improving mechanical properties and weldability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Niobium alloy offers superior tensile strength and enhanced toughness compared to conventional steel alloys, making it ideal for high-stress applications. Its excellent resistance to fatigue and fracture enables improved durability under cyclic loading, surpassing most steel grades. Niobium's lower density also contributes to a higher strength-to-weight ratio, providing weight savings without compromising mechanical performance.
Corrosion Resistance Differences
Niobium significantly enhances the corrosion resistance of steel alloys by forming stable and protective oxide layers that prevent surface degradation, especially in aggressive environments. Steel alone is prone to various types of corrosion such as oxidation and pitting, whereas niobium-alloyed steel exhibits superior resistance against acid-induced corrosion and high-temperature oxidation. This makes niobium-containing alloys more durable in chemical processing, marine, and extreme industrial applications.
Applications in Industry
Niobium enhances the strength and corrosion resistance of steel alloys, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and construction industries. Its addition improves weldability and toughness, enabling the production of lightweight, high-performance steel components in pipelines, pressure vessels, and structural frameworks. Niobium-alloyed steels also excel in cryogenic applications due to their superior low-temperature strength and flexibility.
Weight and Density Analysis
Niobium offers a significantly lower density of approximately 8.57 g/cm3 compared to steel's average density of around 7.85 g/cm3, making steel slightly lighter by weight for similar volumes; however, niobium's unique properties allow for weight reduction in specialized alloy applications due to enhanced strength-to-weight ratios. Alloying niobium with steel improves corrosion resistance and mechanical strength without a substantial increase in overall density, optimizing performance in high-stress, lightweight structural components. The precise density and weight benefits depend on niobium content, typically enhancing steel alloys for aerospace and automotive industries where material efficiency is critical.
Weldability and Fabrication
Niobium-enhanced steel alloys exhibit superior weldability due to their refined grain structure, which minimizes heat-affected zone cracking and improves joint strength. Fabrication processes benefit from niobium's ability to increase toughness and formability without compromising corrosion resistance, enabling more precise and durable welded components. Steel alloys with niobium additions are preferred in heavy-duty applications requiring reliable weld integrity and enhanced mechanical properties during fabrication.
Cost and Availability
Niobium alloy offers superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to traditional steel alloys, but it typically comes at a higher cost due to its rarity and complex extraction processes. Steel remains more cost-effective and widely available globally, benefiting from established manufacturing infrastructure and abundant raw materials. The choice between niobium and steel alloys depends largely on budget constraints and performance requirements in applications such as aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Niobium-enhanced steel alloys significantly improve strength and durability, resulting in lighter structures that reduce material consumption and lower carbon emissions in construction and automotive industries. Niobium's ability to increase steel efficiency allows for less energy-intensive production processes, contributing to reduced environmental impact compared to conventional steel alloys. The recyclability of niobium-steel alloys further supports sustainability by minimizing waste and conserving natural resources throughout their lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Needs
Niobium alloys offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and exceptional corrosion resistance compared to traditional steel alloys, making them ideal for aerospace and chemical processing applications. Steel alloys provide cost-effective durability and versatility suitable for construction and automotive industries, where high strength and toughness are essential. Selecting the right alloy depends on balancing performance requirements with budget constraints and environmental factors specific to the intended use.
Infographic: Niobium vs Steel for Alloy
 azmater.com
azmater.com