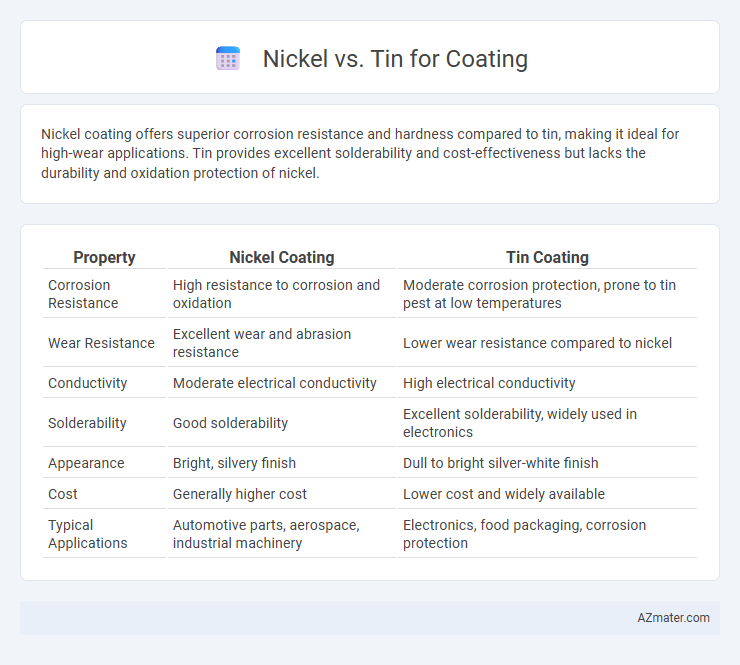
Nickel coating offers superior corrosion resistance and hardness compared to tin, making it ideal for high-wear applications. Tin provides excellent solderability and cost-effectiveness but lacks the durability and oxidation protection of nickel.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nickel Coating | Tin Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to corrosion and oxidation | Moderate corrosion protection, prone to tin pest at low temperatures |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear and abrasion resistance | Lower wear resistance compared to nickel |
| Conductivity | Moderate electrical conductivity | High electrical conductivity |
| Solderability | Good solderability | Excellent solderability, widely used in electronics |
| Appearance | Bright, silvery finish | Dull to bright silver-white finish |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Lower cost and widely available |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, aerospace, industrial machinery | Electronics, food packaging, corrosion protection |
Introduction to Metal Coatings
Metal coatings such as nickel and tin play crucial roles in enhancing surface properties like corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Nickel coatings offer superior hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring durability. Tin coatings provide excellent solderability and corrosion protection, commonly used in electronics and food packaging industries.
Properties of Nickel Coatings
Nickel coatings offer excellent corrosion resistance, high hardness, and superior wear resistance, making them ideal for protecting metal surfaces in harsh environments. Their ability to provide a smooth, aesthetically appealing finish combined with good solderability and corrosion protection surpasses many tin coatings. Nickel's magnetic properties and high melting point also contribute to its widespread use in industrial applications requiring durability and heat resistance.
Properties of Tin Coatings
Tin coatings exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and provide a non-toxic, solderable surface ideal for electronic components and food packaging. Their high thermal conductivity and low contact resistance make them suitable for electrical applications where reliable conductivity is essential. Furthermore, tin's softness allows for easy forming and shaping without cracking, enhancing its protective versatility compared to harder coatings like nickel.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Nickel coatings exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to tin, especially in harsh environments with exposure to moisture and chemicals. Nickel forms a dense, protective oxide layer that effectively prevents rust and degradation, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications. Tin, while providing some corrosion protection and excellent solderability, is more prone to corrosion under acidic or alkaline conditions, limiting its durability in aggressive environments.
Electrical Conductivity: Nickel vs Tin
Tin offers higher electrical conductivity than nickel, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring efficient current flow. Nickel, while providing excellent corrosion resistance and hardness, has lower electrical conductivity, which can impede performance in sensitive electronic components. Selecting between nickel and tin coatings depends on balancing conductivity needs with durability and environmental factors.
Cost Analysis: Nickel and Tin Coatings
Nickel coatings typically incur higher initial costs due to more complex plating processes and raw material prices, whereas tin coatings are generally more affordable and suitable for budget-sensitive applications. The durability and corrosion resistance of nickel often justify its premium price in long-term use, especially in harsh environments. Tin coatings offer cost-efficient corrosion protection for electronic components but may require more frequent reapplication or replacement compared to nickel.
Application Suitability
Nickel coatings offer superior corrosion resistance and hardness, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace components exposed to harsh environments. Tin coatings provide excellent solderability and electrical conductivity, commonly used in electronic connectors and food packaging to prevent contamination. Selecting between nickel and tin depends on the required durability, environmental exposure, and specific industry standards.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Nickel coatings, widely used for corrosion resistance, pose environmental concerns due to toxic byproducts and hazardous waste during plating processes, requiring strict disposal measures. Tin coatings offer a safer alternative with lower toxicity, reduced environmental impact, and easier recycling, making them favorable in applications demanding food-grade and lead-free finishes. Lifecycle assessments reveal tin's superior eco-friendliness by minimizing harmful emissions and occupational health risks compared to conventional nickel plating.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Nickel coatings provide superior durability and wear resistance compared to tin, making them ideal for applications requiring long-lasting protection against corrosion and mechanical abrasion. Nickel's hardness and toughness enable it to withstand heavy wear and harsh environments, extending the lifespan of coated components. Tin, while offering good corrosion resistance, is softer and wears more quickly, limiting its use in high-friction or heavy-load applications.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Needs
Choosing between nickel and tin coatings depends on the specific application requirements such as corrosion resistance, conductivity, and durability. Nickel coatings provide superior hardness, wear resistance, and excellent corrosion protection, making them ideal for industrial and automotive parts. Tin coatings offer good solderability, electrical conductivity, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for electronic components and food-grade applications.
Infographic: Nickel vs Tin for Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com