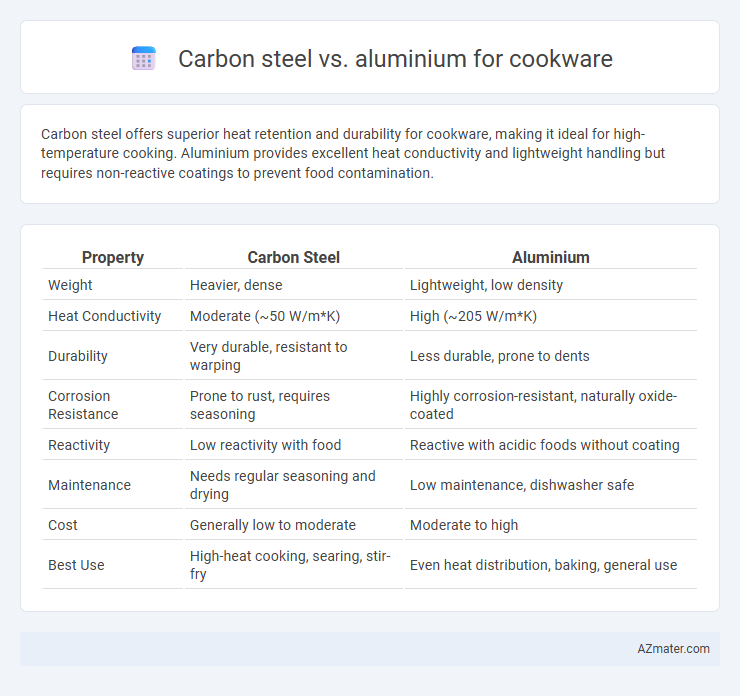
Carbon steel offers superior heat retention and durability for cookware, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking. Aluminium provides excellent heat conductivity and lightweight handling but requires non-reactive coatings to prevent food contamination.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Aluminium |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Heavier, dense | Lightweight, low density |
| Heat Conductivity | Moderate (~50 W/m*K) | High (~205 W/m*K) |
| Durability | Very durable, resistant to warping | Less durable, prone to dents |
| Corrosion Resistance | Prone to rust, requires seasoning | Highly corrosion-resistant, naturally oxide-coated |
| Reactivity | Low reactivity with food | Reactive with acidic foods without coating |
| Maintenance | Needs regular seasoning and drying | Low maintenance, dishwasher safe |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Best Use | High-heat cooking, searing, stir-fry | Even heat distribution, baking, general use |
Introduction to Carbon Steel and Aluminium Cookware
Carbon steel cookware offers exceptional heat conductivity and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking and searing. Aluminium cookware provides excellent lightweight properties and rapid heat distribution, enhancing cooking efficiency and ease of handling. Both materials are popular in kitchens, with carbon steel favored for its seasoning capability and aluminium prized for its affordability and corrosion resistance.
Composition and Material Properties
Carbon steel cookware, composed primarily of iron with a small percentage of carbon (typically 0.5-1.0%), offers high heat conductivity, durability, and excellent heat retention, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking. Aluminium cookware, consisting mainly of pure aluminium or aluminium alloys, provides superior lightweight properties and rapid, even heat distribution but is softer and prone to scratching and warping compared to carbon steel. The differing compositions result in carbon steel's enhanced structural strength and seasoning capability, while aluminium excels in corrosion resistance and ease of handling.
Heat Conductivity and Distribution
Carbon steel exhibits superior heat conductivity and retains heat longer compared to aluminum, enabling even cooking and high-temperature searing. Aluminum offers excellent thermal conductivity, distributing heat rapidly but can lead to uneven cooking if not properly constructed with multilayer bases. Cookware combining aluminum cores with carbon steel exteriors optimizes both fast heat distribution and durable heat retention for versatile culinary performance.
Weight and Maneuverability
Carbon steel cookware is significantly heavier than aluminum, offering increased durability but reduced ease of handling during cooking. Aluminum pans excel in lightweight construction, providing superior maneuverability and quicker response to heat changes, making them ideal for tasks requiring frequent tossing or flipping. The weight difference influences user fatigue and control, with carbon steel preferred for sturdy, long-lasting use and aluminum favored for agility and speed in the kitchen.
Durability and Longevity
Carbon steel cookware offers exceptional durability due to its high carbon content, making it resistant to warping and capable of withstanding high temperatures over extended use. Aluminum cookware, while lightweight and highly conductive, tends to be softer and more prone to dents and scratching, which can reduce its longevity. Properly seasoned carbon steel pans develop a natural non-stick surface and can last decades, whereas aluminum typically has a shorter lifespan, especially when not anodized or treated.
Reactivity with Food and Flavor Impact
Carbon steel cookware exhibits moderate reactivity with acidic foods, which can sometimes impart a metallic taste or alter flavors during cooking. Aluminum is highly reactive, especially with acidic and alkaline ingredients, leading to discoloration and potential metallic flavors that affect the dish's taste. Seasoned carbon steel offers a relatively inert cooking surface compared to untreated aluminum, reducing unwanted flavor changes.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Carbon steel cookware requires seasoning to maintain its non-stick surface and prevent rust, with regular oiling after each use essential for durability. Aluminum cookware is generally easier to clean, as it resists corrosion and does not need seasoning, but it can discolor and react with acidic foods if not anodized. Proper maintenance of carbon steel involves hand washing and drying immediately, while aluminum can often withstand dishwasher cleaning but benefits from gentle hand washing to prolong lifespan.
Cooking Performance and Versatility
Carbon steel offers superior heat retention and rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for high-heat searing and consistent cooking performance. Aluminium cookware excels in lightweight design and exceptional heat conductivity, providing even cooking but may lack the durability and non-stick qualities of carbon steel. Versatility favors carbon steel as it handles diverse cooking methods including frying, sauteing, and baking, while aluminium is best suited for low to medium heat and more delicate tasks.
Price Comparison and Value for Money
Carbon steel cookware typically costs less than aluminum, offering durable performance at a budget-friendly price point. Although aluminum is lightweight and conducts heat efficiently, its higher price and potential for warping may reduce overall value for money. Carbon steel combines affordability with long-lasting quality, making it a preferred choice for cost-conscious cooks seeking reliable cookware.
Choosing the Right Cookware for Your Kitchen
Carbon steel cookware offers excellent heat retention and durability, making it ideal for high-heat cooking such as searing and frying. Aluminium cookware provides superior heat conductivity and lightweight design, perfect for quick and even cooking tasks. Selecting the right cookware depends on your cooking style, with carbon steel favored for professional-style cooking and aluminium suitable for everyday convenience and fast heat response.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Aluminium for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com