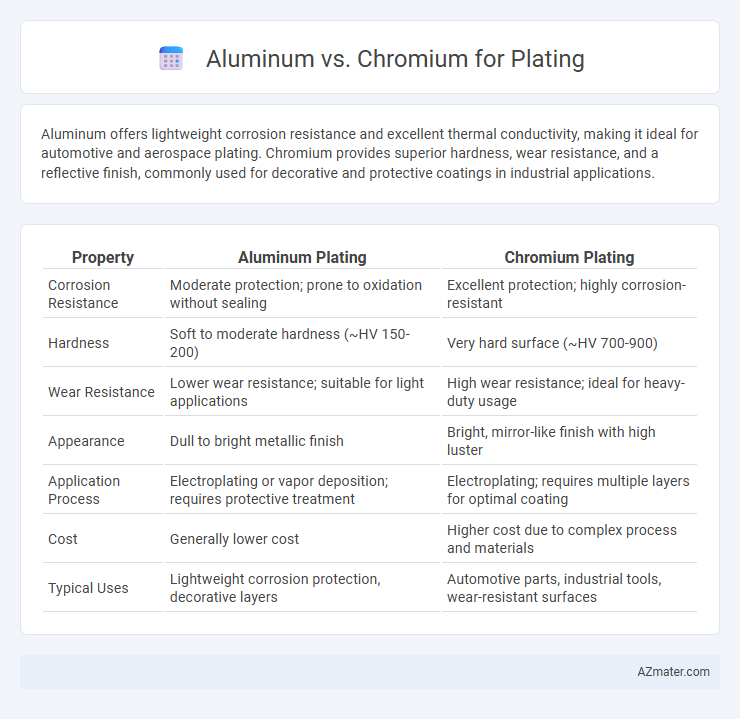
Aluminum offers lightweight corrosion resistance and excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace plating. Chromium provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and a reflective finish, commonly used for decorative and protective coatings in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminum Plating | Chromium Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate protection; prone to oxidation without sealing | Excellent protection; highly corrosion-resistant |
| Hardness | Soft to moderate hardness (~HV 150-200) | Very hard surface (~HV 700-900) |
| Wear Resistance | Lower wear resistance; suitable for light applications | High wear resistance; ideal for heavy-duty usage |
| Appearance | Dull to bright metallic finish | Bright, mirror-like finish with high luster |
| Application Process | Electroplating or vapor deposition; requires protective treatment | Electroplating; requires multiple layers for optimal coating |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complex process and materials |
| Typical Uses | Lightweight corrosion protection, decorative layers | Automotive parts, industrial tools, wear-resistant surfaces |
Introduction to Metal Plating Technologies
Metal plating technologies involve depositing a thin layer of metal onto a substrate to enhance properties such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Aluminum plating offers lightweight corrosion protection with good conductivity, popular in aerospace and automotive industries. Chromium plating provides superior hardness, high corrosion resistance, and a bright, reflective finish, widely used in decorative and industrial applications.
Aluminum Plating: Properties and Applications
Aluminum plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight protection, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive components exposed to harsh environments. Its ability to create a durable, non-toxic barrier with high reflectivity makes aluminum plating valuable for electrical and decorative applications. Compared to chromium, aluminum provides better thermal conductivity and resistance to saltwater corrosion, enhancing the lifespan of marine and industrial equipment.
Chromium Plating: Properties and Applications
Chromium plating offers exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and a brilliant, reflective finish ideal for both decorative and industrial applications. Its superior wear resistance and low friction properties make it essential for automotive parts, tools, and machinery components exposed to harsh environments. Compared to aluminum, chromium plating provides enhanced durability and a longer lifespan in demanding settings, ensuring optimal performance and aesthetic appeal.
Comparative Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum plating offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its natural oxide layer that protects against rust and oxidation, making it ideal for lightweight and outdoor applications. Chromium plating provides superior hardness and aesthetic appeal but is more prone to corrosion in harsh environments without proper maintenance or additional protective coatings. Choosing between aluminum and chromium plating depends on the specific environmental exposure and durability requirements, with aluminum excelling in corrosion protection and chromium offering enhanced surface strength and wear resistance.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Appeal
Aluminum plating offers a lightweight, corrosion-resistant surface with a smooth, matte finish that enhances modern aesthetic appeal, ideal for automotive and consumer electronics. Chromium plating provides a highly reflective, mirror-like surface with superior hardness and scratch resistance, popular in decorative trim and luxury hardware. Both metals complement surface durability, but chromium excels in achieving a striking, polished look that maintains brilliance over time.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Aluminum plating offers moderate durability with good corrosion resistance but tends to wear faster under abrasive conditions compared to chromium plating. Chromium plating exhibits superior hardness, providing excellent wear resistance and prolonged surface lifespan in high-friction or high-impact environments. The superior hardness of chromium, typically around 800-1000 HV (Vickers Hardness), outperforms aluminum coatings, making it the preferred choice for applications requiring enhanced durability and abrasion resistance.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Aluminum plating offers a lower environmental impact due to its reduced use of toxic chemicals and lower energy consumption compared to chromium plating, which involves hexavalent chromium, a known carcinogen requiring stringent safety measures. Chromium plating processes generate hazardous waste and necessitate extensive personal protective equipment (PPE) and ventilation to safeguard workers from exposure to carcinogenic fumes. Choosing aluminum plating can lead to safer working conditions and simpler waste management, promoting sustainability in manufacturing environments.
Cost Analysis: Aluminum vs Chromium Plating
Aluminum plating typically incurs lower material costs compared to chromium, given aluminum's abundance and lower market price, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale applications. Chromium plating demands higher expenses due to costly raw materials and strict environmental regulations governing hexavalent chromium disposal, which increase operational costs. The overall cost analysis reveals aluminum plating is more economical, especially when factoring in energy consumption and waste management associated with chromium plating processes.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Aluminum plating is preferred in automotive and aerospace industries for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, enhancing fuel efficiency and durability. Chromium plating is widely used in automotive, plumbing, and heavy machinery sectors due to its superior hardness, wear resistance, and aesthetic shine. Both materials cater to industry-specific needs, with aluminum excelling in weight-sensitive applications and chromium dominating in high-wear and decorative environments.
Choosing the Right Plating Material for Your Needs
Aluminum plating offers lightweight corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for aerospace and electronics applications. Chromium plating provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and a highly reflective finish, commonly used in automotive parts and decorative accents. Selecting the right plating material depends on balancing factors like durability, environmental exposure, and aesthetic requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Infographic: Aluminum vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com