Aluminum doors offer superior corrosion resistance, lightweight design, and low maintenance compared to heavy, rust-prone iron doors. Aluminum provides excellent durability and energy efficiency, making it ideal for modern door applications.
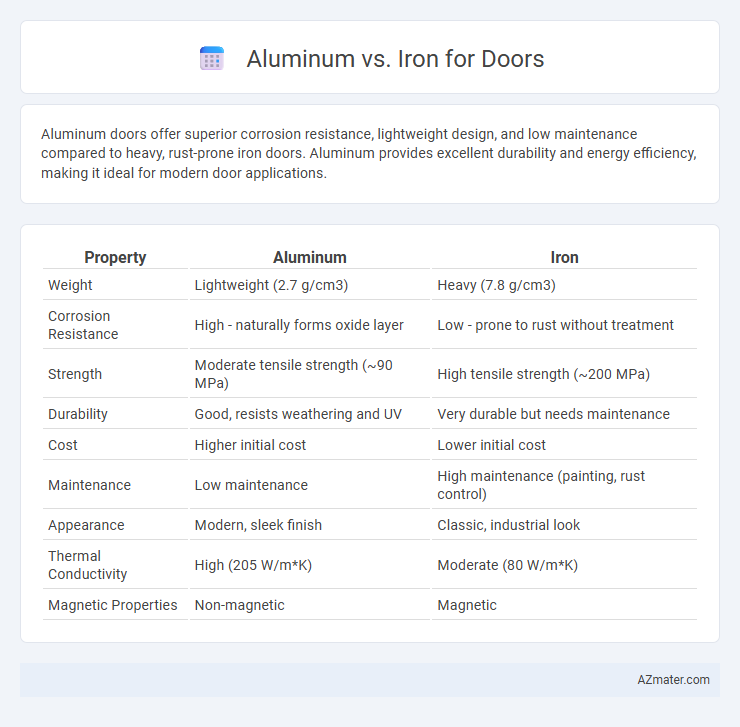
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminum | Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight (2.7 g/cm3) | Heavy (7.8 g/cm3) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High - naturally forms oxide layer | Low - prone to rust without treatment |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength (~90 MPa) | High tensile strength (~200 MPa) |
| Durability | Good, resists weathering and UV | Very durable but needs maintenance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | High maintenance (painting, rust control) |
| Appearance | Modern, sleek finish | Classic, industrial look |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (205 W/m*K) | Moderate (80 W/m*K) |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic | Magnetic |
Introduction to Aluminum and Iron Doors
Aluminum doors offer lightweight durability, corrosion resistance, and low maintenance, making them ideal for modern architectural designs. Iron doors provide unmatched strength, security, and classic aesthetic appeal, often chosen for traditional or robust exterior entrances. Both materials serve unique purposes in door manufacturing, with aluminum excelling in weather resistance and iron standing out for its heavy-duty protection and decorative potential.
Material Properties: Aluminum vs Iron
Aluminum offers significant advantages over iron for doors due to its lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for environments exposed to moisture or requiring frequent handling. Iron, while heavier and prone to rust without protective coatings, provides superior strength and durability, which is beneficial for security-focused door applications. Both materials differ in thermal conductivity, with aluminum conducting heat more readily, affecting energy efficiency and insulation properties in door construction.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Aluminum doors offer superior design flexibility due to their lightweight nature and ability to be molded into sleek, modern profiles with a wide range of finishes and colors. In contrast, iron doors provide a classic, robust aesthetic with intricate detailing options but tend to be heavier and less adaptable to minimalist designs. The choice between aluminum and iron hinges on the desired visual impact, with aluminum excelling in contemporary styles and iron favored for traditional, ornate appearances.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Aluminum doors offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them highly durable in humid or coastal environments, while iron doors excel in raw strength, providing superior impact resistance and security. Despite aluminum's lighter weight, it maintains significant structural integrity through alloy enhancements, whereas iron requires protective coatings to prevent rust and extend lifespan. Choosing between aluminum and iron for doors depends on balancing weight considerations with the need for maximum strength and long-term durability.
Weather Resistance and Corrosion
Aluminum doors offer superior weather resistance due to their natural oxide layer that prevents corrosion, making them ideal for humid or coastal environments. Iron doors, while strong, are prone to rust and require regular maintenance and protective coatings to withstand moisture and harsh weather conditions. Choosing aluminum ensures long-lasting durability with minimal corrosion-related issues compared to iron in outdoor settings.
Security Features and Safety
Aluminum doors offer enhanced security with reinforced frames and corrosion-resistant properties, reducing the risk of structural weakness over time. Iron doors provide superior strength and durability, with their heavy gauge metal construction deterring forced entry and enhancing overall safety. Both materials can be equipped with advanced locking systems, but iron doors generally deliver higher impact resistance and longer-lasting protection against physical attacks.
Maintenance Requirements
Aluminum doors require minimal maintenance due to their resistance to rust, corrosion, and fading, making them ideal for long-lasting exterior use. Iron doors demand regular upkeep to prevent rust and corrosion, including painting or sealing every few years to maintain their appearance and structural integrity. Choosing aluminum reduces the need for frequent repairs and protective treatments, saving time and maintenance costs over the lifespan of the door.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aluminum doors offer superior environmental benefits due to their lightweight nature, which reduces transportation emissions and energy consumption during manufacturing compared to iron doors. Aluminum is highly recyclable, retaining its properties through repeated recycling processes and significantly lowering the ecological footprint associated with raw material extraction. In contrast, iron requires more energy-intensive mining and smelting processes, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation.
Cost Analysis: Aluminum vs Iron Doors
Aluminum doors typically cost more upfront than iron doors due to material and manufacturing expenses but offer lower maintenance costs over time because of aluminum's resistance to rust and corrosion. Iron doors, while generally less expensive initially, often incur higher long-term repair and repainting costs due to susceptibility to rust and weather damage. Choosing between aluminum and iron doors depends on balancing initial investment against projected maintenance and durability expenses.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Door
Aluminum doors offer superior corrosion resistance, lightweight durability, and low maintenance, making them ideal for modern, energy-efficient homes. Iron doors provide exceptional strength, classic aesthetics, and enhanced security but require regular upkeep to prevent rust and wear. Choosing the right material depends on priority factors such as climate exposure, desired maintenance levels, security needs, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Aluminum vs Iron for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com