Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance compared to zinc, enhancing durability in plating applications. Zinc plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for protective coatings on tool steel components.
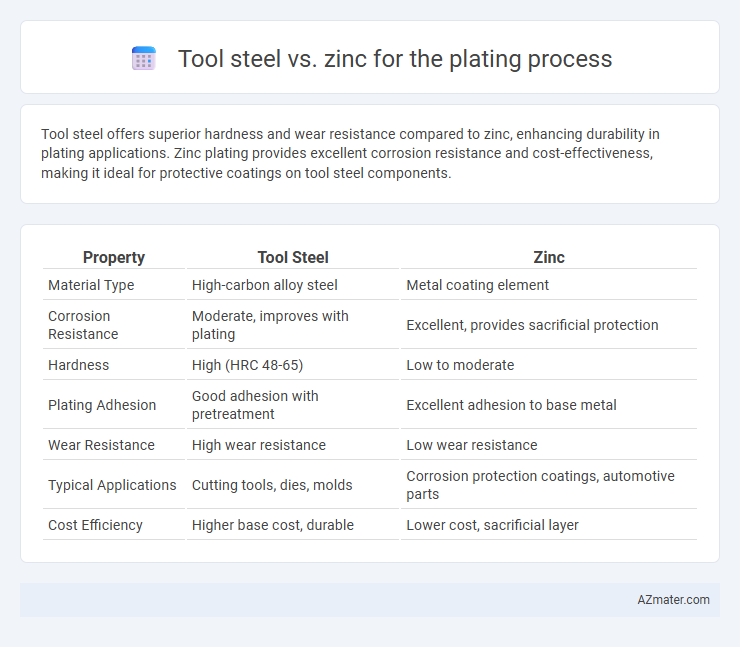
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-carbon alloy steel | Metal coating element |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, improves with plating | Excellent, provides sacrificial protection |
| Hardness | High (HRC 48-65) | Low to moderate |
| Plating Adhesion | Good adhesion with pretreatment | Excellent adhesion to base metal |
| Wear Resistance | High wear resistance | Low wear resistance |
| Typical Applications | Cutting tools, dies, molds | Corrosion protection coatings, automotive parts |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher base cost, durable | Lower cost, sacrificial layer |
Introduction to Tool Steel and Zinc in Plating
Tool steel, known for its high hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain shape at elevated temperatures, is essential in manufacturing cutting tools and molds. Zinc plating offers a corrosion-resistant coating by electroplating a thin layer of zinc onto metal surfaces, including tool steel, to protect against rust and extend the lifespan. The combination of durable tool steel substrates with zinc plating enhances both mechanical strength and environmental resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications.
Chemical Properties: Tool Steel vs Zinc
Tool steel exhibits high carbon content and alloying elements like chromium, vanadium, and molybdenum, providing exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and chemical stability. Zinc, with its lower melting point and excellent corrosion resistance, offers sacrificial protection during plating by forming a stable oxide layer that prevents oxidation of underlying metals. Chemical compatibility between zinc plating and tool steel ensures enhanced surface durability and resistance to rust in harsh environments.
Surface Preparation Requirements
Tool steel requires thorough surface preparation including degreasing, pickling, and abrasive blasting to remove oils, oxides, and scale before zinc plating to ensure optimal adhesion and corrosion resistance. Zinc plating on tool steel surfaces benefits from uniform surface roughness, typically achieved by mechanical polishing or sandblasting, which enhances zinc coating bonding and durability. Proper surface activation with acid etching or electrocleaning is critical for preventing defects such as flaking or poor coverage during the zinc plating process.
Plating Techniques for Tool Steel and Zinc
Electroplating and hot-dip galvanizing are common plating techniques for zinc, offering corrosion resistance and improved surface durability. Tool steel plating often involves physical vapor deposition (PVD) or electroplating with hard coatings such as chromium or nickel to enhance hardness and wear resistance. Both materials require precise surface preparation, with tool steel needing specialized cleaning and activation steps to ensure proper adhesion of coatings.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Tool steel exhibits significantly higher corrosion resistance than zinc when subjected to harsh environments due to its alloy composition, including elements like chromium and vanadium. Zinc plating primarily offers sacrificial protection by corroding first to shield the base metal, which makes it less durable over extended exposure to moisture and chemicals. The superior corrosion resistance of tool steel makes it preferable for high-stress applications where long-term durability is critical.
Adhesion and Durability of Plated Layers
Tool steel plating typically demands superior adhesion and durability due to its use in high-stress environments, where zinc plating provides corrosion resistance but often suffers from weaker adhesion and lower wear resistance. The microstructure of tool steel allows better metallurgical bonding with plating layers, enhancing durability under mechanical load compared to zinc's more sacrificial, less adhesive coating. Optimizing surface preparation and employing advanced zinc alloys can improve adhesion and extend zinc plating's lifespan, but tool steel inherently supports longer-lasting, robust plated layers.
Cost Analysis: Tool Steel Versus Zinc Plating
Tool steel typically incurs higher initial material costs compared to zinc plating, which is a more economical surface treatment option. Zinc plating offers cost-effective corrosion resistance and extends the lifespan of underlying steels at a fraction of the expense of tool steel. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement frequency, highlights zinc plating as a budget-friendly solution for large-scale manufacturing applications.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications that demand durability and precision, such as cutting tools and molds. Zinc plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, often used in automotive and construction industries to protect steel components from rust. While tool steel is best suited for high-stress environments, zinc plating enhances the longevity of softer metals in less abrasive conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tool steel plating typically involves hard, durable coatings that may require heavy metals and toxic chemicals, posing significant environmental disposal challenges and contributing to pollution. Zinc plating offers a more eco-friendly alternative due to its corrosion resistance and lower toxicity, often using less hazardous materials and generating fewer harmful emissions during processing. Sustainable manufacturing increasingly favors zinc plating for its recyclability, reduced environmental footprint, and compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Summary: Choosing the Right Material for Plating
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for plating processes requiring durability and precision. Zinc plating provides excellent corrosion protection and affordability, suitable for applications with moderate mechanical stress. Selecting between tool steel and zinc plating depends on balancing factors such as environmental exposure, mechanical demands, and budget constraints to ensure optimal plating performance.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Zinc for Plating process
 azmater.com
azmater.com