Cast iron valves offer superior durability and corrosion resistance in high-pressure applications, while brass valves provide excellent machinability and are ideal for low to medium pressure systems with good corrosion resistance. Choosing between cast iron and brass depends on the specific pressure requirements and environmental conditions of the valve's application.
Table of Comparison
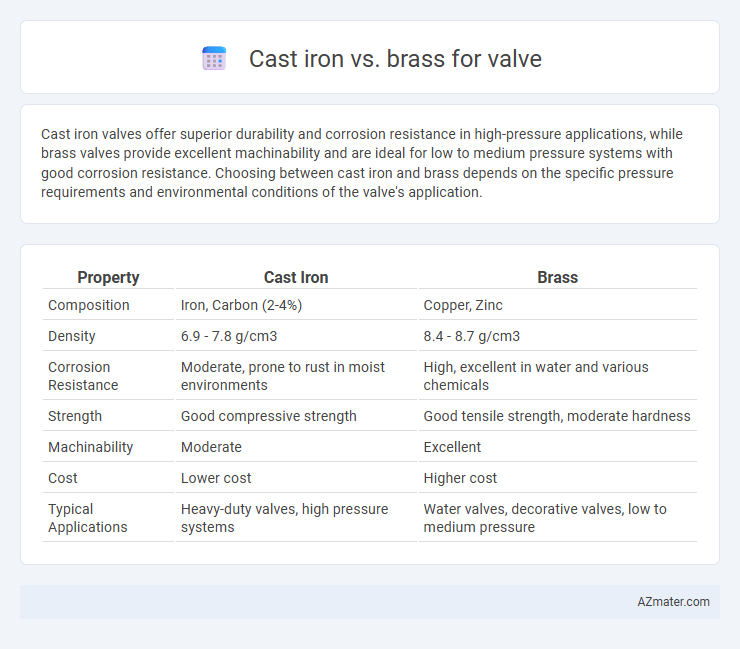
| Property | Cast Iron | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron, Carbon (2-4%) | Copper, Zinc |
| Density | 6.9 - 7.8 g/cm3 | 8.4 - 8.7 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, prone to rust in moist environments | High, excellent in water and various chemicals |
| Strength | Good compressive strength | Good tensile strength, moderate hardness |
| Machinability | Moderate | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Applications | Heavy-duty valves, high pressure systems | Water valves, decorative valves, low to medium pressure |
Introduction to Valve Material Selection
Cast iron valves offer excellent durability and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for water, steam, and gas applications in industrial systems. Brass valves provide superior machinability, corrosion resistance in potable water systems, and enhanced resistance to dezincification, ideal for residential plumbing and HVAC setups. Selecting valve material depends on factors like fluid type, pressure, temperature, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Overview of Cast Iron and Brass Valves
Cast iron valves are valued for their high strength, durability, and excellent resistance to corrosion and wear, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications and water supply systems. Brass valves offer superior corrosion resistance, especially against saltwater and acidic environments, along with good machinability and thermal conductivity, which are ideal for plumbing and fluid control in residential and commercial settings. Both materials provide reliable sealing capabilities, but cast iron valves excel in high-pressure scenarios while brass valves are preferred for precision control and aesthetic appeal.
Mechanical Properties: Cast Iron vs Brass
Cast iron valves exhibit superior compressive strength and hardness, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, while brass valves offer greater ductility and corrosion resistance, ensuring durability in water and low-pressure systems. The tensile strength of cast iron ranges from 150 to 300 MPa, whereas brass typically provides tensile strength between 200 and 500 MPa, allowing for enhanced flexibility and fatigue resistance. Cast iron's brittleness limits its impact resistance compared to the more malleable and shock-absorbing nature of brass, which is advantageous in dynamic environments.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Brass valves exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to cast iron, especially in environments exposed to water, chemicals, and humidity. Cast iron tends to oxidize and develop rust over time, compromising valve integrity and performance. Brass valves resist corrosion from saltwater and acidic conditions, making them ideal for plumbing and marine applications.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Cast iron valves offer superior durability due to their high resistance to wear, corrosion, and temperature extremes, resulting in an extended lifespan often exceeding 20 years in industrial applications. Brass valves provide excellent corrosion resistance in water and mildly corrosive environments but have lower strength compared to cast iron, typically achieving a lifespan of 10 to 15 years under normal operating conditions. The choice between cast iron and brass valves depends on environmental factors and mechanical stress, with cast iron favored for heavy-duty, high-pressure systems and brass preferred for lighter, low-corrosion applications.
Cost Efficiency and Budget Considerations
Cast iron valves offer superior cost efficiency due to their lower material and manufacturing expenses, making them ideal for budget-conscious projects requiring durability and corrosion resistance. Brass valves, while more expensive upfront, provide resistance to dezincification and better machinability, potentially reducing maintenance costs over time in specialized applications. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, including initial investment and long-term maintenance, is essential when choosing between cast iron and brass for valves in cost-sensitive environments.
Applications and Suitability by Industry
Cast iron valves excel in heavy-duty applications such as water supply, wastewater treatment, and oil and gas pipelines due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Brass valves offer superior performance in plumbing, HVAC systems, and fuel handling where resistance to dezincification, ease of machining, and enhanced sealing capabilities are essential. Industries requiring high pressure and temperature tolerance favor cast iron, while those needing precision and chemical stability often select brass valves for optimal functionality.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Cast iron valves require careful handling during installation due to their brittle nature and heavier weight, often necessitating additional support and precise alignment to prevent cracking. Brass valves offer easier installation with their lighter weight and corrosion-resistant properties, typically allowing for straightforward threading or soldering without special tools. Maintenance for cast iron valves can involve routine inspections for corrosion and potential repairs to protect against rust, while brass valves usually demand less frequent maintenance thanks to their natural resistance to corrosion and fouling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cast iron valves have a lower environmental impact due to their recyclability and longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and raw material extraction. Brass valves, while corrosion-resistant and durable, require energy-intensive mining and refining processes that contribute more to carbon emissions. Sustainable valve selection favors cast iron as it supports circular economy principles through easier recycling and less resource depletion.
Final Recommendations: Choosing Between Cast Iron and Brass for Valves
Cast iron valves offer excellent durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications in water, steam, and gas lines. Brass valves provide superior machinability, corrosion resistance in potable water systems, and precision control, suitable for residential and light industrial uses. Select cast iron for cost-effective durability in high-pressure environments and brass for reliable performance in low-pressure, corrosion-sensitive settings.
Infographic: Cast iron vs Brass for Valve
 azmater.com
azmater.com