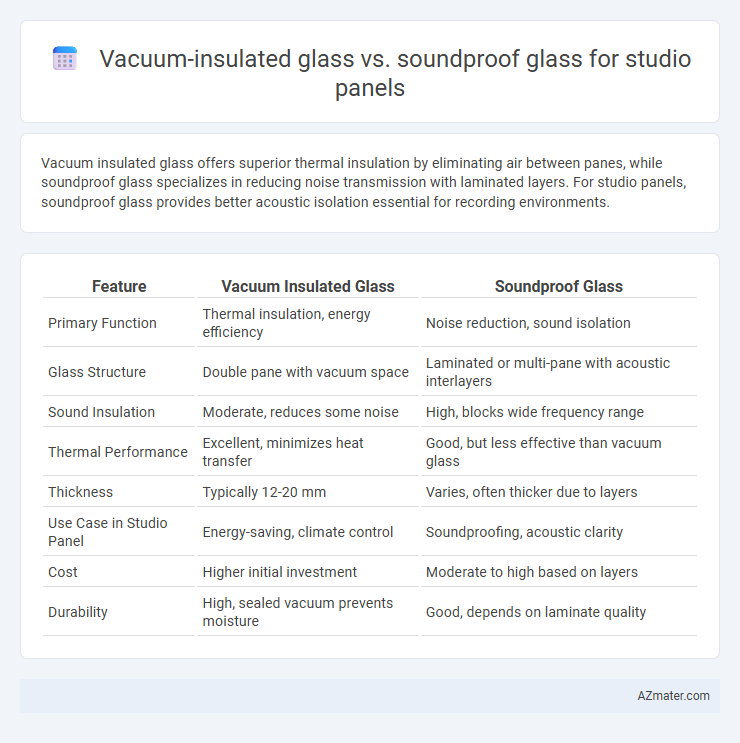
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by eliminating air between panes, while soundproof glass specializes in reducing noise transmission with laminated layers. For studio panels, soundproof glass provides better acoustic isolation essential for recording environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass | Soundproof Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermal insulation, energy efficiency | Noise reduction, sound isolation |
| Glass Structure | Double pane with vacuum space | Laminated or multi-pane with acoustic interlayers |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate, reduces some noise | High, blocks wide frequency range |
| Thermal Performance | Excellent, minimizes heat transfer | Good, but less effective than vacuum glass |
| Thickness | Typically 12-20 mm | Varies, often thicker due to layers |
| Use Case in Studio Panel | Energy-saving, climate control | Soundproofing, acoustic clarity |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate to high based on layers |
| Durability | High, sealed vacuum prevents moisture | Good, depends on laminate quality |
Introduction to Studio Panel Glass Options
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer through a near-complete vacuum between glass layers, ideal for maintaining controlled studio environments. Soundproof glass utilizes laminated layers with sound-damping interlayers to effectively reduce noise transmission, critical for high-quality audio recording studios. Studio panel glass options balance thermal performance and acoustic isolation, with vacuum insulated glass excelling in temperature regulation and soundproof glass optimizing sound attenuation.
Understanding Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG)
Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum, significantly reducing heat transfer and providing superior thermal insulation compared to conventional soundproof glass. This vacuum layer eliminates convective and conductive heat flow, making VIG an energy-efficient choice for studio panels without compromising natural light transmission. While soundproof glass prioritizes acoustic insulation through laminated or multiple layers, VIG excels in thermal performance, essential for climate control in studio environments.
What is Soundproof Glass?
Soundproof glass is a specialized type of glazing designed to significantly reduce noise transmission, often featuring multiple layers of glass with acoustic interlayers or varying glass thicknesses to disrupt sound waves. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, which primarily focuses on thermal insulation by using a vacuum space to minimize heat transfer, soundproof glass targets acoustic performance by enhancing sound absorption and blocking capabilities. In studio panels, soundproof glass ensures clearer audio recording environments by minimizing external noise interference while maintaining visual transparency.
Key Differences Between VIG and Soundproof Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) employs a near-vacuum layer between panes to drastically reduce thermal conductivity, making it highly effective for insulation but less focused on sound attenuation. Soundproof glass incorporates laminated layers with acoustic interlayers designed to dampen and block a wide range of noise frequencies, providing superior sound isolation for studio environments. Key differences include VIG's thermal efficiency due to vacuum technology versus soundproof glass's enhanced noise reduction through specialized multilayer construction.
Acoustic Performance: VIG vs Soundproof Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation but typically provides moderate acoustic performance due to its thin glass layers and vacuum gap, which minimally dampen sound transmission. Soundproof glass, often consisting of laminated layers with varying thickness and acoustic interlayers, excels in reducing noise by disrupting sound waves and increasing sound transmission loss, making it ideal for studio panels requiring high acoustic isolation. For maximizing soundproofing in studio environments, soundproof glass outperforms VIG by significantly lowering noise levels across a broad frequency range.
Thermal Insulation Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by eliminating air gaps and reducing heat transfer through conduction and convection, achieving U-values as low as 0.3 W/m2K, ideal for studio panels requiring stable indoor temperatures. Soundproof glass primarily focuses on acoustic dampening and typically features laminated layers, but its thermal insulation performance is moderate with U-values around 1.1 to 1.8 W/m2K. Selecting vacuum insulated glass enhances energy efficiency and temperature control in studio environments more effectively than standard soundproof glass options.
Durability and Maintenance Factors
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior durability due to its sealed space that resists moisture and prevents fogging, making it ideal for long-term studio panel use. Soundproof glass incorporates multiple laminated layers designed to absorb and block sound waves but may require more frequent inspections for seal integrity to maintain acoustic performance. Both types demand minimal maintenance, though vacuum insulated glass generally provides a longer lifespan with less risk of degradation under typical studio conditions.
Installation Considerations for Studios
Vacuum insulated glass requires precise installation to maintain the airtight seal critical for thermal and acoustic performance, demanding professional handling and specialized framing systems to avoid seal failure in studio panels. Soundproof glass, often laminated with acoustic interlayers, allows more flexibility in installation but requires careful sealing around edges and junctions to prevent sound leaks in studio environments. Both types benefit from acoustic-rated mounting and complementary treatments like airtight frames and sound-damping materials to optimize sound isolation in studio panels.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Vacuum insulated glass typically incurs higher initial costs than standard soundproof glass due to advanced manufacturing processes that create a near-perfect vacuum layer, significantly enhancing thermal insulation alongside sound reduction. Soundproof glass panels often offer a more affordable upfront investment with effective noise control but lack the superior energy-saving benefits, potentially leading to higher long-term utility expenses compared to vacuum insulated options. Evaluating return on investment involves balancing upfront expenses with ongoing savings, where vacuum insulated glass can deliver greater overall cost-efficiency in studio panels by reducing energy bills while maintaining sound quality.
Best Applications and Recommendations for Studio Panels
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance, making it ideal for studios requiring precise temperature control and energy efficiency. Soundproof glass excels in blocking a wide range of noise frequencies, providing optimal acoustic isolation crucial for recording studios focused on clear sound capture. For studio panels, combining vacuum insulated glass with laminated soundproof layers delivers the best balance of thermal regulation and noise reduction, enhancing both environmental comfort and audio quality.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Soundproof glass for Studio panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com