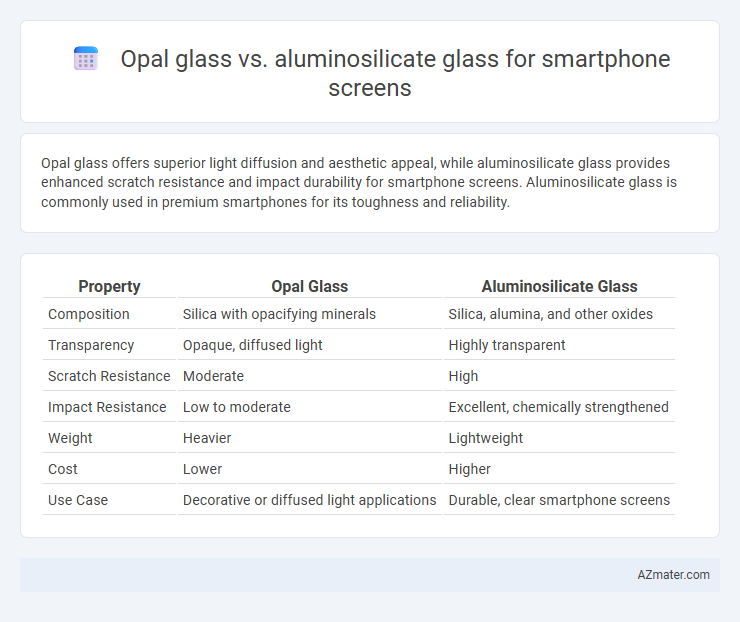
Opal glass offers superior light diffusion and aesthetic appeal, while aluminosilicate glass provides enhanced scratch resistance and impact durability for smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass is commonly used in premium smartphones for its toughness and reliability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Opal Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica with opacifying minerals | Silica, alumina, and other oxides |
| Transparency | Opaque, diffused light | Highly transparent |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Impact Resistance | Low to moderate | Excellent, chemically strengthened |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Use Case | Decorative or diffused light applications | Durable, clear smartphone screens |
Introduction: Opal Glass vs Aluminosilicate Glass
Opal glass offers a unique translucent appearance and moderate durability, making it less common for smartphone screens compared to aluminosilicate glass, which is engineered for high strength and scratch resistance. Aluminosilicate glass, such as Corning Gorilla Glass, incorporates aluminum and silicon oxide to provide enhanced impact protection and clarity, optimizing touchscreen responsiveness and durability. The superior chemical composition and manufacturing process of aluminosilicate glass make it the preferred choice for modern smartphone displays demanding robust performance and longevity.
Composition and Material Science
Opal glass primarily consists of silica with dispersed microscopic inclusions that create its characteristic opaque appearance, while aluminosilicate glass is composed of silica, alumina, and other oxides, offering enhanced strength and chemical resistance. The high alumina content in aluminosilicate glass increases its hardness and fracture toughness, making it ideal for smartphone screens requiring scratch resistance and durability. In contrast, opal glass's microstructure reduces transparency but can provide diffused light effects, though it lacks the mechanical robustness needed for high-impact applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens, offers superior strength and scratch resistance compared to Opal glass due to its high aluminum oxide content, which enhances hardness and impact resistance. Opal glass, primarily a decorative and less dense material, lacks the structural integrity and toughness required for durable smartphone displays, making it more prone to cracking and surface damage. The advanced chemical strengthening process applied to aluminosilicate glass, such as ion exchange, significantly increases its durability and resilience under daily mechanical stress, outperforming Opal glass in long-term use.
Scratch Resistance and Hardness
Opal glass typically exhibits lower hardness and scratch resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass, which contains higher aluminum oxide content, enhancing durability. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in premium smartphones, offers superior resistance to scratches and impacts due to its chemically strengthened structure. This makes aluminosilicate glass the preferred choice for maintaining screen clarity and longevity under daily wear and tear.
Transparency and Visual Quality
Opal glass typically has lower transparency compared to aluminosilicate glass, resulting in reduced visual clarity and brightness for smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior optical clarity and higher light transmittance, which enhances color accuracy and overall display sharpness. The enhanced transparency of aluminosilicate glass significantly improves user experience by delivering vibrant visuals and minimizing distortions.
Weight and Thickness Differences
Opal glass typically weighs more and is thicker compared to aluminosilicate glass, which offers a lighter and slimmer profile ideal for modern smartphones emphasizing portability. Aluminosilicate glass provides enhanced strength and scratch resistance at reduced thickness, contributing to overall device weight reduction and improved handling. These material differences directly impact smartphone design, influencing both ergonomic feel and durability.
Manufacturing Process Overview
Opal glass is produced through controlled fusion and slow cooling of silica-based materials, resulting in a semi-translucent, durable surface optimized for aesthetic applications but less common in smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, widely used in smartphone manufacturing, undergoes a chemical strengthening process known as ion exchange, where smaller sodium ions are replaced by larger potassium ions to enhance scratch resistance and toughness. The precise thermal treatments in aluminosilicate glass production ensure high clarity and mechanical strength crucial for touchscreen durability and performance.
Cost Implications for Manufacturers
Opal glass offers a lower production cost due to its simpler manufacturing process and readily available raw materials, making it an attractive option for budget smartphone models. Aluminosilicate glass, although more expensive to produce because of its high-purity components and complex tempering techniques, provides superior scratch resistance and durability, which can justify higher pricing in premium devices. Manufacturers must balance the trade-off between initial material costs and long-term performance benefits when choosing between opal and aluminosilicate glass for smartphone screens.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Opal glass, primarily composed of silica and alumina, offers moderate durability but presents challenges in recyclability due to embedded opacifying agents that complicate material recovery processes. Aluminosilicate glass, favored in premium smartphone screens like those from Corning's Gorilla Glass line, combines high strength with enhanced chemical resistance, enabling longer device lifespans and reduced waste generation. The superior durability of aluminosilicate glass significantly lowers environmental impact by decreasing the frequency of screen replacements and supporting more efficient recycling streams, thus fostering sustainability in electronic device manufacturing.
Which Glass Is Best for Smartphone Screens?
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength and scratch resistance compared to Opal glass, making it the preferred choice for smartphone screens. Its high durability and excellent optical clarity enhance touch sensitivity and display quality under various conditions. Opal glass, while aesthetically unique, lacks the mechanical resilience and protective qualities crucial for everyday smartphone use.
Infographic: Opal glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com