Low-iron glass offers high transparency and clarity, making it ideal for aesthetic security windows, while bullet-resistant glass provides enhanced protection through layered laminated construction designed to stop projectiles. Choosing between these materials depends on whether priority lies in visual clarity or ballistic protection for the security window.
Table of Comparison
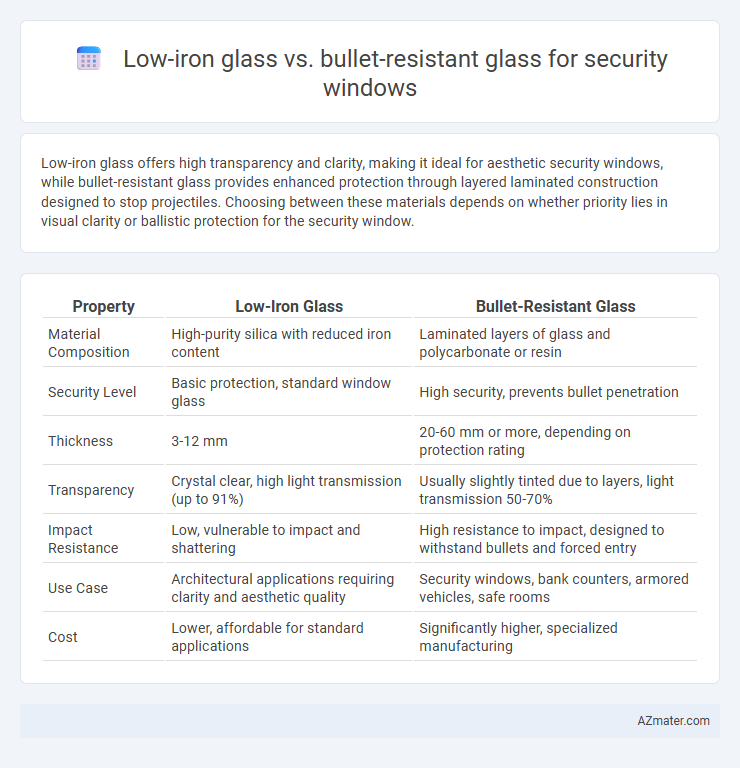
| Property | Low-Iron Glass | Bullet-Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity silica with reduced iron content | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate or resin |
| Security Level | Basic protection, standard window glass | High security, prevents bullet penetration |
| Thickness | 3-12 mm | 20-60 mm or more, depending on protection rating |
| Transparency | Crystal clear, high light transmission (up to 91%) | Usually slightly tinted due to layers, light transmission 50-70% |
| Impact Resistance | Low, vulnerable to impact and shattering | High resistance to impact, designed to withstand bullets and forced entry |
| Use Case | Architectural applications requiring clarity and aesthetic quality | Security windows, bank counters, armored vehicles, safe rooms |
| Cost | Lower, affordable for standard applications | Significantly higher, specialized manufacturing |
Understanding Low-Iron Glass: Composition and Features
Low-iron glass contains reduced iron oxide content compared to standard glass, resulting in higher clarity and enhanced light transmission, making it ideal for security windows where visibility is crucial. Its composition minimizes the typical greenish tint found in regular glass, offering a more transparent and true-to-color appearance. While low-iron glass enhances aesthetics and natural light, it does not inherently provide the impact resistance or protection characteristic of bullet-resistant glass, which incorporates multiple laminated layers and polycarbonate materials to absorb and dissipate ballistic energy.
What Is Bullet-Resistant Glass? Key Characteristics
Bullet-resistant glass is a multi-layered composite made from laminated glass and polycarbonate materials designed to prevent bullets from penetrating. It features high impact resistance, thickness ranging from 7mm to over 50mm, and is tested to meet standards like UL 752 or NIJ levels for ballistic protection. This glass combines transparency with advanced strength, making it ideal for security windows in banks, government buildings, and high-risk facilities.
Comparing Optical Clarity: Low-Iron vs Bullet-Resistant Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior optical clarity with its reduced iron content, resulting in higher light transmission and minimal green tint, ideal for security windows requiring clear visibility. Bullet-resistant glass, typically laminated with multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate, tends to have slightly lower optical clarity due to its thickness and materials, which can cause distortion or haze. When prioritizing transparency for security windows, low-iron glass excels in clarity, whereas bullet-resistant glass balances optical performance with enhanced protective capabilities.
Security Performance: Strength and Protection Levels
Low-iron glass offers enhanced clarity but provides limited security performance compared to bullet-resistant glass, which features multiple laminated layers designed to absorb and disperse ballistic impacts. Bullet-resistant glass is tested to meet stringent standards such as UL 752, ensuring high resistance against firearm projectiles and forced entry attempts. The strength and protection levels of bullet-resistant glass make it the preferred choice for security windows in high-risk environments requiring reliable defense against ballistic threats.
Applications: Where Each Glass Type Excels
Low-iron glass is ideal for architectural applications requiring maximum clarity and natural light, such as museum display cases and high-end retail store windows, where visual aesthetics are paramount. Bullet-resistant glass excels in security-sensitive environments like banks, government buildings, and armored vehicles, offering critical protection against firearm threats. Each glass type optimizes safety and functionality tailored to specific security and visual requirements.
Installation Considerations for Security Windows
Installing low-iron glass in security windows requires precise handling to maintain its clarity and reduce the risk of damage during fitting, typically suited for environments prioritizing aesthetic transparency. Bullet-resistant glass installation demands adherence to strict safety standards and reinforced framing to accommodate its multi-layered structure, ensuring optimal ballistic protection without compromising window integrity. Proper alignment and secure sealing methods are critical in both types to enhance durability, weather resistance, and overall security performance.
Cost Analysis: Low-Iron Glass vs Bullet-Resistant Glass
Low-iron glass typically costs between $10 and $15 per square foot, making it a budget-friendly option for security windows that prioritize clarity and aesthetic appeal. Bullet-resistant glass, composed of multiple layers like polycarbonate and laminated glass, can range from $70 to $150 per square foot due to its advanced protective properties and thickness requirements. When comparing cost-effectiveness, low-iron glass is suitable for standard security needs, while bullet-resistant glass justifies its higher price through superior ballistic resistance and enhanced safety features.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection Comparison
Low-iron glass offers enhanced clarity and natural light transmission, contributing to improved energy efficiency by reducing the need for artificial lighting, whereas bullet-resistant glass prioritizes security with thicker layers that may slightly reduce visible light transmission. Bullet-resistant glass typically incorporates laminated interlayers that block up to 99% of harmful UV rays, providing superior UV protection compared to standard low-iron glass, which has limited UV filtering properties. When selecting security windows, bullet-resistant glass balances energy considerations with advanced UV protection, while low-iron glass focuses more on maximizing daylight and aesthetic appeal.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and a near-colorless appearance, enhancing aesthetics with minimal green tint and enabling seamless integration into modern architectural designs. Bullet-resistant glass typically incorporates multiple laminate layers that can slightly reduce transparency and increase thickness, limiting design flexibility but providing essential security. Choosing between the two involves balancing the desire for pristine visual quality in security windows with the required level of ballistic protection.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Security Needs
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and is ideal for applications where aesthetic transparency is a priority, while bullet-resistant glass combines multiple layers of laminated materials to provide enhanced protection against ballistic threats. When choosing the right glass for security windows, consider the specific level of threat, such as forced entry or projectile impact, alongside visual requirements and budget constraints. Bullet-resistant glass is essential for high-risk environments demanding certified impact resistance, whereas low-iron glass works best in settings requiring crisp visibility with moderate security.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Bullet-resistant glass for Security window
 azmater.com
azmater.com