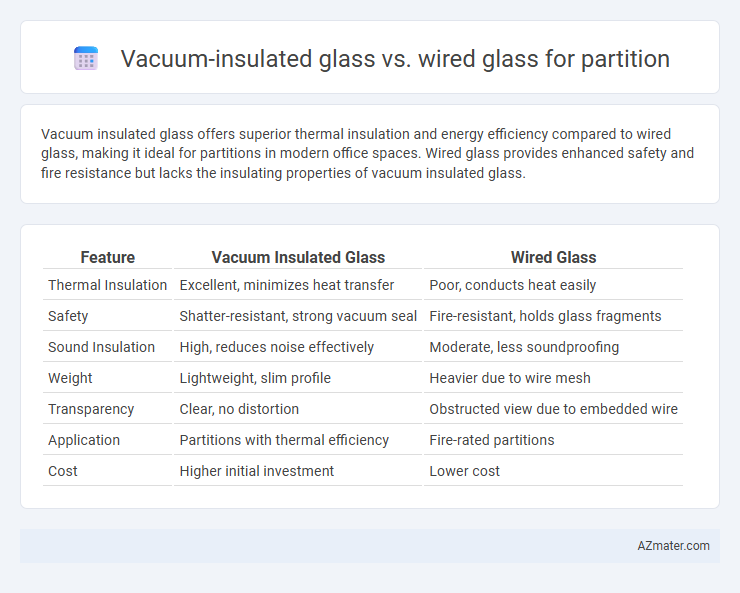
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency compared to wired glass, making it ideal for partitions in modern office spaces. Wired glass provides enhanced safety and fire resistance but lacks the insulating properties of vacuum insulated glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, minimizes heat transfer | Poor, conducts heat easily |
| Safety | Shatter-resistant, strong vacuum seal | Fire-resistant, holds glass fragments |
| Sound Insulation | High, reduces noise effectively | Moderate, less soundproofing |
| Weight | Lightweight, slim profile | Heavier due to wire mesh |
| Transparency | Clear, no distortion | Obstructed view due to embedded wire |
| Application | Partitions with thermal efficiency | Fire-rated partitions |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost |
Introduction to Partition Glass Types
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and soundproofing, making it ideal for energy-efficient partitions in commercial and residential spaces. Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, provides enhanced safety and fire resistance, commonly used in areas requiring impact protection and fire-rated barriers. Both glass types serve distinct functional needs, with vacuum insulated glass prioritizing energy performance and wired glass emphasizing safety and durability.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer that eliminates heat transfer, significantly enhancing thermal insulation compared to wired glass. Unlike wired glass, which incorporates wire mesh for safety but offers limited thermal performance, VIG provides superior energy efficiency and sound insulation, making it ideal for partitions in modern buildings. Its slim profile and enhanced clarity also contribute to aesthetic appeal without compromising durability or strength.
What is Wired Glass?
Wired glass consists of a sheet of glass embedded with a wire mesh, designed primarily to prevent shattering and enhance fire resistance in partitions. It offers limited thermal insulation compared to vacuum insulated glass, which uses a vacuum layer to significantly reduce heat transfer. While wired glass enhances safety in high-heat environments, vacuum insulated glass provides superior energy efficiency and soundproofing for partition applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal performance for partitions due to its near-airless space between panes, drastically reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency compared to wired glass. Wired glass contains embedded metal mesh, which increases thermal conductivity and reduces its insulation capabilities, making it less effective in controlling indoor temperatures. Choosing VIG enhances thermal comfort and lowers heating and cooling costs, whereas wired glass primarily prioritizes safety and fire resistance over thermal efficiency.
Acoustic Insulation: Which Performs Better?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior acoustic insulation compared to wired glass due to its airtight vacuum layer that effectively minimizes sound transmission. Wired glass typically provides basic safety benefits but lacks significant soundproofing capabilities, as its wired mesh does not block noise efficiently. For partitions requiring enhanced acoustic performance, VIG significantly reduces noise pollution by creating a sound barrier that wired glass cannot match.
Safety and Security Features
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior safety and security features due to its multi-layer construction that enhances impact resistance and prevents shattering, making it ideal for secure partitions. Wired glass incorporates embedded metal mesh to maintain structural integrity upon breakage, providing fire resistance and preventing dangerous glass shards. While vacuum insulated glass excels in energy efficiency and soundproofing, wired glass is preferred in environments requiring stringent fire safety standards.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Vacuum insulated glass offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with its clear, uninterrupted view and minimalistic frame, making it ideal for contemporary partitions that emphasize transparency and light flow. Wired glass, characterized by its embedded metal mesh, provides a more industrial or vintage look but can disrupt visual continuity and reduce clarity. Designers often choose vacuum insulated glass for its refined appearance and superior optical quality, while wired glass suits spaces requiring enhanced safety with a distinctive textured aesthetic.
Cost Implications of Both Options
Vacuum insulated glass typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior thermal performance, making it a long-term investment for energy efficiency. Wired glass tends to be more budget-friendly upfront, commonly used for fire resistance and safety features, but may lack the same insulation benefits, potentially increasing heating and cooling expenses. Considering maintenance and durability, vacuum insulated glass often reduces lifecycle costs, whereas wired glass may require more frequent replacement or repair in partition applications.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and reduces condensation, requiring precise installation with airtight sealing and specialized tools, while wired glass is simpler to install but lacks advanced insulation properties. Maintenance for vacuum insulated glass involves careful handling to avoid seal damage and costly repairs, whereas wired glass is more durable and easier to clean but prone to rusting if not properly sealed. Choosing between the two depends on insulation needs and long-term maintenance commitment for partition applications.
Best Applications: Vacuum Insulated Glass vs Wired Glass
Vacuum insulated glass excels in thermal insulation and soundproofing, making it ideal for office partitions and climate-controlled environments where energy efficiency is critical. Wired glass offers superior safety and fire resistance, suitable for partitions in industrial settings and high-traffic areas requiring enhanced security and compliance with fire codes. Choosing between vacuum insulated glass and wired glass depends on prioritizing either energy efficiency and acoustic performance or safety and fire protection in partition applications.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Wired glass for Partition
 azmater.com
azmater.com