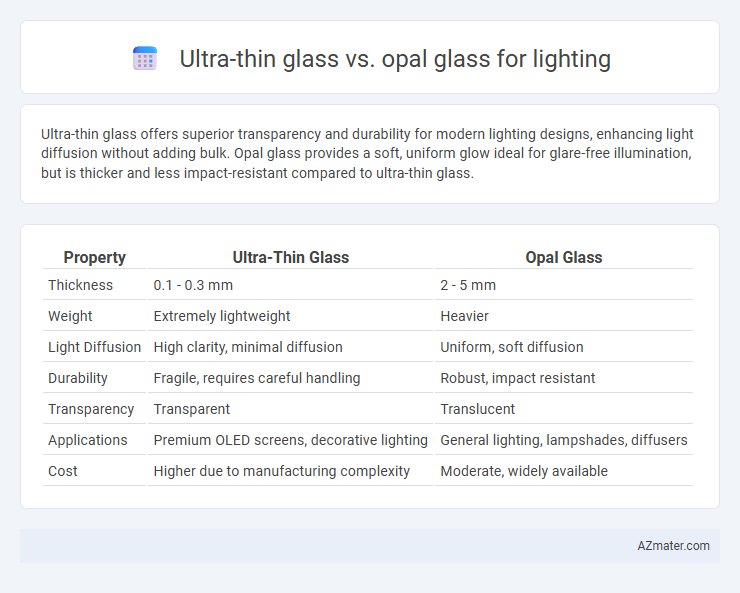
Ultra-thin glass offers superior transparency and durability for modern lighting designs, enhancing light diffusion without adding bulk. Opal glass provides a soft, uniform glow ideal for glare-free illumination, but is thicker and less impact-resistant compared to ultra-thin glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ultra-Thin Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.1 - 0.3 mm | 2 - 5 mm |
| Weight | Extremely lightweight | Heavier |
| Light Diffusion | High clarity, minimal diffusion | Uniform, soft diffusion |
| Durability | Fragile, requires careful handling | Robust, impact resistant |
| Transparency | Transparent | Translucent |
| Applications | Premium OLED screens, decorative lighting | General lighting, lampshades, diffusers |
| Cost | Higher due to manufacturing complexity | Moderate, widely available |
Introduction to Lighting Glass Materials
Ultra-thin glass offers exceptional transparency and durability, making it ideal for modern LED lighting fixtures requiring lightweight and sleek designs. Opal glass provides diffused light with a soft, uniform glow, enhancing ambiance and reducing glare in residential and commercial lighting applications. Selecting between ultra-thin and opal glass depends on desired light diffusion, aesthetic preference, and structural requirements.
What is Ultra-Thin Glass?
Ultra-thin glass for lighting is a highly durable, lightweight material typically less than 100 microns thick, offering exceptional clarity and flexibility compared to traditional glass types like opal glass. It enables sleek, modern light fixture designs with enhanced light diffusion and minimal thickness, making it ideal for applications requiring both aesthetic appeal and functional performance. Unlike opal glass, which is thicker and has a frosted, opaque finish to diffuse light, ultra-thin glass provides superior mechanical strength and precision in lighting technology.
Key Features of Opal Glass
Opal glass features a milky, diffused surface that evenly distributes light and reduces glare, making it ideal for soft, ambient lighting applications. Its higher opacity compared to ultra-thin glass enhances light diffusion while preventing harsh shadows, contributing to a more comfortable lighting environment. Opal glass also offers excellent durability and heat resistance, ensuring consistent performance in various lighting fixtures.
Light Transmission and Clarity Comparison
Ultra-thin glass offers superior light transmission rates, typically exceeding 90%, providing clearer and more precise illumination compared to opal glass, which generally transmits around 60-70% of light due to its frosted, diffuser properties. The transparency of ultra-thin glass ensures minimal light scattering, resulting in sharper and more vibrant lighting effects, while opal glass diffuses light evenly to reduce glare and soften shadows. For applications prioritizing maximum clarity and brightness, ultra-thin glass is the optimal choice, whereas opal glass suits environments requiring uniform light diffusion and reduced harshness.
Durability and Strength: Ultra-Thin vs. Opal Glass
Ultra-thin glass offers exceptional strength despite its minimal thickness, utilizing advanced chemical strengthening processes to resist cracks and impact damage, making it ideal for modern lighting fixtures requiring sleek designs with durability. Opal glass, known for its diffused light effect, provides moderate strength but is more prone to chipping and breakage under impact due to its thicker, less flexible composition. Compared to opal glass, ultra-thin glass delivers a higher strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing longevity and robustness in both residential and commercial lighting applications.
Aesthetic Differences in Lighting Applications
Ultra-thin glass offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with high transparency and exceptional clarity, allowing light to pass through almost unaltered, which enhances brightness and sharpness in lighting fixtures. Opal glass provides a soft, diffused glow by scattering light evenly, creating a warm and inviting ambiance ideal for reducing glare and enhancing mood in residential and hospitality settings. The choice between ultra-thin and opal glass significantly impacts the visual effect and atmosphere of a space, with ultra-thin glass emphasizing minimalism and opal glass focusing on comfort and softness.
Energy Efficiency and Light Diffusion
Ultra-thin glass offers superior energy efficiency for lighting applications by allowing higher light transmission with minimal heat retention, reducing overall energy consumption. Opal glass excels in light diffusion, providing a soft, uniform glow that minimizes glare and enhances visual comfort in illuminated spaces. Choosing between ultra-thin and opal glass depends on whether prioritizing maximum light efficiency or optimal diffusion for ambient lighting quality.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Ultra-thin glass offers a lightweight and durable option for lighting, yet its cost remains higher due to complex manufacturing processes and limited production scale. Opal glass provides a more affordable alternative with widespread availability, benefiting from established production methods and material sourcing. Balancing budget constraints and project design often leads to opal glass as the preferred choice for cost-effective lighting solutions.
Ideal Use-Cases for Ultra-Thin Glass
Ultra-thin glass is ideal for lighting applications requiring high transparency and lightweight design, such as modern LED fixtures and smart lighting panels where minimal thickness enhances heat dissipation and aesthetics. Its durability and flexibility make it suitable for curved or flexible light sources in automotive and wearable technology, outperforming opal glass's diffusive properties. While opal glass excels in soft, uniform light diffusion for ambient lighting, ultra-thin glass is preferred for precision lighting and advanced electronic integration.
Advantages of Opal Glass in Modern Lighting
Opal glass offers superior light diffusion, creating a soft, even illumination that reduces glare and enhances visual comfort in modern lighting designs. Its durability and resistance to yellowing ensure long-lasting aesthetic appeal and consistent performance over time. Opal glass also provides excellent compatibility with LED technology, optimizing energy efficiency and contributing to sustainable lighting solutions.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Opal glass for Lighting
 azmater.com
azmater.com