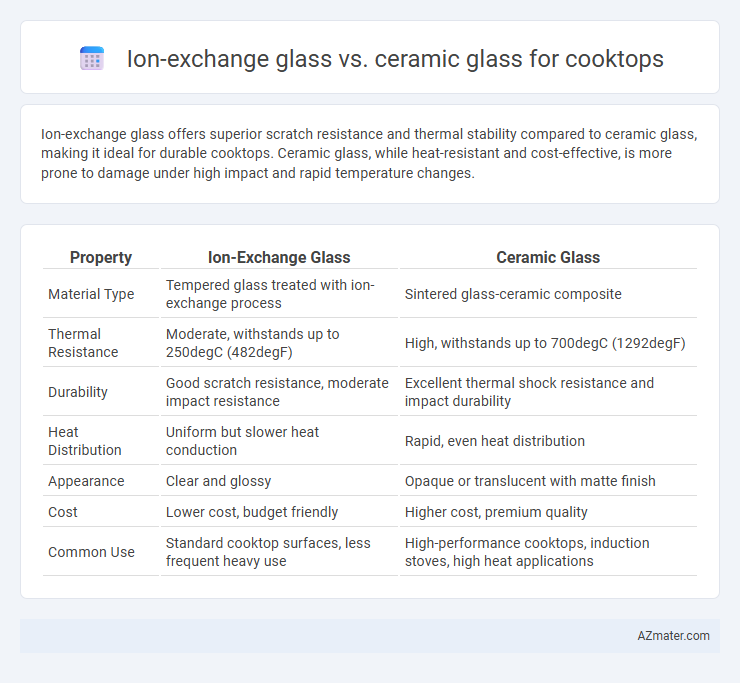
Ion-exchange glass offers superior scratch resistance and thermal stability compared to ceramic glass, making it ideal for durable cooktops. Ceramic glass, while heat-resistant and cost-effective, is more prone to damage under high impact and rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ion-Exchange Glass | Ceramic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Tempered glass treated with ion-exchange process | Sintered glass-ceramic composite |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, withstands up to 250degC (482degF) | High, withstands up to 700degC (1292degF) |
| Durability | Good scratch resistance, moderate impact resistance | Excellent thermal shock resistance and impact durability |
| Heat Distribution | Uniform but slower heat conduction | Rapid, even heat distribution |
| Appearance | Clear and glossy | Opaque or translucent with matte finish |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget friendly | Higher cost, premium quality |
| Common Use | Standard cooktop surfaces, less frequent heavy use | High-performance cooktops, induction stoves, high heat applications |
Introduction to Cooktop Glass Technologies
Ion-exchange glass for cooktops offers enhanced strength and scratch resistance by replacing smaller ions with larger ones through a chemical process, creating a durable surface ideal for high-heat cooking. Ceramic glass cooktops utilize a crystalline structure capable of withstanding thermal shock and distributing heat evenly, making them a preferred choice for kitchens requiring both performance and aesthetic appeal. Both technologies prioritize safety and efficiency, but ion-exchange glass excels in durability while ceramic glass is favored for its superior heat tolerance and uniform heat distribution.
What is Ion-Exchange Glass?
Ion-exchange glass is a type of toughened glass enhanced through a chemical process where smaller sodium ions are replaced by larger potassium ions in the glass surface, increasing its strength and resistance to thermal shock. This process creates a compressive stress layer that improves durability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for cooktops subject to high heat and frequent impact. Compared to ceramic glass, ion-exchange glass offers superior mechanical strength but may have slightly lower heat resistance, requiring careful consideration for high-temperature cooking applications.
What is Ceramic Glass?
Ceramic glass is a durable, heat-resistant material commonly used for cooktop surfaces, composed primarily of glass-ceramic composites that offer excellent thermal shock resistance and smooth finish. Its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes makes it ideal for electric and induction cooktops, providing uniform heat distribution and energy efficiency. Ion-exchange glass, while strong and scratch-resistant, lacks the thermal stability of ceramic glass, making ceramic glass the preferred choice for high-performance cooking applications.
Heat Resistance: Ion-Exchange vs Ceramic Glass
Ion-exchange glass offers moderate heat resistance suitable for everyday cooking but may be prone to thermal shock under sudden temperature changes. Ceramic glass demonstrates superior heat resistance, withstanding higher temperatures and rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking. For cooktops, ceramic glass provides enhanced durability and longevity due to its ability to maintain structural integrity under intense heat conditions.
Durability and Safety Comparison
Ion-exchange glass offers superior durability due to its chemically strengthened surface, making it highly resistant to scratches, cracks, and thermal shock compared to ceramic glass. Ceramic glass cooktops, while heat-resistant, are more prone to chipping and breakage under impact or sudden temperature changes. Safety is enhanced with ion-exchange glass as it maintains structural integrity under high heat, reducing the risk of shattering and ensuring long-term reliable performance in kitchen environments.
Thermal Shock and Stress Performance
Ion-exchange glass cooktops exhibit superior thermal shock resistance due to a chemically strengthened surface that enhances durability under rapid temperature changes. Ceramic glass cooktops, while offering excellent heat distribution and aesthetic appeal, are more prone to stress fractures when exposed to sudden temperature fluctuations. The ion-exchange process increases the glass's compressive stress layer, making it more resilient against thermal stress compared to standard ceramic glass surfaces.
Aesthetic Options and Surface Finishes
Ion-exchange glass cooktops offer a sleek, glossy surface with a mirror-like finish that enhances modern kitchen aesthetics, available in a range of deep black and smooth monochrome hues. Ceramic glass cooktops provide a matte or semi-gloss finish, allowing for diverse color options and subtle texture variations that complement both contemporary and traditional kitchen designs. The durability of ion-exchange glass ensures long-lasting surface shine, while ceramic glass surfaces offer versatile aesthetic customization through different glazing techniques.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Ion-exchange glass cooktops resist scratches and stains more effectively than ceramic glass, simplifying routine cleaning tasks. Ceramic glass requires gentle, non-abrasive cleaning agents to avoid surface damage and maintain its sleek appearance. Both materials benefit from prompt spill removal, but ion-exchange glass generally demands less frequent maintenance due to its enhanced durability.
Cost Differences and Value Analysis
Ion-exchange glass cooktops typically cost 20-30% more than ceramic glass due to their enhanced durability and scratch resistance. Ceramic glass offers a lower upfront price but may incur higher maintenance or replacement costs over time because of its lower resistance to thermal and impact stress. Evaluating value, ion-exchange glass provides longer lifespan and improved performance, delivering better cost-efficiency for frequent or heavy use.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Cooktop
Ion-exchange glass offers superior scratch resistance and durability due to a chemical strengthening process, making it ideal for cooktops needing long-lasting, resilient surfaces. Ceramic glass excels in heat resistance and thermal shock tolerance, providing a smooth, easy-to-clean surface that withstands rapid temperature changes common in cooking environments. Choosing between ion-exchange and ceramic glass depends on prioritizing either maximum surface toughness or enhanced heat resistance for your cooktop's performance and longevity.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Ceramic glass for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com