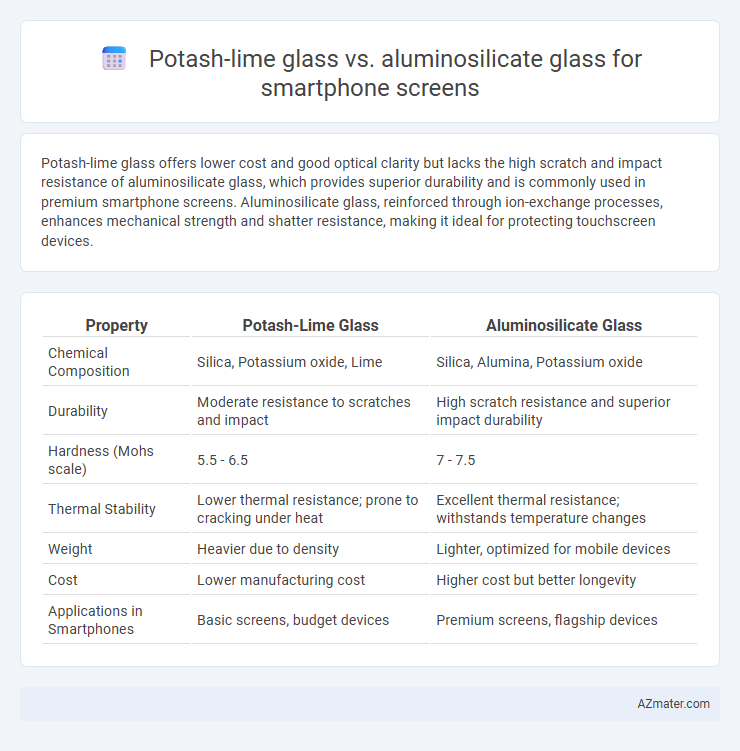
Potash-lime glass offers lower cost and good optical clarity but lacks the high scratch and impact resistance of aluminosilicate glass, which provides superior durability and is commonly used in premium smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, reinforced through ion-exchange processes, enhances mechanical strength and shatter resistance, making it ideal for protecting touchscreen devices.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Potash-Lime Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Silica, Potassium oxide, Lime | Silica, Alumina, Potassium oxide |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to scratches and impact | High scratch resistance and superior impact durability |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 5.5 - 6.5 | 7 - 7.5 |
| Thermal Stability | Lower thermal resistance; prone to cracking under heat | Excellent thermal resistance; withstands temperature changes |
| Weight | Heavier due to density | Lighter, optimized for mobile devices |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher cost but better longevity |
| Applications in Smartphones | Basic screens, budget devices | Premium screens, flagship devices |
Introduction to Smartphone Screen Glass Types
Potash-lime glass and aluminosilicate glass are two primary materials used in smartphone screen manufacturing, each offering distinct properties. Potash-lime glass, commonly known as soda-lime glass, is cost-effective and easy to produce but lacks the durability and scratch resistance required for modern smartphones. Aluminosilicate glass, reinforced through ion-exchange processes like in Corning Gorilla Glass, provides superior hardness, impact resistance, and enhanced longevity, making it the preferred choice for premium smartphone displays.
Composition of Potash-lime Glass
Potash-lime glass, primarily composed of silica (SiO2), potassium oxide (K2O), and lime (CaO), offers enhanced chemical durability and resistance to thermal shock compared to soda-lime glass. Its high potassium oxide content increases the glass's hardness and improves its ability to withstand mechanical stress, making it a viable option for smartphone screens requiring moderate impact resistance. However, aluminosilicate glass surpasses potash-lime glass in strength and scratch resistance due to its aluminum oxide (Al2O3) content, which reinforces the glass matrix for superior protective performance.
Composition of Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass used in smartphone screens is primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), aluminum oxide (Al2O3), and smaller amounts of alkali metals, which enhance its durability and scratch resistance. This composition creates a strong, chemically stable network that offers superior thermal resistance and impact strength compared to potash-lime glass, which mainly contains potassium oxide (K2O) and calcium oxide (CaO). The higher aluminum oxide content in aluminosilicate glass significantly improves mechanical performance, making it the preferred choice for high-performance mobile devices.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass demonstrates superior mechanical strength compared to potash-lime glass, with increased resistance to scratches, cracks, and impacts due to its enhanced chemical composition and thermal stability. This glass type exhibits higher fracture toughness and greater surface hardness, making it more suitable for smartphone screens that endure frequent drops and pressure. Potash-lime glass, while more cost-effective, lacks the durability required for modern mobile device protection, leading to quicker damage under mechanical stress.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Aluminosilicate glass boasts superior scratch resistance compared to potash-lime glass due to its higher hardness and chemical durability, making it less prone to surface abrasions from everyday use. It also offers enhanced impact resistance through its ion-exchange strengthening process, which creates a compressive stress layer, significantly reducing the risk of screen shattering upon drops. Potash-lime glass, while more cost-effective, lacks this advanced strengthening and hardness, resulting in lower durability against scratches and impacts in smartphone applications.
Optical Clarity and Touch Sensitivity
Potash-lime glass offers moderate optical clarity and basic touch sensitivity, but Aluminosilicate glass excels with superior transparency and enhanced touch responsiveness, making it the preferred choice for high-end smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its chemical durability and higher hardness, minimizes optical distortions and provides smoother, more accurate touchscreen interactions. This glass type also reduces glare and fingerprint visibility, significantly improving user experience compared to potash-lime variants.
Chemical Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Potash-lime glass exhibits lower chemical durability and is more prone to corrosion due to its higher alkali content, making it less suitable for smartphone screens exposed to sweat and environmental moisture. Aluminosilicate glass contains aluminum oxide, which significantly enhances its chemical resistance and structural integrity, providing superior protection against scratches, acids, and alkalis. This improved corrosion resistance in aluminosilicate glass results in longer-lasting, more durable smartphone screens with better performance in harsh conditions.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Potash-lime glass offers lower manufacturing costs due to its abundance and simpler production processes, making it a budget-friendly option for smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, although more expensive, provides superior scratch resistance and durability, justifying higher upfront costs in premium device manufacturing. The trade-off between cost and strength impacts material selection, with potash-lime favored for economy models while aluminosilicate is preferred for high-end phones demanding enhanced performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Potash-lime glass, commonly used in smartphone screens, has a higher environmental impact due to its energy-intensive production and limited recyclability compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance, reducing the frequency of screen replacements and electronic waste. Sustainable smartphone design increasingly favors aluminosilicate glass for its longer lifespan and potential for improved recycling processes, contributing to reduced resource consumption and lower carbon emissions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Smartphones
Potash-lime glass offers cost-effectiveness and reasonable durability, making it suitable for budget smartphones, while aluminosilicate glass provides superior scratch resistance, higher strength, and increased impact resistance ideal for premium devices. Aluminosilicate glass, such as Corning Gorilla Glass, significantly enhances smartphone screen longevity and user satisfaction through advanced chemical strengthening processes. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing price, durability requirements, and user experience expectations in smartphone design.
Infographic: Potash-lime glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com