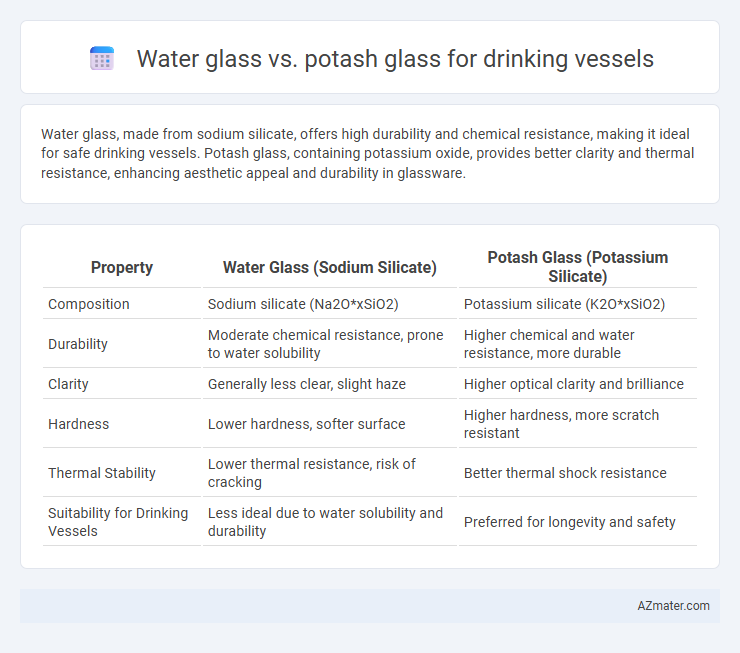
Water glass, made from sodium silicate, offers high durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for safe drinking vessels. Potash glass, containing potassium oxide, provides better clarity and thermal resistance, enhancing aesthetic appeal and durability in glassware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Water Glass (Sodium Silicate) | Potash Glass (Potassium Silicate) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium silicate (Na2O*xSiO2) | Potassium silicate (K2O*xSiO2) |
| Durability | Moderate chemical resistance, prone to water solubility | Higher chemical and water resistance, more durable |
| Clarity | Generally less clear, slight haze | Higher optical clarity and brilliance |
| Hardness | Lower hardness, softer surface | Higher hardness, more scratch resistant |
| Thermal Stability | Lower thermal resistance, risk of cracking | Better thermal shock resistance |
| Suitability for Drinking Vessels | Less ideal due to water solubility and durability | Preferred for longevity and safety |
Introduction to Water Glass and Potash Glass
Water glass, also known as sodium silicate glass, features a clear, durable composition ideal for everyday drinking vessels due to its resistance to water and heat. Potash glass, composed primarily of potassium oxide, offers a higher refractive index and brilliance, making it a preferred choice for decorative glassware and fine drinking tumblers. Both types provide unique chemical properties influencing clarity, strength, and usability in beverage containers.
Chemical Composition Differences
Water glass, primarily composed of sodium silicate (Na2SiO3), differs significantly from potash glass, which is based on potassium silicate (K2SiO3). The higher sodium content in water glass results in greater water solubility and alkaline properties, while potash glass offers enhanced chemical durability and resistance to thermal shock due to its potassium content. These compositional differences influence the suitability of each glass type as drinking vessels, impacting factors such as leaching potential and mechanical strength.
Manufacturing Processes Explained
Water glass drinking vessels are produced using sodium silicate solutions, which are hardened through evaporation and heat treatment, resulting in a durable, non-porous surface ideal for safe drinking use. Potash glass, also known as potassium glass, is manufactured by melting potassium carbonate with silica and other materials, creating a higher refractive index and improved chemical resistance compared to water glass. The manufacturing process of potash glass involves higher temperature melting and annealing stages to enhance clarity and strength, making it a preferred choice for premium drinking vessels.
Clarity and Aesthetic Appeal
Water glass, made primarily from sodium silicate, offers moderate clarity with a slightly cloudy appearance due to its composition, making it less ideal for high-end drinking vessels. Potash glass, containing potassium oxide, provides superior clarity and brilliance, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of drinking vessels through its higher refractive index. The enhanced transparency and lustrous finish of potash glass make it a preferred choice for elegant drinkware where visual presentation is crucial.
Durability and Resistance to Breakage
Water glass, typically made from soda-lime silica, offers moderate durability and is more prone to scratches and chips compared to potash glass. Potash glass, composed with potassium oxide, exhibits higher density and superior resistance to breakage, making it more resilient for daily use as drinking vessels. Its enhanced strength and chemical stability contribute to better longevity and durability under frequent handling.
Taste Preservation in Drinking Vessels
Water glass, made from sodium silicate, offers excellent taste preservation due to its non-reactive surface that prevents flavor alteration in drinking vessels. Potash glass, containing potassium oxide, provides superior resistance to chemical leaching, maintaining the purity and original taste of beverages over time. Both materials ensure minimal impact on flavor, but potash glass is often preferred for delicate drinks due to its enhanced chemical stability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Water glass, primarily made from sodium silicate, is more eco-friendly due to its recyclability and lower energy consumption during production compared to potash glass, which uses potassium oxide. Potash glass offers higher durability but involves more intensive mining and processing of potash, increasing its environmental footprint. Choosing water glass supports sustainability goals by reducing resource depletion and greenhouse gas emissions in manufacturing.
Price Comparison and Availability
Water glass drinking vessels are generally more affordable and widely available due to extensive manufacturing and lower material costs, making them a budget-friendly choice for everyday use. Potash glass, known for its higher refractive index and superior clarity, tends to be more expensive and less commonly stocked in retail outlets, primarily due to the costlier ingredients and specialized production process. Availability of potash glass is often limited to specialty stores or online platforms, whereas water glass can be found easily in supermarkets and general kitchenware shops.
Common Uses in Modern Tableware
Water glass and potash glass differ in composition but both serve unique roles in modern tableware. Water glass, known for its higher silica content, is favored for everyday drinking vessels due to its durability and clarity. Potash glass, containing potassium oxide, is prized for its brilliance and smooth finish, often used in elegant glassware for special occasions and decorative pieces.
Choosing the Best Glass for Drinking
Water glass, typically made from soda-lime glass, offers durability and affordability but may contain higher levels of impurities compared to potash glass, which is crafted with potassium oxide, providing a smoother texture and enhanced chemical resistance. Potash glass is less prone to leaching and often preferred for superior drinking vessel quality because it maintains the beverage's taste and purity better than water glass. Choosing the best glass for drinking involves considering factors like clarity, safety, and chemical stability, with potash glass generally recognized for offering a premium drinking experience.
Infographic: Water glass vs Potash glass for Drinking vessel
 azmater.com
azmater.com