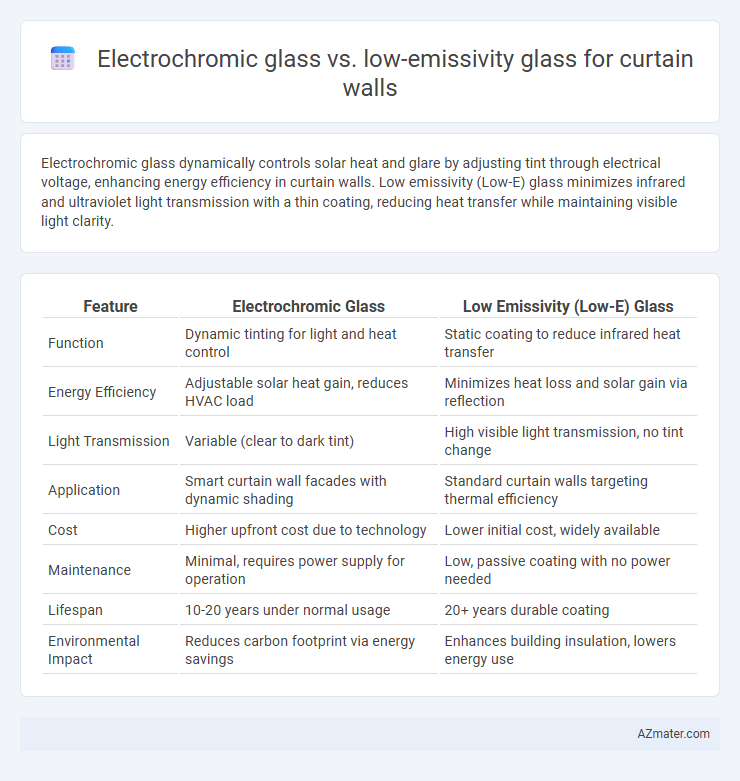
Electrochromic glass dynamically controls solar heat and glare by adjusting tint through electrical voltage, enhancing energy efficiency in curtain walls. Low emissivity (Low-E) glass minimizes infrared and ultraviolet light transmission with a thin coating, reducing heat transfer while maintaining visible light clarity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Low Emissivity (Low-E) Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Dynamic tinting for light and heat control | Static coating to reduce infrared heat transfer |
| Energy Efficiency | Adjustable solar heat gain, reduces HVAC load | Minimizes heat loss and solar gain via reflection |
| Light Transmission | Variable (clear to dark tint) | High visible light transmission, no tint change |
| Application | Smart curtain wall facades with dynamic shading | Standard curtain walls targeting thermal efficiency |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to technology | Lower initial cost, widely available |
| Maintenance | Minimal, requires power supply for operation | Low, passive coating with no power needed |
| Lifespan | 10-20 years under normal usage | 20+ years durable coating |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint via energy savings | Enhances building insulation, lowers energy use |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Technologies
Curtain wall glazing technologies include Electrochromic glass, which allows dynamic control of light and heat transmission through voltage-driven tinting, and Low emissivity (Low-E) glass, engineered with thin metal oxide coatings to reduce infrared and ultraviolet light while maintaining visible transparency. Electrochromic glass enhances energy efficiency by adapting to changing environmental conditions, whereas Low-E glass passively limits solar heat gain and improves thermal insulation in building envelopes. Both technologies contribute to sustainable curtain wall systems by optimizing occupant comfort and reducing HVAC energy consumption.
What is Electrochromic Glass?
Electrochromic glass is a type of smart glass that changes its tint when an electric voltage is applied, enabling dynamic control of solar heat and glare in curtain wall applications. Unlike low emissivity (Low-E) glass, which passively reduces infrared heat transfer by reflecting radiant energy, electrochromic glass actively adjusts its transparency to optimize daylight and energy efficiency. This technology enhances occupant comfort and reduces HVAC costs by adapting to changing sunlight conditions in real-time.
Understanding Low Emissivity (Low-E) Glass
Low Emissivity (Low-E) glass enhances curtain wall performance by minimizing infrared and ultraviolet light transmission while maintaining visible light clarity, significantly improving energy efficiency and indoor comfort. It features a microscopically thin, transparent coating that reflects heat back to its source, reducing heating and cooling costs in commercial buildings. Unlike electrochromic glass, which dynamically darkens to control solar gain, Low-E glass provides a consistent thermal barrier without the need for electrical operation or complex control systems.
How Electrochromic Glass Works in Curtain Walls
Electrochromic glass in curtain walls functions by using a thin, transparent coating that changes its light transmission properties when an electrical voltage is applied, allowing for dynamic control of solar heat gain and glare. This smart glass system adjusts tint levels in response to user input or automated sensors, optimizing energy efficiency and occupant comfort by reducing reliance on HVAC systems and artificial lighting. Unlike low emissivity (Low-E) glass that primarily limits infrared heat transfer through a static coating, electrochromic glass actively modulates visible light and solar radiation in real time.
Key Features and Benefits of Low-E Glass
Low emissivity (Low-E) glass for curtain walls features a microscopically thin, transparent coating that reduces infrared and ultraviolet light penetration while maintaining visible light transmission. This key characteristic enhances energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer, leading to lower heating and cooling costs and improved occupant comfort. Low-E glass also reduces UV damage to interiors, supports passive solar heating, and contributes to sustainable building practices through better thermal performance.
Energy Efficiency Comparison: Electrochromic vs Low-E Glass
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic solar control by adjusting tint based on sunlight intensity, significantly reducing cooling loads and improving energy efficiency in curtain walls. Low emissivity (Low-E) glass enhances thermal insulation by minimizing infrared heat transfer, effectively retaining indoor temperatures and lowering heating and cooling demands. While Low-E glass provides consistent energy savings year-round, electrochromic glass excels in climates with variable solar radiation, enabling adaptive energy management and reducing reliance on HVAC systems.
Daylight and Glare Control: Which Performs Better?
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic daylight and glare control by adjusting tint levels in response to sunlight, significantly reducing glare and improving occupant comfort in curtain wall applications. Low emissivity (Low-E) glass primarily enhances thermal performance by reflecting infrared radiation but has limited effectiveness in modulating visible light and controlling glare. For superior daylight management and glare reduction in curtain walls, electrochromic glass outperforms Low-E glass due to its active, adaptable shading capabilities.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Long-term Savings
Electrochromic glass for curtain walls involves higher initial installation costs due to advanced technology and wiring requirements, whereas low emissivity (Low-E) glass presents a more affordable upfront expense with simpler integration. Over time, electrochromic glass delivers greater energy savings by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and improving occupant comfort, which can reduce HVAC costs significantly. Low-E glass offers consistent thermal insulation and UV protection, resulting in moderate long-term utility savings while maintaining lower maintenance expenses.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic solar control by adjusting tint in response to sunlight, reducing HVAC energy consumption and enhancing occupant comfort in curtain wall systems. Low emissivity (Low-E) glass minimizes heat transfer through a coated surface, providing consistent thermal insulation that lowers heating and cooling demands. Both technologies contribute to sustainability by improving building energy efficiency, but electrochromic glass enables adaptive performance for varying environmental conditions, potentially yielding higher long-term energy savings and reduced carbon footprint.
Choosing the Best Glass Type for Your Curtain Wall Project
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light and heat control by changing tint in response to electrical signals, ideal for enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in curtain walls. Low emissivity (Low-E) glass provides a fixed, highly effective thermal barrier that reduces heat transfer by reflecting infrared energy, optimizing insulation and reducing HVAC loads. When choosing the best glass type for your curtain wall project, prioritize dynamic solar control benefits of electrochromic glass for flexible environments or the consistent thermal insulation performance of Low-E glass for cost-effective, passive energy savings.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Low emissivity glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com