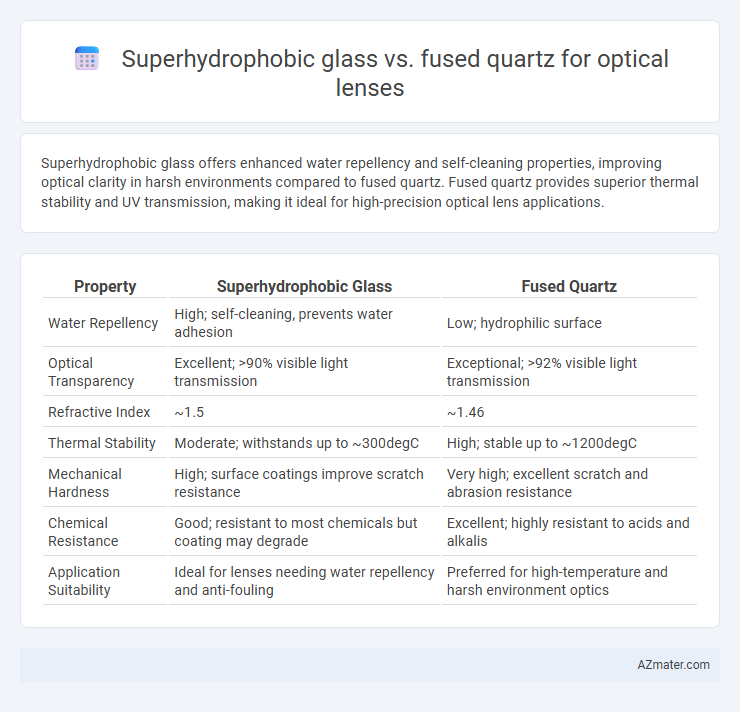
Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced water repellency and self-cleaning properties, improving optical clarity in harsh environments compared to fused quartz. Fused quartz provides superior thermal stability and UV transmission, making it ideal for high-precision optical lens applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Superhydrophobic Glass | Fused Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Water Repellency | High; self-cleaning, prevents water adhesion | Low; hydrophilic surface |
| Optical Transparency | Excellent; >90% visible light transmission | Exceptional; >92% visible light transmission |
| Refractive Index | ~1.5 | ~1.46 |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate; withstands up to ~300degC | High; stable up to ~1200degC |
| Mechanical Hardness | High; surface coatings improve scratch resistance | Very high; excellent scratch and abrasion resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good; resistant to most chemicals but coating may degrade | Excellent; highly resistant to acids and alkalis |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for lenses needing water repellency and anti-fouling | Preferred for high-temperature and harsh environment optics |
Introduction: Optical Lens Materials in Focus
Superhydrophobic glass and fused quartz represent advanced materials widely used in optical lens manufacturing, each offering unique benefits tailored to precision applications. Superhydrophobic glass features a water-repellent surface that enhances lens durability and clarity by minimizing contamination and moisture accumulation, critical in outdoor and harsh environments. Fused quartz, renowned for its exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and high transmission in ultraviolet and infrared spectra, delivers superior performance in high-precision optical systems and scientific instruments.
Understanding Superhydrophobic Glass
Superhydrophobic glass features a nano-structured surface that repels water, reduces fogging, and enhances optical clarity compared to traditional fused quartz lenses. Its high water contact angle, often exceeding 150deg, minimizes surface contamination and maintains consistent light transmission in humid or wet environments. This advanced surface treatment improves lens durability and performance in applications requiring superior hydrophobicity and anti-reflective properties.
Exploring Fused Quartz Properties
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional optical clarity and low thermal expansion, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and ideal for precision optical lenses. Its high transmission range from ultraviolet to infrared wavelengths outperforms many conventional materials, including superhydrophobic glass, which primarily offers surface water repellency without enhancing fundamental optical properties. The superior durability, chemical inertness, and stability of fused quartz ensure consistent lens performance in extreme environmental conditions, crucial for advanced optical applications.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Superhydrophobic glass offers excellent optical clarity with reduced surface reflections and water repellency, enhancing light transmission by minimizing scattering and smudges. Fused quartz provides superior intrinsic transparency across UV to near-infrared wavelengths, maintaining high light transmission with minimal absorption and scattering. While fused quartz excels in ultra-high purity and UV performance, superhydrophobic coatings on glass improve durability and clarity in wet or contaminated environments.
Resistance to Water and Contaminants
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits extraordinary water repellency and resists contaminants effectively, maintaining optical clarity by preventing water droplet adhesion and reducing surface fouling. In contrast, fused quartz, while highly durable and resistant to chemical attack, lacks inherent superhydrophobic properties, making it more prone to water retention and contamination buildup on the lens surface. The superior performance of superhydrophobic coatings on glass significantly enhances lens longevity and performance in wet or dirty environments compared to untreated fused quartz optics.
Scratch and Impact Durability
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior scratch resistance due to its specialized nano-coatings that repel water and abrasive particles, enhancing lens longevity in harsh environments. Fused quartz, known for its exceptional impact resistance and high mechanical strength, provides robust durability against physical shocks but lacks inherent scratch resistance without additional coatings. Combining superhydrophobic coatings on fused quartz substrates creates an optimal optical lens material with enhanced scratch protection and impact durability for demanding applications.
Thermal and Chemical Stability
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits enhanced thermal stability withstanding temperatures up to 600degC, while fused quartz endures extreme heat up to 1100degC, making quartz superior for high-temperature optical applications. Chemically, fused quartz is highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and corrosive environments, surpassing standard glass which may degrade over time under harsh chemicals despite its hydrophobic coating. The long-term performance of optical lenses relies on fused quartz's unparalleled chemical inertness and broad thermal tolerance, critical for demanding scientific and industrial uses.
Maintenance and Cleaning Ease
Superhydrophobic glass surfaces repel water and contaminants, significantly reducing the frequency and effort required for cleaning optical lenses compared to fused quartz, which tends to accumulate dirt and smudges more readily. The coating on superhydrophobic glass minimizes maintenance by preventing adhesion of dust and oils, enhancing lens longevity and preserving optical clarity. In contrast, fused quartz lenses require regular cleaning with solvents or specialized wipes to maintain performance, increasing maintenance time and risk of surface abrasion.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Superhydrophobic glass offers a cost-effective solution with enhanced water and dirt repellency, reducing maintenance and improving lens longevity, while fused quartz provides superior optical clarity and thermal resistance but at a higher manufacturing expense due to complex processing. The manufacturing of superhydrophobic coatings involves scalable chemical vapor deposition or sol-gel techniques, suitable for mass production, whereas fused quartz requires precision melting and forming at elevated temperatures, increasing production time and cost. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements in demanding optical applications.
Choosing the Best Material for Optical Applications
Superhydrophobic glass offers excellent water repellency and self-cleaning properties, enhancing lens durability in harsh environments, while fused quartz provides superior optical clarity, high thermal stability, and minimal birefringence, making it ideal for precision optical lenses. Optical applications requiring resistance to environmental contaminants benefit from superhydrophobic coatings on glass, whereas high-performance systems demanding exceptional ultraviolet transmission and mechanical strength often prefer fused quartz. Selecting between these materials depends on specific application needs such as environmental exposure, wavelength requirements, and mechanical durability.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Fused quartz for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com