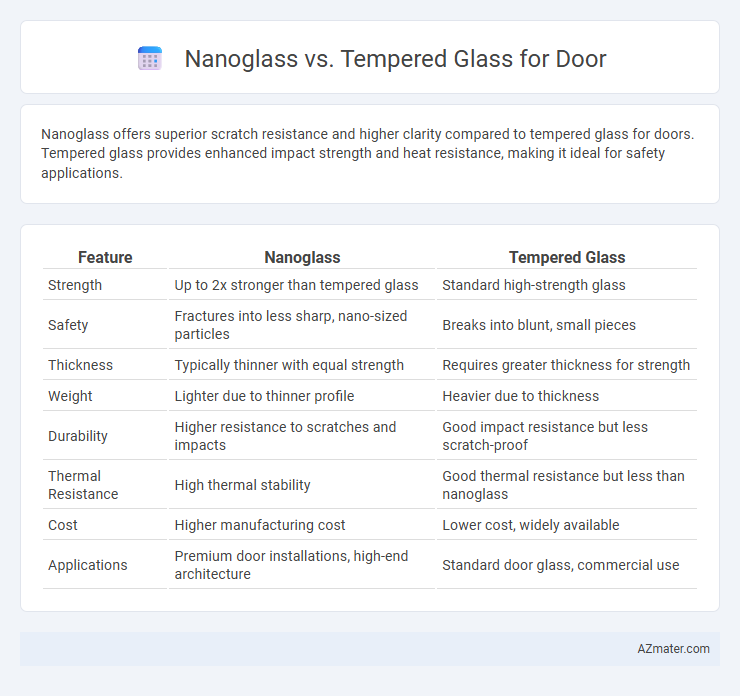
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and higher clarity compared to tempered glass for doors. Tempered glass provides enhanced impact strength and heat resistance, making it ideal for safety applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanoglass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Up to 2x stronger than tempered glass | Standard high-strength glass |
| Safety | Fractures into less sharp, nano-sized particles | Breaks into blunt, small pieces |
| Thickness | Typically thinner with equal strength | Requires greater thickness for strength |
| Weight | Lighter due to thinner profile | Heavier due to thickness |
| Durability | Higher resistance to scratches and impacts | Good impact resistance but less scratch-proof |
| Thermal Resistance | High thermal stability | Good thermal resistance but less than nanoglass |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Premium door installations, high-end architecture | Standard door glass, commercial use |
Introduction to Nanoglass and Tempered Glass
Nanoglass features a nano-scale coating that enhances scratch resistance, clarity, and durability, making it an innovative choice for modern door applications. Tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that increases its strength by up to five times compared to ordinary glass, providing superior safety and impact resistance. Comparing both, nanoglass offers advanced surface protection and aesthetic appeal, while tempered glass ensures enhanced structural integrity and shatter resistance.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Nanoglass for doors is composed of ultra-thin, nano-engineered silica particles that enhance strength and flexibility through advanced sol-gel processes, creating a uniform, scratch-resistant surface. Tempered glass undergoes thermal or chemical tempering, where the glass is rapidly cooled or chemically treated to induce compressive stresses, resulting in a robust and shatter-resistant structure. The sol-gel synthesis in nanoglass enables precise control of nanoparticle distribution, while tempered glass relies on controlled heating and cooling cycles to improve mechanical performance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Nanoglass exhibits superior strength and durability compared to tempered glass, featuring nano-engineered layers that enhance impact resistance and scratch prevention. Tempered glass, while robust due to heat treatment, is more prone to surface damage and less flexible under extreme stress conditions. Nanoglass outperforms in long-term durability, maintaining clarity and structural integrity even with frequent use and environmental exposure.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Nanoglass offers superior aesthetic appeal for doors with its ultra-clear transparency and smooth, glossy finish that enhances natural light and modern spaces. It allows for greater design flexibility due to its thin profile and ability to be custom-shaped or colored, making it ideal for sleek, contemporary door designs. Tempered glass provides strength and safety but is typically thicker and less adaptable to intricate designs, limiting creative architectural applications.
Safety Features and Impact Resistance
Nanoglass offers superior impact resistance for doors by utilizing a nano-structured coating that enhances strength and shatterproof properties compared to traditional tempered glass. Tempered glass, while strong and heat-treated to resist breaking, tends to break into small granular pieces upon impact, reducing injury risk but potentially compromising security. Nanoglass improves safety features by maintaining structural integrity even under high-impact conditions, minimizing shards and providing enhanced durability for door applications.
Thermal and Sound Insulation Properties
Nanoglass offers superior thermal insulation compared to tempered glass due to its advanced nanocoating technology that reduces heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency in door applications. Tempered glass provides good impact resistance but falls short in minimizing sound transmission, whereas nanoglass significantly improves acoustic insulation by damping sound vibrations. In door installations, choosing nanoglass results in better temperature regulation and quieter environments compared to conventional tempered glass.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Nanoglass doors require minimal maintenance due to their hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings that resist fingerprints, smudges, and water stains, reducing the need for frequent cleaning. Tempered glass, while durable and resistant to impact, tends to accumulate fingerprints and smudges more easily, demanding regular cleaning with non-abrasive glass cleaners to maintain clarity and appearance. Both materials benefit from gentle cleaning techniques, but nanoglass offers a distinct advantage in preserving cleanliness with less effort over time.
Cost Analysis: Nanoglass vs Tempered Glass
Nanoglass doors tend to have a higher upfront cost than tempered glass due to advanced manufacturing techniques and enhanced durability features. Tempered glass is more budget-friendly but may require more frequent replacements over time, potentially increasing long-term expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including maintenance and lifespan, highlights nanoglass as a cost-effective investment despite its premium price.
Environmental Sustainability and Lifespan
Nanoglass offers superior environmental sustainability compared to tempered glass due to its lower energy consumption during manufacturing and enhanced recyclability. Its longer lifespan arises from increased scratch resistance and greater durability, reducing the frequency of replacements. Tempered glass, while strong, requires more energy-intensive production processes and typically has a shorter service life, leading to higher environmental impact over time.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Door
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced clarity compared to tempered glass, making it ideal for modern door designs that prioritize aesthetics and durability. Tempered glass provides excellent impact resistance and safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon breakage, which is crucial for high-traffic areas or commercial doors. Selecting between nanoglass and tempered glass depends on whether clarity and scratch resistance or enhanced safety and impact strength are the primary requirements for your door application.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com