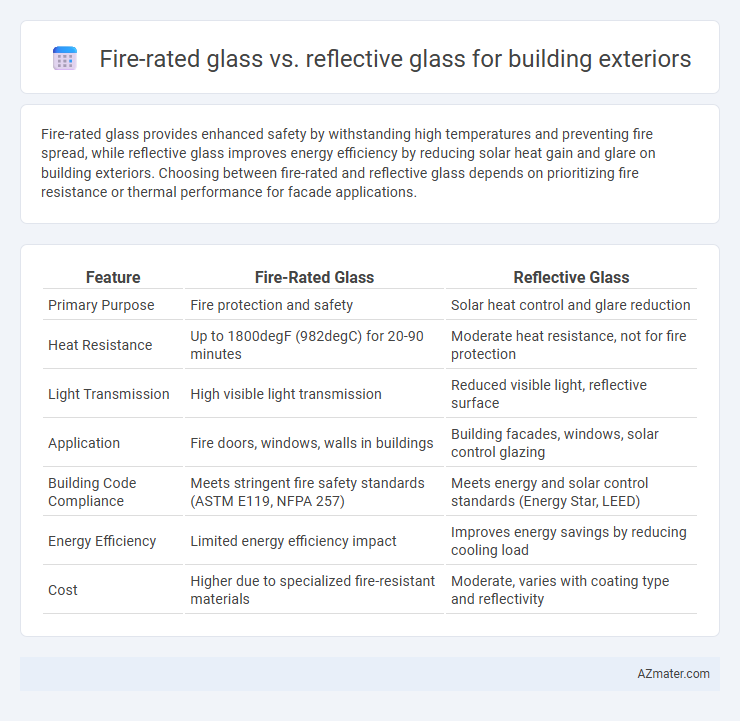
Fire-rated glass provides enhanced safety by withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire spread, while reflective glass improves energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain and glare on building exteriors. Choosing between fire-rated and reflective glass depends on prioritizing fire resistance or thermal performance for facade applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Rated Glass | Reflective Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Fire protection and safety | Solar heat control and glare reduction |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1800degF (982degC) for 20-90 minutes | Moderate heat resistance, not for fire protection |
| Light Transmission | High visible light transmission | Reduced visible light, reflective surface |
| Application | Fire doors, windows, walls in buildings | Building facades, windows, solar control glazing |
| Building Code Compliance | Meets stringent fire safety standards (ASTM E119, NFPA 257) | Meets energy and solar control standards (Energy Star, LEED) |
| Energy Efficiency | Limited energy efficiency impact | Improves energy savings by reducing cooling load |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized fire-resistant materials | Moderate, varies with coating type and reflectivity |
Introduction to Fire-Rated and Reflective Glass
Fire-rated glass is specially designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke, providing crucial safety in building exteriors during a fire event. Reflective glass, on the other hand, enhances energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain and glare through its metallic coating, making it ideal for climate control and privacy. Both glass types serve distinct functions: fire-rated glass prioritizes safety and building code compliance, while reflective glass emphasizes energy performance and aesthetic appeal.
Defining Fire-Rated Glass: Essential Features
Fire-rated glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, making it crucial for building safety and compliance with fire codes. It typically consists of multiple layers, including intumescent interlayers that expand when heated to maintain structural integrity and insulation. This type of glass must meet rigorous standards such as ASTM E119 or UL 972 to ensure fire resistance, setting it apart from reflective glass, which is primarily designed to reduce solar heat and glare without fire protection capabilities.
Reflective Glass: Properties and Applications
Reflective glass features a metallic coating that reduces solar heat gain and glare, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in building exteriors. Its low emissivity properties help control ultraviolet and infrared radiation, making it ideal for commercial skyscrapers and office buildings with large glass facades. Reflective glass also provides privacy during daylight hours while maintaining significant natural light transmission, supporting sustainable architectural design.
Safety Standards and Building Codes
Fire-rated glass is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, meeting strict safety standards such as UL 9 and BS 476, making it essential for building exteriors in fire-prone areas and compliant with international building codes like NFPA 80. Reflective glass primarily enhances energy efficiency and privacy but does not meet fire resistance standards, thus it cannot replace fire-rated glass in fire-rated assemblies. Compliance with local fire safety regulations mandates the use of fire-rated glass for exterior applications where fire protection is critical, ensuring both occupant safety and legal building code adherence.
Fire Protection Capabilities and Performance
Fire-rated glass is specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the passage of flames and smoke, ensuring critical fire protection in building exteriors. Reflective glass primarily enhances energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal by reducing solar heat gain and glare but lacks fire-resistant properties. Selecting fire-rated glass is essential for compliance with fire safety codes and maintaining structural integrity during fire incidents.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Fire-rated glass offers superior thermal insulation by withstanding extreme heat and preventing fire spread, which enhances the safety and integrity of a building's exterior while maintaining energy efficiency. Reflective glass reduces solar heat gain by reflecting a significant portion of infrared and ultraviolet rays, lowering cooling loads and improving energy savings in hot climates. Choosing between fire-rated and reflective glass depends on balancing fire safety requirements with the need for solar control and thermal performance in building design.
Aesthetic Impact on Building Facades
Fire-rated glass enhances building facades by combining safety with sleek transparency, maintaining natural light while providing vital fire protection. Reflective glass offers dynamic visual effects with mirrored surfaces, reducing solar glare and heat gain, thus creating a modern, polished aesthetic. Both materials influence exterior design but cater to different priorities: fire-rated glass emphasizes safety without sacrificing light, while reflective glass focuses on energy efficiency and visual impact.
Cost Comparison and Installation Considerations
Fire-rated glass typically costs significantly more than reflective glass due to its specialized materials and rigorous safety certifications necessary for building exteriors. Installation of fire-rated glass demands precise fitting and compliance with fire safety codes, often requiring experienced professionals, which can increase labor expenses. Reflective glass installation is generally more straightforward with standard glazing techniques, making it a cost-effective option for projects prioritizing aesthetics and solar control over fire resistance.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Fire-rated glass offers exceptional durability by withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire spread, making it essential for safety-critical building exteriors. Reflective glass, designed primarily for energy efficiency and glare reduction, provides moderate durability but requires regular cleaning to maintain its reflective coating and visual performance. Maintenance demands for fire-rated glass are generally lower due to its robust construction, whereas reflective glass necessitates more frequent upkeep to avoid surface degradation and maintain optimal reflectivity.
Choosing the Right Glass: Key Decision Factors
Fire-rated glass offers critical safety by preventing fire and smoke spread, making it essential for compliance with fire safety codes in building exteriors. Reflective glass enhances energy efficiency and privacy by reducing solar heat gain and glare, contributing to sustainable building design. Key decision factors include fire resistance requirements, energy performance goals, aesthetic preferences, and local building regulations to ensure optimal safety and functionality.
Infographic: Fire-rated glass vs Reflective glass for Building exterior
 azmater.com
azmater.com