Gorilla Glass offers high durability and scratch resistance but has limited insulation properties compared to Fiberglass, which provides superior thermal and acoustic insulation due to its fibrous structure. Fiberglass insulation is widely used in construction for energy efficiency, while Gorilla Glass is preferred in electronic device screens for impact protection.
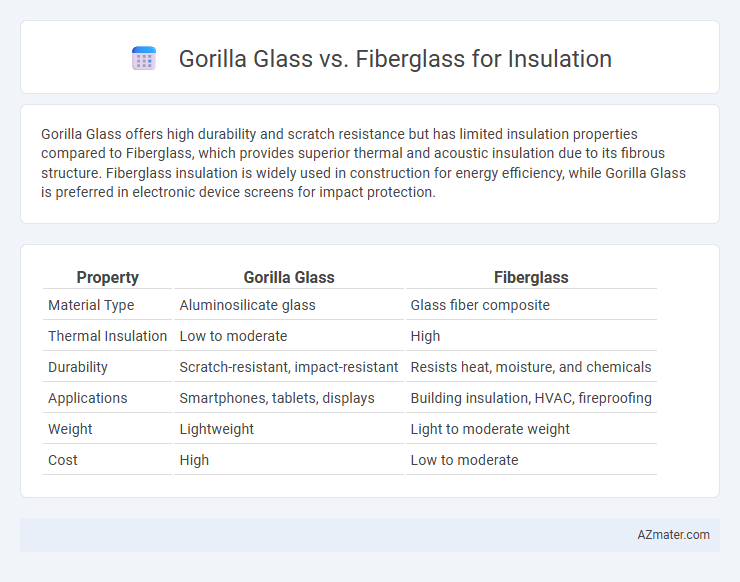
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gorilla Glass | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aluminosilicate glass | Glass fiber composite |
| Thermal Insulation | Low to moderate | High |
| Durability | Scratch-resistant, impact-resistant | Resists heat, moisture, and chemicals |
| Applications | Smartphones, tablets, displays | Building insulation, HVAC, fireproofing |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to moderate weight |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
Introduction: Gorilla Glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
Gorilla Glass offers exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, making it a durable choice for protective surfaces but less effective for insulation due to its low thermal resistance. Fiberglass insulation provides superior thermal performance with excellent heat retention and soundproofing qualities, commonly used in residential and commercial buildings to enhance energy efficiency. Comparing Gorilla Glass to fiberglass reveals that fiberglass is the preferred material for insulation purposes, while Gorilla Glass excels in impact and abrasion resistance applications.
Material Composition and Properties
Gorilla Glass is a chemically strengthened alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass known for its high scratch resistance and durability, primarily used in electronic displays rather than insulation applications. Fiberglass insulation consists of fine glass fibers made from molten glass spun into a fibrous mat, providing excellent thermal resistance and sound absorption due to its lightweight, non-combustible, and moisture-resistant properties. Unlike Gorilla Glass, which is rigid and dense, fiberglass's porous structure effectively traps air, making it a superior material for building insulation and thermal performance.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Gorilla Glass offers exceptional thermal resistance with a low thermal conductivity rating around 1.1 W/m*K, making it effective at reducing heat transfer in insulation applications. Fiberglass insulation typically has a thermal conductivity range of 0.035 to 0.045 W/m*K, significantly lower than glass, enabling superior thermal performance by trapping air within its fibers. The denser structure of Gorilla Glass limits its insulating efficiency compared to the porous nature of fiberglass, which excels in minimizing heat flow and maintaining energy efficiency in buildings.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Gorilla Glass exhibits superior strength and scratch resistance compared to fiberglass, making it highly durable under mechanical stress and impact. Fiberglass, while offering good thermal insulation properties, tends to be more prone to wear and degradation over time when exposed to moisture or UV radiation. The choice between Gorilla Glass and fiberglass for insulation applications hinges on the balance between required mechanical durability and thermal performance.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Gorilla Glass offers superior lightweight properties compared to fiberglass, making it ideal for applications where reduced weight is critical, such as in portable electronics and automotive components. Its exceptional flexibility allows it to bend without cracking, providing enhanced durability under stress, unlike fiberglass, which is heavier and more rigid, leading to potential brittleness and cracking under flexing. Weight and flexibility advantages of Gorilla Glass contribute to improved performance and longevity in insulating materials where dynamic movement or weight restrictions are factors.
Cost and Availability
Gorilla Glass, primarily designed for durability and scratch resistance in consumer electronics, is significantly more expensive and less available for insulation purposes compared to fiberglass. Fiberglass insulation, widely produced and distributed globally, offers cost-effective thermal resistance and easy installation, making it the preferred choice for construction and retrofitting. The high production costs and limited supply chain of Gorilla Glass render it impractical for large-scale insulation projects, emphasizing fiberglass as the economical and readily accessible option.
Installation Processes and Ease
Gorilla Glass offers a sleek, durable surface that requires specialized cutting tools and professional installation due to its brittle nature, making it less flexible but aesthetically appealing for insulated panels. Fiberglass insulation is easier to install, often available in batts or rolls that can be cut with standard tools and fitted into wall cavities by DIY enthusiasts or professionals alike. The ease of handling fiberglass, combined with its adaptability, generally results in quicker installation times compared to the meticulous handling required for Gorilla Glass panels.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Gorilla Glass and fiberglass differ significantly in environmental impact and recyclability; Gorilla Glass, made from aluminosilicate glass, is highly recyclable and reduces landfill waste due to its durability and reusability in electronics and construction. Fiberglass, composed of fine glass fibers, poses challenges in recycling as it often contaminates other materials and is less efficiently reclaimed, contributing to landfill accumulation and potential respiratory hazards during manufacturing and disposal. Choosing Gorilla Glass enhances sustainability by promoting closed-loop recycling and lowering energy consumption during production compared to the energy-intensive processing and limited recyclability of fiberglass insulation.
Common Applications in Insulation
Gorilla Glass, known for its high durability and scratch resistance, is primarily used in electronic device displays rather than traditional insulation. Fiberglass insulation is widely utilized in residential and commercial buildings for thermal and acoustic insulation due to its excellent heat resistance and cost-effectiveness. Common applications of fiberglass include wall cavities, attics, and HVAC systems, making it the preferred choice over Gorilla Glass in construction insulation.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Insulation Material
Gorilla Glass, known for its durability and scratch resistance, offers limited insulating properties compared to Fiberglass, which excels in thermal insulation and is widely used for energy efficiency in buildings. Fiberglass insulation provides superior thermal resistance (R-value), soundproofing capabilities, and fire resistance, making it ideal for most residential and commercial insulation applications. For optimal insulation performance and cost-effectiveness, Fiberglass remains the preferred choice over Gorilla Glass for thermal and acoustic insulation needs.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com