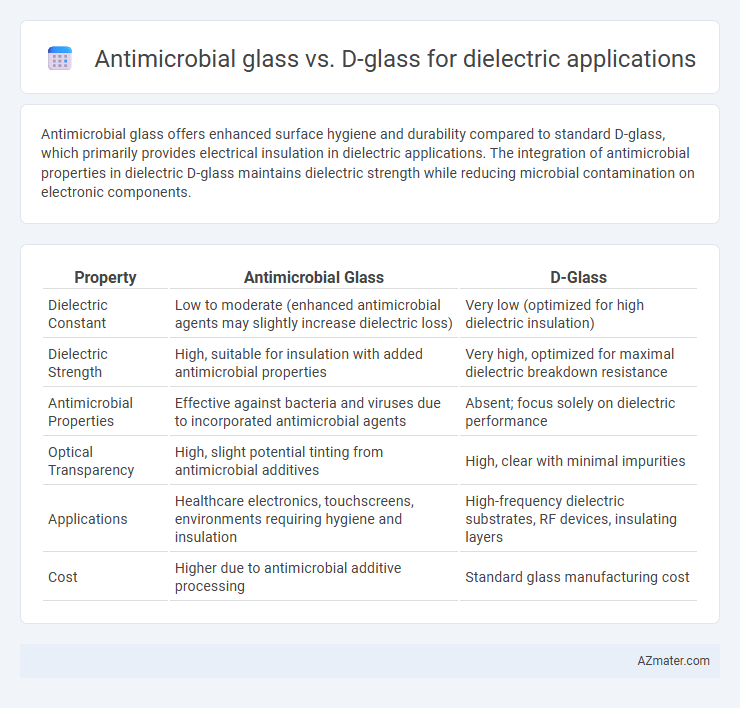
Antimicrobial glass offers enhanced surface hygiene and durability compared to standard D-glass, which primarily provides electrical insulation in dielectric applications. The integration of antimicrobial properties in dielectric D-glass maintains dielectric strength while reducing microbial contamination on electronic components.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Antimicrobial Glass | D-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant | Low to moderate (enhanced antimicrobial agents may slightly increase dielectric loss) | Very low (optimized for high dielectric insulation) |
| Dielectric Strength | High, suitable for insulation with added antimicrobial properties | Very high, optimized for maximal dielectric breakdown resistance |
| Antimicrobial Properties | Effective against bacteria and viruses due to incorporated antimicrobial agents | Absent; focus solely on dielectric performance |
| Optical Transparency | High, slight potential tinting from antimicrobial additives | High, clear with minimal impurities |
| Applications | Healthcare electronics, touchscreens, environments requiring hygiene and insulation | High-frequency dielectric substrates, RF devices, insulating layers |
| Cost | Higher due to antimicrobial additive processing | Standard glass manufacturing cost |
Introduction to Dielectric Applications
Dielectric applications require materials with excellent electrical insulation and minimal conductivity to prevent energy loss and ensure device performance. Antimicrobial glass offers the added benefit of inhibiting microbial growth, making it ideal for environments where hygiene is critical, while maintaining comparable dielectric properties. D-glass, a type of high-purity glass fiber, provides superior dielectric strength and thermal stability, making it a preferred choice in electronic substrates and insulation systems.
Overview of Antimicrobial Glass
Antimicrobial glass incorporates surface treatments or coatings that inhibit bacterial growth, enhancing hygiene in dielectric applications where contamination control is critical. It combines traditional dielectric properties such as high resistivity and dielectric strength with biocidal functions, making it ideal for environments requiring both electrical insulation and microbial resistance. This glass type is particularly advantageous in medical, food processing, and public infrastructure settings where reducing microbial presence prolongs device lifespan and ensures safer operation.
Defining D-Glass and Its Properties
D-glass is a specialized type of glass fiber known for its low dielectric constant and high electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for dielectric applications in electronics and telecommunications. It features enhanced chemical durability and mechanical strength compared to standard glass fibers, enabling improved performance in high-frequency, high-temperature environments. Antimicrobial glass, in contrast, primarily targets surface hygiene and is not optimized for dielectric properties, positioning D-glass as the superior choice for electrical insulation needs.
Comparative Analysis: Dielectric Performance
Antimicrobial glass exhibits comparable dielectric strength and permittivity to conventional D-glass, making it suitable for high-frequency applications with added hygiene benefits. D-glass, known for its low dielectric constant and loss tangent, provides superior insulating properties with minimal signal attenuation in dielectric substrates. The choice between antimicrobial glass and D-glass hinges on balancing dielectric performance with antimicrobial functionality, where D-glass maintains a slight edge in pure dielectric efficiency.
Surface Modification and Antimicrobial Activity
Antimicrobial glass incorporates surface modification techniques such as ion exchange or coating with metal ions like silver or copper, enhancing its antimicrobial activity by disrupting microbial cell membranes and reducing biofilm formation. In contrast, D-glass, primarily used for its superior dielectric properties, typically lacks inherent surface modifications aimed at antimicrobial effects, focusing instead on low dielectric loss and high electrical insulation. The integration of antimicrobial agents on glass surfaces significantly improves hygiene in dielectric applications where contamination control is critical without compromising electrical performance.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Antimicrobial glass maintains high electrical insulation capabilities by integrating antimicrobial agents without compromising dielectric strength, ensuring reliable performance in sensitive electronic applications. D-glass, known for its superior dielectric properties and low dielectric constant, offers enhanced electrical insulation, making it ideal for high-frequency and high-voltage applications. Comparative studies highlight D-glass's advantage in minimizing dielectric losses, while antimicrobial glass is preferred where hygiene and insulation coexist as critical factors.
Longevity and Durability in Harsh Environments
Antimicrobial glass incorporates silver ions or other biocides, providing enhanced resistance to microbial contamination and maintaining surface integrity over time, which is crucial for longevity in hygienic environments. D-glass, a type of dielectric glass specifically engineered for electrical insulation, offers superior dielectric strength and thermal stability, ensuring durability under high-voltage and fluctuating temperature conditions. In harsh environments, antimicrobial glass excels in preventing microbial degradation, while D-glass provides robustness against mechanical stress and dielectric breakdown, making the choice dependent on the specific operational demands.
Cost Analysis: Antimicrobial Glass vs D-Glass
Antimicrobial glass generally incurs higher manufacturing costs due to specialized coatings and treatments that enhance its resistance to microbial growth, whereas D-glass offers a more cost-effective option with its superior dielectric properties and lower production expenses. D-glass, commonly used in high-frequency dielectric applications, provides competitive pricing while maintaining stable electrical performance, making it preferable for budget-sensitive projects. Cost analysis highlights that although antimicrobial glass adds value through hygiene benefits, D-glass remains a more economical choice for dielectric applications focused primarily on electrical insulation and efficiency.
Potential Applications in Electronics and Healthcare
Antimicrobial glass incorporates silver ions to inhibit microbial growth, making it ideal for healthcare environments requiring sterile surfaces in medical devices and hospital equipment. D-glass offers low dielectric loss and high electrical insulation, enhancing signal integrity in high-frequency electronics and telecommunications. Combining antimicrobial properties with superior dielectric performance could revolutionize electronic medical devices by improving both hygiene and electrical reliability.
Future Trends and Innovations in Dielectric Glass
Antimicrobial glass incorporates silver or copper ions to prevent microbial growth, enhancing hygiene without compromising dielectric properties, while D-glass offers low dielectric constant and loss, making it ideal for high-frequency applications. Future trends focus on integrating nanotechnology and multifunctional coatings to boost dielectric performance and antimicrobial efficiency simultaneously. Innovations aim to develop environmentally friendly, sustainable dielectric glasses with improved thermal stability and enhanced electrical insulation for next-generation electronics and communication systems.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs D-glass for Dielectric application
 azmater.com
azmater.com