Fire-rated glass offers enhanced fire resistance and safety in curtain walls by preventing flame and heat spread, while insulated glass primarily provides superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency. Selecting between fire-rated and insulated glass depends on prioritizing fire protection or energy performance in building facade design.
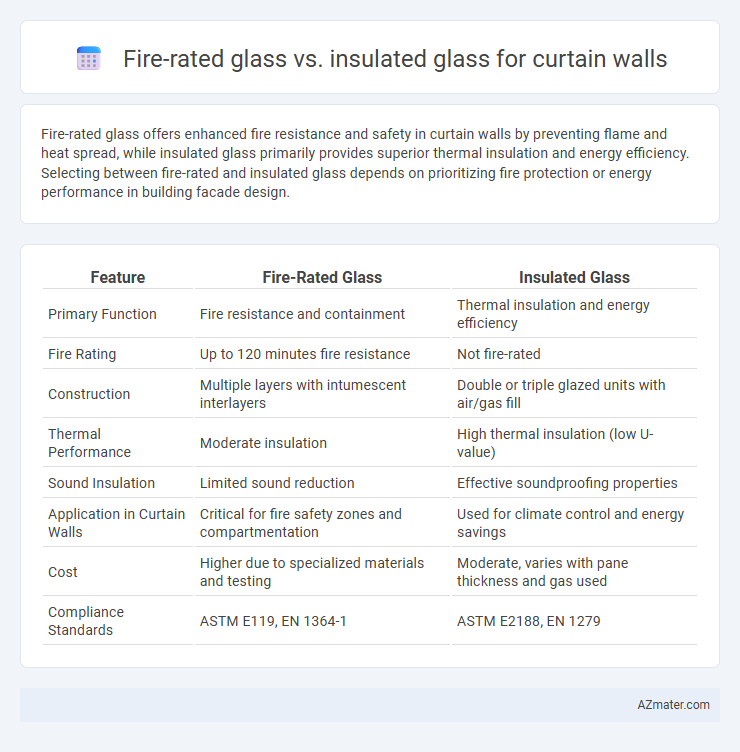
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Rated Glass | Insulated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Fire resistance and containment | Thermal insulation and energy efficiency |
| Fire Rating | Up to 120 minutes fire resistance | Not fire-rated |
| Construction | Multiple layers with intumescent interlayers | Double or triple glazed units with air/gas fill |
| Thermal Performance | Moderate insulation | High thermal insulation (low U-value) |
| Sound Insulation | Limited sound reduction | Effective soundproofing properties |
| Application in Curtain Walls | Critical for fire safety zones and compartmentation | Used for climate control and energy savings |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials and testing | Moderate, varies with pane thickness and gas used |
| Compliance Standards | ASTM E119, EN 1364-1 | ASTM E2188, EN 1279 |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Options
Fire-rated glass offers vital fire resistance and containment for curtain walls, meeting strict safety codes while maintaining transparency. Insulated glass enhances thermal performance by reducing heat transfer through multi-pane assemblies with gas fills, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Selecting between fire-rated and insulated glass depends on balancing fire safety requirements with thermal insulation needs in modern building facade design.
What is Fire-Rated Glass?
Fire-rated glass is specially engineered glazing designed to resist high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke within curtain wall systems for a specified duration, typically ranging from 20 minutes to 2 hours. It incorporates multiple layers of intumescent interlayers or specialized coatings that expand or seal gaps during a fire event, maintaining the integrity of the barrier. This type of glass is essential in meeting stringent fire safety codes and protecting building occupants by compartmentalizing fire zones without sacrificing natural light.
What is Insulated Glass?
Insulated glass for curtain walls consists of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer and sealed to create an air or gas-filled gap, significantly enhancing thermal insulation and energy efficiency. This design reduces heat transfer and helps maintain indoor temperature, making it ideal for sustainable building envelopes. Unlike fire-rated glass, insulated glass focuses primarily on improving thermal performance rather than providing fire resistance.
Key Performance Differences
Fire-rated glass in curtain walls provides superior fire resistance by withstanding high temperatures and preventing flame and smoke passage for specified durations, ensuring occupant safety and structural integrity during fire incidents. Insulated glass primarily enhances thermal performance, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency through multiple glass panes separated by air or gas-filled spaces, but does not offer significant fire protection. While fire-rated glass meets stringent fire safety standards such as ASTM E119 or BS 476, insulated glass focuses on meeting energy codes like ENERGY STAR or LEED, highlighting their distinct roles in building envelope performance.
Safety and Fire Resistance Comparison
Fire-rated glass in curtain walls provides superior fire resistance by withstanding temperatures up to 1700degF and preventing flame and smoke spread for specified durations, ensuring occupant safety during fire emergencies. Insulated glass, primarily designed for thermal insulation and energy efficiency, lacks the fire-resistance properties essential for protecting structural integrity under fire conditions. Choosing fire-rated glass enhances fire safety compliance and structural protection, while insulated glass focuses on energy performance without offering significant fire resistance.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Fire-rated glass in curtain walls primarily provides enhanced fire resistance by preventing heat transfer and fire passage, achieving fire ratings from 20 minutes up to 2 hours, but typically offers lower thermal insulation compared to insulated glass. Insulated glass units (IGUs) consist of multiple glass panes separated by a spacer filled with inert gas, delivering superior thermal insulation with U-values as low as 0.20 W/m2K and effective acoustic insulation by reducing sound transmission through lamination and gas fills. Combining fire-rated glass with insulating properties remains challenging, so curtain wall designs often integrate both types separately to balance fire safety with optimal thermal and acoustic performance.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Considerations
Fire-rated glass in curtain walls offers enhanced safety while maintaining design flexibility through various thicknesses, tints, and coatings that blend with architectural aesthetics. Insulated glass prioritizes thermal performance and energy efficiency, available in multiple configurations that reduce heat transfer yet allow expansive views with minimal visual distortion. Both types can be customized to complement modern facades, but fire-rated glass integrates safety regulations seamlessly without compromising on transparency or style.
Cost Implications and Budgeting
Fire-rated glass generally incurs higher costs compared to insulated glass due to its specialized materials and certifications required to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread. Budgeting for curtain walls with fire-rated glass must account for increased fabrication, installation, and potential maintenance expenses, while insulated glass offers more cost-effective thermal performance without providing fire protection. Project budgets should carefully weigh the trade-offs between fire safety requirements and energy efficiency to determine the appropriate glass type for curtain wall systems.
Building Code Requirements and Compliance
Fire-rated glass for curtain walls meets stringent building code requirements by providing specified fire resistance ratings, preventing the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, and maintaining structural integrity for a designated period. Insulated glass, while enhancing thermal performance and energy efficiency, generally lacks the fire-resistance properties mandated by codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) for fire-rated assemblies. Compliance with building codes necessitates selecting fire-rated glass that is tested and certified according to standards like ASTM E119 or UL 263 to ensure occupant safety and regulatory adherence in curtain wall applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Curtain Wall
When choosing the right glass for your curtain wall, fire-rated glass offers critical protection by withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire spread, ensuring safety compliance in high-risk buildings. Insulated glass, on the other hand, provides superior thermal performance and energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer, ideal for enhancing building comfort and lowering energy costs. Selecting between fire-rated and insulated glass depends on balancing safety requirements with energy efficiency goals tailored to the specific building code and environmental conditions.
Infographic: Fire-rated glass vs Insulated glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com