Dichroic glass features a multi-layer coating that reflects and transmits varying colors, providing vibrant visual effects and enhanced privacy for doors. Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety by undergoing thermal treatment, making it resistant to impact and shattering, ideal for secure door installations.
Table of Comparison
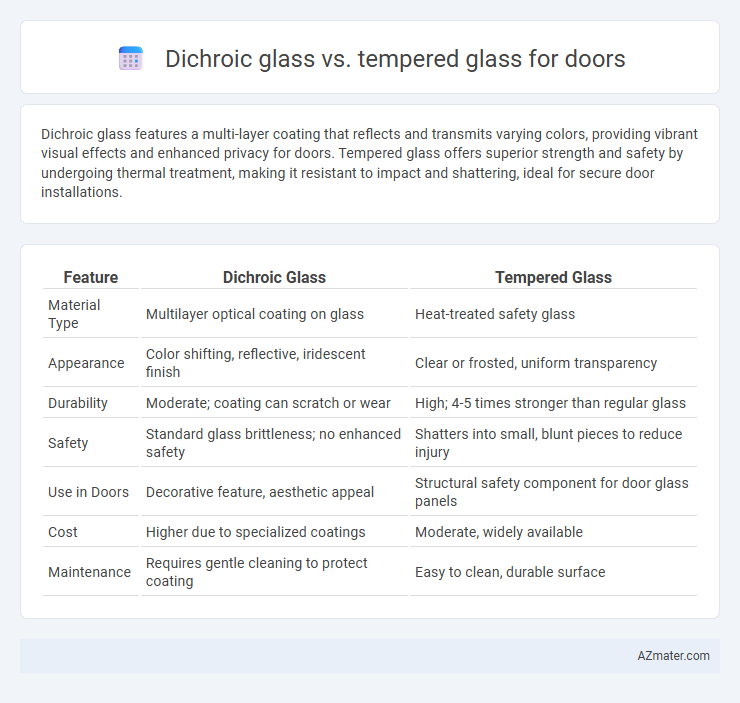
| Feature | Dichroic Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Multilayer optical coating on glass | Heat-treated safety glass |
| Appearance | Color shifting, reflective, iridescent finish | Clear or frosted, uniform transparency |
| Durability | Moderate; coating can scratch or wear | High; 4-5 times stronger than regular glass |
| Safety | Standard glass brittleness; no enhanced safety | Shatters into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury |
| Use in Doors | Decorative feature, aesthetic appeal | Structural safety component for door glass panels |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized coatings | Moderate, widely available |
| Maintenance | Requires gentle cleaning to protect coating | Easy to clean, durable surface |
Introduction to Dichroic Glass and Tempered Glass
Dichroic glass contains multiple ultra-thin layers of metal oxides, creating a unique light-reflecting and color-shifting effect used for decorative and architectural doors. Tempered glass undergoes a heat-treatment process that increases its strength and safety, making it highly resistant to impact and thermal stress, ideal for secure entryways and high-traffic areas. Comparing these, dichroic glass offers aesthetic versatility in door design, while tempered glass ensures robust durability and safety performance.
What Is Dichroic Glass?
Dichroic glass is a type of glass that displays multiple colors by reflecting and transmitting light due to multiple ultra-thin layers of metals or oxides within its surface. Unlike tempered glass, which is heat-treated for strength and safety and typically transparent, dichroic glass offers a striking iridescent appearance that changes color depending on the angle and lighting conditions. This unique optical effect makes dichroic glass ideal for decorative door applications where aesthetic appeal is prioritized over purely structural functions.
What Is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to standard glass, making it ideal for door applications requiring durability and impact resistance. When broken, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces to minimize injury risk, meeting strict building codes and safety standards. In contrast to dichroic glass, which emphasizes aesthetic and color effects through multilayer coatings, tempered glass prioritizes structural integrity and safety for functional use in doors.
Key Differences Between Dichroic and Tempered Glass
Dichroic glass displays a unique color-shifting effect due to multiple ultra-thin metal oxide layers, making it highly decorative and ideal for aesthetic door designs, whereas tempered glass prioritizes safety with enhanced strength and shatter-resistant properties achieved through controlled thermal or chemical treatments. Tempered glass is widely used in doors for durability and impact resistance, meeting stringent building codes, while dichroic glass is selected primarily for its visual appeal and light-reflective qualities. The key difference lies in tempered glass's structural performance versus dichroic glass's ornamental value, influencing their application in door construction and design.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass offers superior strength with its heat-treated process, resulting in up to four times the durability of regular glass, making it highly resistant to impact and thermal stress in door applications. Dichroic glass, while visually striking due to its color-shifting properties created by multiple ultra-thin metallic oxide layers, generally lacks the structural toughness of tempered glass and is more susceptible to scratching and breakage under heavy use. For door durability and long-term strength, tempered glass remains the optimal choice, especially in high-traffic or security-sensitive environments.
Aesthetic and Design Options
Dichroic glass offers a unique aesthetic with its multi-colored, iridescent appearance that changes hues depending on the angle of light, providing dynamic and artistic design options for doors. Tempered glass, while primarily valued for its strength and safety features, presents a sleek and modern look with clarity or frosted finishes, complementing minimalist and contemporary door styles. Combining dichroic glass with tempered safety technology enhances both visual appeal and durability, making it an ideal choice for innovative architectural designs.
Performance in Door Applications
Dichroic glass offers exceptional aesthetic performance with dynamic color shifts and high light transmission, enhancing door designs without compromising visibility. Tempered glass provides superior structural strength and safety by resisting impact and shattering into small, blunt pieces, making it ideal for high-traffic door applications. The performance choice depends on prioritizing visual appeal with dichroic glass or safety and durability with tempered glass in door installations.
Safety Features of Each Glass Type
Dichroic glass offers unique optical properties with a multi-layer coating that enhances aesthetic appeal but lacks the impact resistance necessary for high-safety applications in doors. Tempered glass undergoes controlled thermal treatment that increases its strength and causes it to shatter into small, blunt pieces on impact, significantly reducing injury risk. For door safety, tempered glass provides superior protection against breakage and safer failure patterns compared to the decorative but less robust dichroic glass.
Cost Considerations
Dichroic glass for doors typically costs significantly more than tempered glass due to its complex manufacturing process and unique light-reflecting properties. Tempered glass offers a more budget-friendly option, combining safety features with durability at a lower price point. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing the desire for aesthetic appeal with budget constraints in door installations.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Door
Dichroic glass offers a vibrant, color-shifting effect that enhances aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for decorative doors where visual impact is a priority. Tempered glass provides superior strength and safety, shattering into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury risk, which is essential for high-traffic or exterior doors requiring durability and security. Selecting the right glass for your door depends on balancing design preferences with functional needs such as safety, strength, and environmental exposure.
Infographic: Dichroic glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com