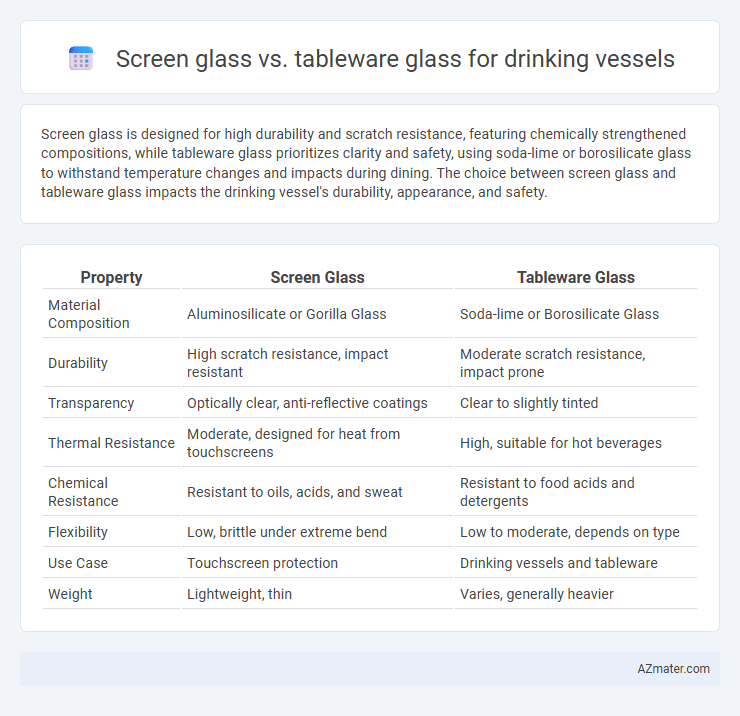
Screen glass is designed for high durability and scratch resistance, featuring chemically strengthened compositions, while tableware glass prioritizes clarity and safety, using soda-lime or borosilicate glass to withstand temperature changes and impacts during dining. The choice between screen glass and tableware glass impacts the drinking vessel's durability, appearance, and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Screen Glass | Tableware Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Aluminosilicate or Gorilla Glass | Soda-lime or Borosilicate Glass |
| Durability | High scratch resistance, impact resistant | Moderate scratch resistance, impact prone |
| Transparency | Optically clear, anti-reflective coatings | Clear to slightly tinted |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, designed for heat from touchscreens | High, suitable for hot beverages |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, acids, and sweat | Resistant to food acids and detergents |
| Flexibility | Low, brittle under extreme bend | Low to moderate, depends on type |
| Use Case | Touchscreen protection | Drinking vessels and tableware |
| Weight | Lightweight, thin | Varies, generally heavier |
Introduction to Screen Glass and Tableware Glass
Screen glass, typically made from tempered or laminated glass, is engineered for durability and impact resistance, often used in architectural and electronic displays rather than drinkware. Tableware glass, including soda-lime and borosilicate varieties, is specifically designed for durability, clarity, and safety in everyday drinking vessels. Understanding the distinct manufacturing processes and material properties helps differentiate screen glass's structural resilience from tableware glass's suitability for food contact and thermal stability.
Composition Differences: Screen Glass vs Tableware Glass
Screen glass primarily consists of high-strength aluminosilicate or borosilicate compositions designed for enhanced durability and resistance to scratches and thermal shock. Tableware glass is commonly made from soda-lime silica or lead glass, optimized for clarity, aesthetic appeal, and ease of manufacturing rather than extreme mechanical resistance. These compositional differences result in screen glass exhibiting increased hardness and fracture toughness, while tableware glass prioritizes optical qualities and cost-effectiveness.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Screen glass used for drinking vessels undergoes a tempered glass manufacturing process involving heating to around 620degC followed by rapid cooling to enhance strength and resistance to thermal stress. Tableware glass, typically soda-lime or lead crystal, is produced through melting raw materials at approximately 1400degC, shaping via blowing or pressing, and annealing to relieve internal stress, resulting in clarity and durability suited to fine dining. The key manufacturing difference lies in thermal treatment focus for screen glass to improve toughness versus precision forming and finishing techniques in tableware glass to achieve aesthetic elegance.
Physical Properties and Durability
Screen glass typically features high scratch resistance and enhanced hardness due to its specialized tempered or chemically strengthened surfaces, making it less prone to surface damage compared to tableware glass. Tableware glass often prioritizes clarity and aesthetic appeal, using soda-lime or lead crystal compositions that offer moderate durability but greater susceptibility to chipping and breakage under impact. The thicker and more impact-resistant nature of screen glass provides superior durability for frequent handling and rough use, while tableware glass balances elegance with adequate strength for everyday dining scenarios.
Chemical Resistance and Safety
Screen glass, typically made from tempered or laminated glass, offers superior chemical resistance against acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it highly durable for various applications. Tableware glass, often crafted from soda-lime or borosilicate glass, provides adequate chemical resistance but can be more susceptible to etching and corrosion when exposed to harsh chemicals or detergents. Safety-wise, tempered screen glass is designed to shatter into small, less harmful granules upon breakage, while tableware glass may break into sharp shards, posing a higher injury risk.
Suitability for Drinking Vessels
Screen glass, characterized by its durability and scratch resistance, offers excellent suitability for everyday drinking vessels, especially in environments requiring robustness and ease of cleaning. Tableware glass, often crafted with higher clarity and refined aesthetics, is preferred for formal settings where visual appeal and light refraction enhance the drinking experience. Both types provide safety and functionality, but screen glass excels in practicality while tableware glass prioritizes elegance and traditional use in dining contexts.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Screen glass for drinking vessels offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with smooth, transparent surfaces that enhance visual clarity and highlight the beverage's color, ideal for contemporary settings. Tableware glass often features intricate patterns, textures, or frosting that contribute to a classic, decorative appeal, complementing traditional dining atmospheres. Design considerations favor screen glass for minimalistic elegance and tableware glass for ornamental richness, influencing ambiance and user experience.
Cost and Availability
Screen glass for drinking vessels is typically less expensive than tableware glass due to lower manufacturing costs and simpler production processes. Tableware glass, designed for durability, aesthetics, and clarity, is often pricier and less widely available in bulk compared to screen glass, which is mass-produced. The availability of screen glass is generally higher in industrial markets, while tableware glass is more common in retail and specialty stores.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Screen glass used in drinking vessels often contains specialized coatings and toughening agents that complicate recycling processes and increase environmental impact due to energy-intensive manufacturing. Tableware glass, typically made from soda-lime or borosilicate glass, is more easily recyclable and has a lower environmental footprint because it can be melted down and reused multiple times without significant quality loss. Choosing tableware glass supports circular economy practices by reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources through efficient glass recycling systems.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Glass for Drinking Vessels
Screen glass offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for outdoor or heavy-use environments where longevity is crucial. Tableware glass provides superior clarity and elegance, perfect for formal dining settings prioritizing aesthetic appeal and lightweight handling. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing durability needs against visual refinement, with screen glass excelling in toughness and tableware glass in presentation quality.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Tableware glass for Drinking vessel
 azmater.com
azmater.com