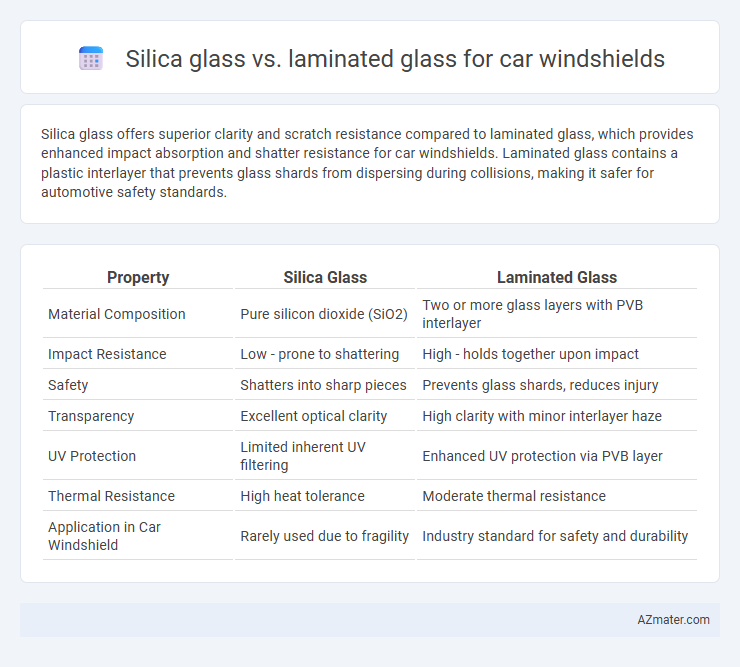
Silica glass offers superior clarity and scratch resistance compared to laminated glass, which provides enhanced impact absorption and shatter resistance for car windshields. Laminated glass contains a plastic interlayer that prevents glass shards from dispersing during collisions, making it safer for automotive safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Two or more glass layers with PVB interlayer |
| Impact Resistance | Low - prone to shattering | High - holds together upon impact |
| Safety | Shatters into sharp pieces | Prevents glass shards, reduces injury |
| Transparency | Excellent optical clarity | High clarity with minor interlayer haze |
| UV Protection | Limited inherent UV filtering | Enhanced UV protection via PVB layer |
| Thermal Resistance | High heat tolerance | Moderate thermal resistance |
| Application in Car Windshield | Rarely used due to fragility | Industry standard for safety and durability |
Introduction: Importance of Windshield Material Selection
Selecting the right material for car windshields directly impacts safety, durability, and clarity on the road. Silica glass offers high thermal resistance and excellent optical clarity, essential for withstanding temperature changes and providing clear vision. Laminated glass combines multiple layers, enhancing impact resistance and preventing shattering, which is critical for occupant protection during collisions.
What is Silica Glass?
Silica glass, also known as fused silica, is a high-purity glass composed primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with exceptional thermal stability and optical clarity, making it resistant to thermal shock and weathering. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer for safety and impact resistance, silica glass offers superior durability and chemical inertness but lacks the layered structure that enhances shatter resistance. In automotive applications, silica glass is less common for windshields compared to laminated glass, which is preferred for its safety features such as preventing glass shards from dispersing during impacts.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass for car windshields consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an inner layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) that enhances safety by preventing shattering upon impact. Silica glass, while highly resistant to heat and chemical corrosion, lacks the flexibility and safety features inherent in laminated glass used in automotive applications. Laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and maintains visibility by holding broken shards in place, making it the industry standard for car windshields.
Manufacturing Process: Silica vs Laminated Windshields
Silica glass used in car windshields undergoes a high-temperature melting and refining process to create a pure, transparent, and durable material with excellent thermal resistance. Laminated glass manufacturing involves bonding two layers of glass with a plastic interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), under heat and pressure to enhance impact resistance and safety. The laminated process ensures the windshield remains intact during collisions, whereas silica glass alone prioritizes clarity and temperature endurance but lacks the impact-resistant benefits of lamination.
Safety Features Comparison
Silica glass offers superior scratch resistance and clarity but lacks impact absorption compared to laminated glass, which incorporates a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, reducing injury risks. Laminated glass excels in preventing glass shattering during collisions, enhancing occupant safety by maintaining windshield integrity and improving structural support in rollovers. Safety standards such as FMVSS 205 mandate laminated glass for windshields due to its proven effectiveness in minimizing injury severity during accidents.
Durability and Resistance to Impact
Silica glass offers exceptional durability due to its high thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, but it is typically more brittle under impact compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass comprises multiple layers of glass and polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing superior impact resistance by holding shards together upon breakage, significantly enhancing passenger safety. The laminated structure also ensures better durability against cracks and debris, making it the preferred choice for car windshields in safety-critical applications.
Optical Clarity and Visibility
Silica glass offers superior optical clarity and high light transmittance, providing drivers with enhanced visibility and reduced distortion compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, slightly diminishes optical clarity due to the interlayer's presence but significantly improves safety by preventing shattering. For optimal visibility and precise optical performance in car windshields, silica glass remains the preferred option, although laminated glass balances clarity with safety benefits.
Cost Differences: Silica vs Laminated Glass
Silica glass, primarily used for specialized automotive applications, tends to be more expensive than laminated glass due to its higher purity and manufacturing complexity. Laminated glass, commonly used for car windshields, offers cost-effective impact resistance by combining layers of glass with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayers, reducing both production and replacement expenses. The significant price difference between silica and laminated glass influences automotive manufacturers' preference for laminated glass in standard vehicle windshields to balance safety and affordability.
Repairability and Replacement Considerations
Silica glass used in car windshields offers superior durability and scratch resistance, making repairs more effective and long-lasting compared to laminated glass, which tends to crack more easily and often requires full replacement. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers including a PVB interlayer, provides enhanced safety by holding shards together on impact but complicates repair processes due to its layered structure. Repairability of laminated glass is limited to minor chips, often necessitating complete replacement, whereas silica glass windshields can sustain more extensive repairs, reducing replacement frequency and overall maintenance costs.
Conclusion: Which Glass is Best for Car Windshields?
Laminated glass is the best choice for car windshields due to its superior safety features and impact resistance, as it holds together when shattered, reducing the risk of injury. Silica glass, while offering high clarity and heat resistance, lacks the structural integrity needed for automotive safety standards. Therefore, laminated glass remains the industry standard for durable and secure car windshields.
Infographic: Silica glass vs Laminated glass for Car windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com