Bioactive glass offers superior biocompatibility and antibacterial properties, ideal for medical imaging applications, while optical glass provides higher clarity, refractive accuracy, and durability essential for conventional camera lenses. Optical glass materials like BK7 and ED glass are optimized for minimal chromatic aberration and high light transmission in photography.
Table of Comparison
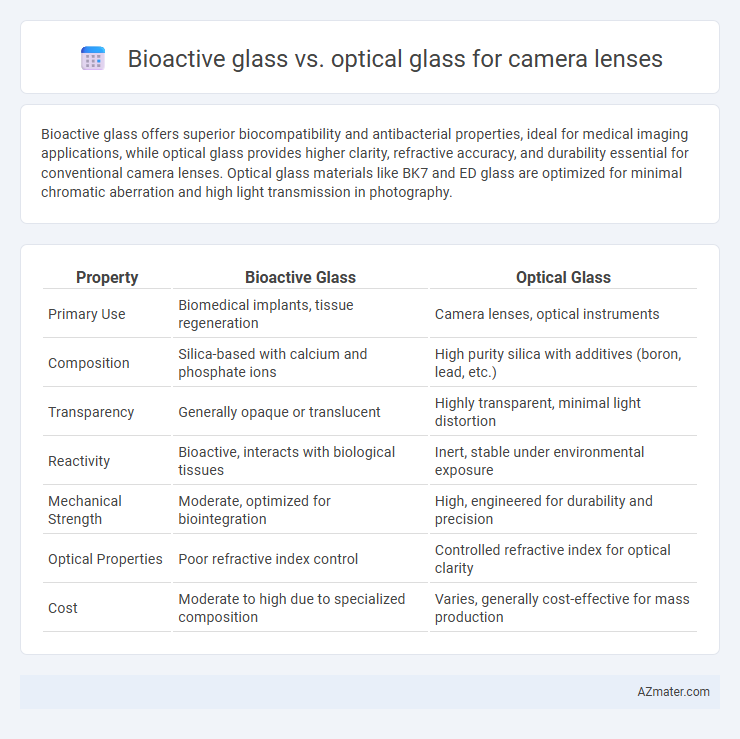
| Property | Bioactive Glass | Optical Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Biomedical implants, tissue regeneration | Camera lenses, optical instruments |
| Composition | Silica-based with calcium and phosphate ions | High purity silica with additives (boron, lead, etc.) |
| Transparency | Generally opaque or translucent | Highly transparent, minimal light distortion |
| Reactivity | Bioactive, interacts with biological tissues | Inert, stable under environmental exposure |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, optimized for biointegration | High, engineered for durability and precision |
| Optical Properties | Poor refractive index control | Controlled refractive index for optical clarity |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to specialized composition | Varies, generally cost-effective for mass production |
Introduction to Bioactive Glass and Optical Glass
Bioactive glass, composed of silica-based compositions with trace elements like calcium and phosphorus, is engineered for biological interaction and healing applications rather than optical clarity. Optical glass, specifically designed for camera lenses, features precise refractive indices and minimal dispersion to ensure sharp image capture and accurate color reproduction. While optical glass is optimized for clarity and light transmission, bioactive glass prioritizes biocompatibility and regenerative properties, making it unsuitable for imaging purposes.
Key Material Properties of Bioactive Glass
Bioactive glass offers unique key material properties such as superior biocompatibility, high surface reactivity, and the ability to bond chemically with biological tissues, which are not typically required or present in optical glass used for camera lenses. Optical glass excels in precise refractive index control, low dispersion, and high transparency, essential for image clarity and lens performance. Bioactive glass's porous structure and ionic release capacity make it ideal for biomedical applications but are less suitable for the optical clarity and durability demands of camera lens manufacturing.
Characteristics of Optical Glass in Camera Lenses
Optical glass in camera lenses is engineered for high clarity, precise refractive index, and minimal chromatic aberration, ensuring sharp and accurate image capture. Its homogeneity and low dispersion qualities enhance color fidelity and contrast, crucial for professional photography. Compared to bioactive glass, optical glass offers superior mechanical strength and durability, vital for withstanding environmental stresses during camera operation.
Light Transmission and Refractive Index Comparison
Bioactive glass exhibits lower light transmission and a refractive index typically ranging from 1.4 to 1.5, making it less effective for camera lenses compared to optical glass, which generally offers higher light transmission efficiency and refractive indices between 1.5 and 1.9. Optical glass is specifically engineered to minimize light dispersion and maximize clarity, essential for high-quality image capture. The superior refractive index and transmission properties of optical glass contribute to enhanced resolution and reduced chromatic aberrations in camera lenses.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Bioactive glass exhibits superior durability and scratch resistance compared to traditional optical glass due to its unique composition, which provides enhanced hardness and chemical stability. Optical glass, commonly used in camera lenses, tends to be more prone to scratching and environmental wear, which can degrade image quality over time. The increased abrasion resistance of bioactive glass makes it an ideal choice for lenses requiring long-term durability and clearer optical performance in harsh conditions.
Impact on Image Quality and Clarity
Bioactive glass offers superior durability and resistance to scratches compared to traditional optical glass, enhancing long-term image clarity for camera lenses. Its unique composition reduces internal light scattering, resulting in higher contrast and sharper image quality. Optical glass, while widely used, often requires additional coatings to achieve similar levels of clarity and may be more prone to degradation over time.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Bioactive glass for camera lenses offers enhanced durability and potential self-cleaning properties but involves higher material costs and complex manufacturing processes compared to optical glass. Optical glass remains the industry standard due to its proven clarity, lower raw material expenses, and well-established, cost-efficient production techniques. Manufacturing bioactive glass requires specialized equipment and longer fabrication times, leading to increased overall lens production costs.
Applications in Modern Camera Technology
Bioactive glass is rarely used in camera lenses due to its primary applications in medical and dental fields, where its regenerative properties are valued, whereas optical glass remains the standard material for camera lenses due to its superior light transmission, refractive index stability, and resistance to environmental factors. Modern camera technology relies on various specialized optical glasses such as low-dispersion and aspherical glass to reduce chromatic aberrations and enhance image clarity. The durability, optical precision, and customizable refractive properties of optical glass materials make them essential for advanced imaging systems in smartphones, DSLRs, and mirrorless cameras.
Environmental and Health Implications
Bioactive glass, known for its biocompatibility and eco-friendly degradation properties, offers significant environmental advantages over traditional optical glass used in camera lenses, which typically relies on energy-intensive manufacturing and contains potentially hazardous heavy metals. The use of bioactive glass reduces the environmental footprint by promoting recyclability and minimizing toxic waste, as it can safely interact with natural ecosystems after disposal. Health implications favor bioactive glass due to its non-toxic composition, whereas optical glass manufacturing and disposal may expose workers and ecosystems to harmful substances such as lead and arsenic.
Future Trends in Camera Lens Materials
Future trends in camera lens materials emphasize the integration of bioactive glass for its superior biocompatibility and environmental sustainability, contrasting with traditional optical glass known for high refractive index and exceptional optical clarity. Research explores bioactive glass composites to reduce lens weight and enhance anti-reflective properties while maintaining precision imaging performance. As demand for eco-friendly technology grows, bioactive glass may revolutionize camera lens manufacturing, complementing or potentially surpassing optical glass in next-generation camera optics.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs Optical glass for Camera lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com