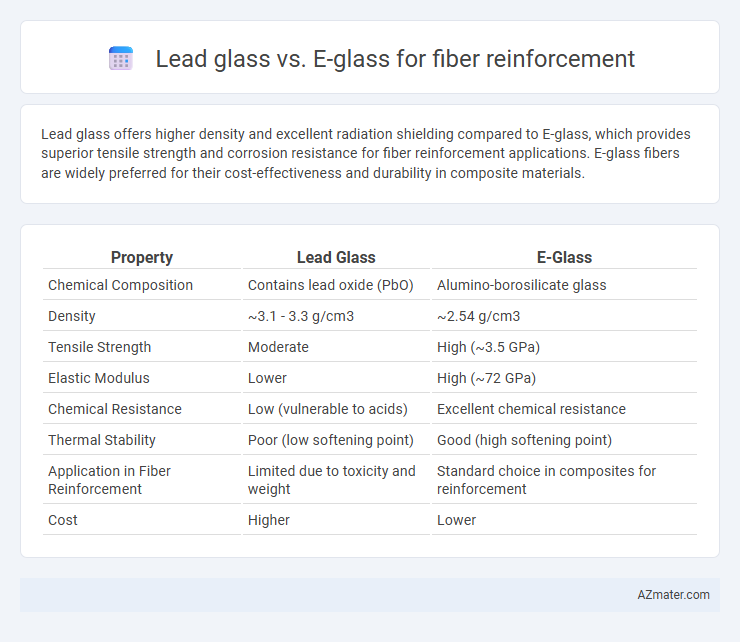
Lead glass offers higher density and excellent radiation shielding compared to E-glass, which provides superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance for fiber reinforcement applications. E-glass fibers are widely preferred for their cost-effectiveness and durability in composite materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Contains lead oxide (PbO) | Alumino-borosilicate glass |
| Density | ~3.1 - 3.3 g/cm3 | ~2.54 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate | High (~3.5 GPa) |
| Elastic Modulus | Lower | High (~72 GPa) |
| Chemical Resistance | Low (vulnerable to acids) | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Poor (low softening point) | Good (high softening point) |
| Application in Fiber Reinforcement | Limited due to toxicity and weight | Standard choice in composites for reinforcement |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforcement Materials
Lead glass and E-glass are commonly used fiber reinforcement materials, each offering distinct properties for composite applications. Lead glass fibers provide high density and excellent radiation shielding capabilities, making them suitable for specialized environments, while E-glass fibers deliver superior tensile strength, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, widely preferred in structural and marine composites. Selecting between lead glass and E-glass depends on the specific mechanical requirements, environmental exposure, and functional performance desired in the reinforced composite material.
What is Lead Glass?
Lead glass is a type of glass that contains a significant amount of lead oxide, typically between 18-40%, which enhances its refractive index and density, making it clearer and heavier than standard glass. In fiber reinforcement, lead glass fibers provide superior X-ray shielding and radiation protection due to their high atomic number, unlike E-glass fibers, which are composed chiefly of alumino-borosilicate and excel in mechanical strength and chemical resistance. The incorporation of lead glass fibers is preferred in applications requiring enhanced radiation attenuation alongside the structural benefits of fiber reinforcement composites.
What is E-Glass?
E-Glass, or Electrical-grade glass, is a widely used fiberglass material characterized by its high tensile strength, excellent electrical insulation properties, and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for fiber reinforcement in composite materials. Compared to lead glass, E-Glass offers superior mechanical performance and durability without the environmental and health concerns associated with lead content. Its lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness contribute to its extensive application in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries for enhancing composite strength and reliability.
Key Differences Between Lead Glass and E-Glass
Lead glass and E-glass differ primarily in composition and application, with lead glass containing lead oxide that increases density and refractive index, enhancing radiation shielding but reducing mechanical strength. E-glass, or electrical glass, is alumino-borosilicate-based, offering high tensile strength, excellent electrical insulation, and superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for fiber reinforcement in composites. The choice between lead glass and E-glass hinges on the required balance of mechanical durability, electrical properties, and environmental performance in fiber-reinforced applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Lead glass fibers exhibit higher density and increased stiffness but lower tensile strength compared to E-glass fibers, making E-glass preferable for applications requiring superior mechanical durability. E-glass fibers demonstrate tensile strengths typically ranging from 2.5 to 3.5 GPa and possess excellent impact resistance, while lead glass fibers have reduced mechanical resilience due to lead content affecting fiber integrity. The enhanced fracture toughness and thermal stability of E-glass fibers contribute to their widespread use in structural fiber-reinforced composites over lead glass alternatives.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Lead glass fibers exhibit higher chemical resistance compared to E-glass fibers, particularly against acidic and alkaline environments, due to their unique lead oxide composition. E-glass fibers, composed primarily of silica, alumina, and calcium oxide, provide good mechanical strength but are more susceptible to chemical degradation in harsh conditions. Durability of lead glass fibers in corrosive environments surpasses that of E-glass, making them preferable for applications requiring long-term resistance to chemical exposure.
Applications in Construction and Industry
Lead glass fiber reinforcement offers superior radiation shielding and is primarily used in specialized construction applications such as nuclear facilities and medical imaging rooms, where protective barriers are essential. E-glass fibers provide excellent tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for widespread use in structural reinforcements, composites, and industrial components like wind turbine blades and automotive parts. Selection between lead glass and E-glass depends on application-specific requirements including strength, durability, and environmental safety standards in construction and industrial environments.
Cost Analysis: Lead Glass vs E-Glass
Lead glass fibers typically incur higher production costs due to the use of heavy metals like lead, resulting in increased raw material expenses compared to E-glass fibers. E-glass fibers remain the most cost-effective option in fiber reinforcement applications due to their abundant raw material availability and established manufacturing processes. Cost analysis reveals that while lead glass may offer specific performance benefits, E-glass's lower price point and scalability make it the preferred choice for budget-sensitive composite manufacturing.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Lead glass fibers pose significant environmental and health risks due to the toxicity of lead, which can leach during manufacturing, use, and disposal, causing severe contamination and long-term ecological damage. E-glass fibers, composed mainly of alumino-borosilicate, offer a safer alternative with minimal hazardous emissions and better recyclability, reducing occupational exposure and environmental impact. Choosing E-glass over lead glass aligns with regulatory standards aimed at minimizing toxic waste and safeguarding worker health in composite manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Glass Fiber for Your Project
Lead glass fibers offer enhanced radiation shielding and higher density, making them suitable for specialized applications requiring protection against radiation and weight retention. E-glass fibers, composed primarily of alumino-borosilicate, provide excellent tensile strength, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for general-purpose fiber reinforcement in composites. Selecting the right glass fiber depends on project requirements such as mechanical performance, environmental exposure, weight considerations, and cost constraints.
Infographic: Lead glass vs E-glass for Fiber reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com