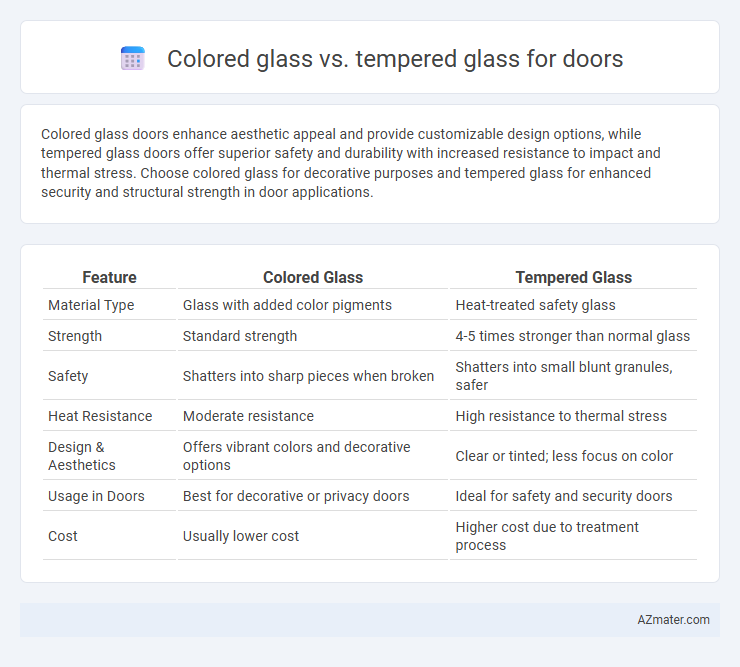
Colored glass doors enhance aesthetic appeal and provide customizable design options, while tempered glass doors offer superior safety and durability with increased resistance to impact and thermal stress. Choose colored glass for decorative purposes and tempered glass for enhanced security and structural strength in door applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Colored Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glass with added color pigments | Heat-treated safety glass |
| Strength | Standard strength | 4-5 times stronger than normal glass |
| Safety | Shatters into sharp pieces when broken | Shatters into small blunt granules, safer |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate resistance | High resistance to thermal stress |
| Design & Aesthetics | Offers vibrant colors and decorative options | Clear or tinted; less focus on color |
| Usage in Doors | Best for decorative or privacy doors | Ideal for safety and security doors |
| Cost | Usually lower cost | Higher cost due to treatment process |
Introduction to Door Glass Options
Colored glass for doors provides aesthetic appeal and privacy by incorporating tinted or stained hues, enhancing design versatility in residential and commercial spaces. Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety by undergoing heat treatment, making it resistant to impact and shattering into small, blunt pieces upon breakage. Both glass types cater to distinct functional and decorative needs, with colored glass primarily focusing on style and tempered glass emphasizing durability and security.
What is Colored Glass?
Colored glass for doors refers to glass that has been infused or coated with pigments to achieve a variety of hues and tints, enhancing aesthetic appeal while providing privacy and light filtering. Unlike tempered glass, which is heat-treated for increased strength and safety, colored glass prioritizes decorative function and can be either laminated, annealed, or toughened depending on installation needs. Common applications include interior doors, cabinet panels, and custom architectural designs where both color and translucency are desired.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass, making it highly resistant to impact and thermal stress. Colored glass, while primarily used for aesthetic purposes, does not undergo the same reinforcement process, making tempered glass a superior choice for door applications where durability and safety are critical. Tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces upon breaking, reducing injury risk and enhancing door security standards.
Aesthetic Appeal: Colored vs. Tempered Glass
Colored glass offers vibrant hues and customized designs that enhance door aesthetics with personalized visual interest, while tempered glass provides a clear, sleek look emphasizing modern minimalism and safety. The reflective qualities of colored glass cast unique light patterns, creating dynamic ambiance, whereas tempered glass maintains transparency and uniformity, highlighting architectural elements without color distraction. Choosing between them depends on desired style: colored glass for artistic flair, tempered glass for a clean, contemporary appearance combined with enhanced durability.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Tempered glass offers superior strength and durability compared to colored glass due to its heat-treated process that increases resistance to impact and thermal stress. Colored glass, while aesthetically versatile, is generally less resistant to breakage and may chip or crack under heavy pressure or rapid temperature changes. For door applications requiring enhanced safety and longevity, tempered glass is the preferred choice because it shatters into small, less harmful pieces, reducing injury risk.
Safety Features: Tempered vs. Colored Glass
Tempered glass offers superior safety features compared to colored glass due to its enhanced strength and shatter-resistant properties, breaking into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards. Colored glass primarily provides aesthetic appeal and UV protection but lacks the structural integrity and safety performance of tempered glass. For door applications requiring high safety standards, tempered glass is the optimal choice due to its ability to withstand impact and thermal stress.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Colored glass doors enhance energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain, which lowers cooling costs in warm climates while maintaining natural light. Tempered glass, known for its strength and safety, provides moderate insulation but lacks the heat-reflective properties of colored glass. Combining colored glass with tempered glass can optimize both energy efficiency and durability for exterior door applications.
Privacy and Light Control
Colored glass offers enhanced privacy by obscuring visibility while allowing soft natural light to pass through, making it ideal for door applications requiring moderate light control. Tempered glass provides superior strength and safety but is typically transparent, offering minimal privacy unless combined with frosted or tinted treatments. For optimal privacy and adjustable light control in doors, colored glass is generally preferred over plain tempered glass, though tempered glass can be customized for additional privacy features.
Maintenance and Longevity
Colored glass doors require regular cleaning with non-abrasive cleaners to maintain their vibrant appearance and prevent discoloration over time, while tempered glass doors demand minimal maintenance due to their durable, scratch-resistant surface. Tempered glass offers superior longevity and safety benefits, as it is heat-treated for increased strength and shatters into small, less harmful pieces upon impact, unlike colored glass which may fade or chip under harsh conditions. Choosing tempered glass ensures a long-lasting, low-maintenance option ideal for high-traffic areas and exterior door applications.
Cost Considerations and Value
Colored glass for doors often incurs higher initial costs due to specialized manufacturing and pigmentation processes, offering aesthetic value and unique design appeal. Tempered glass, while generally more affordable, provides enhanced safety and durability, reducing long-term replacement expenses. Evaluating cost considerations involves balancing upfront investment in colored glass with its decorative benefits against tempered glass's practical value and lower maintenance over time.
Infographic: Colored glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com