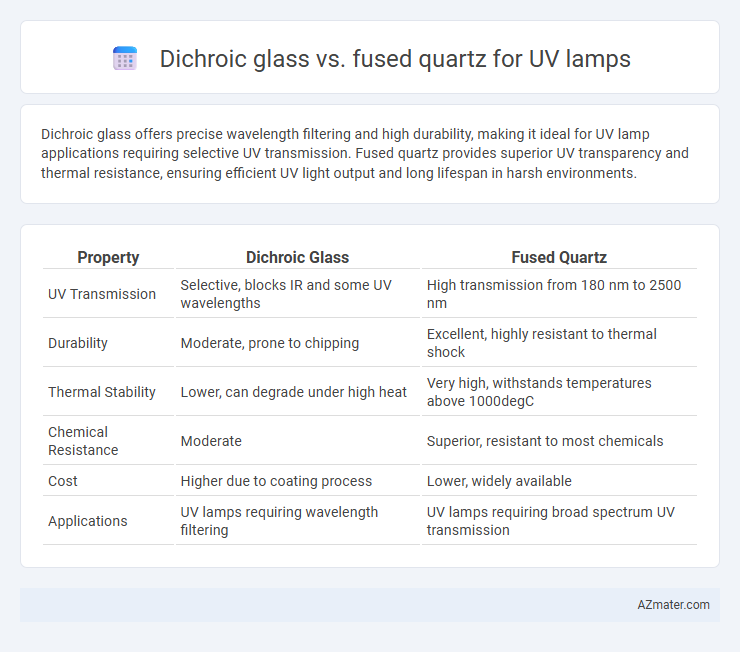
Dichroic glass offers precise wavelength filtering and high durability, making it ideal for UV lamp applications requiring selective UV transmission. Fused quartz provides superior UV transparency and thermal resistance, ensuring efficient UV light output and long lifespan in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dichroic Glass | Fused Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| UV Transmission | Selective, blocks IR and some UV wavelengths | High transmission from 180 nm to 2500 nm |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | Excellent, highly resistant to thermal shock |
| Thermal Stability | Lower, can degrade under high heat | Very high, withstands temperatures above 1000degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Superior, resistant to most chemicals |
| Cost | Higher due to coating process | Lower, widely available |
| Applications | UV lamps requiring wavelength filtering | UV lamps requiring broad spectrum UV transmission |
Introduction to UV Lamp Materials
Dichroic glass and fused quartz serve distinct roles in UV lamp technology, with fused quartz favored for its exceptional UV transmission and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-intensity UV applications. Dichroic glass, coated with multiple layers, selectively filters wavelengths and protects components from unwanted UV exposure, enhancing lamp efficiency and lifespan. Material selection critically impacts UV lamp performance, durability, and application-specific wavelength control.
Overview of Dichroic Glass
Dichroic glass features multiple thin layers of metal oxides that selectively reflect and transmit specific wavelengths, making it ideal for controlling UV light in lamps. Unlike fused quartz, which primarily offers high UV transmission and thermal stability, dichroic glass enhances UV lamp efficiency by filtering unwanted visible and infrared radiation. Its precision in wavelength selection contributes to optimized UV output and extended lamp lifespan in various phototherapy and sterilization applications.
Overview of Fused Quartz
Fused quartz is a high-purity form of silicon dioxide known for its excellent ultraviolet (UV) transmission and thermal stability, making it ideal for UV lamp applications. Its low thermal expansion and high resistance to thermal shock ensure durability under intense UV radiation, outperforming dichroic glass, which tends to filter and reflect specific wavelengths rather than transmit UV light efficiently. Fused quartz's optical clarity and chemical inertness contribute to its widespread use in UV lamps for sterilization, lithography, and scientific research.
UV Transmission Capabilities
Dichroic glass typically exhibits lower UV transmission, with around 70-80% efficiency in the UV spectrum, making it less suitable for high-intensity UV lamp applications where maximum UV output is crucial. Fused quartz, in contrast, offers exceptional UV transmission, often exceeding 90% across the UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C ranges, due to its low absorption and high purity silica composition. This superior UV transparency makes fused quartz the preferred material for UV lamp envelopes and optical components requiring optimal UV light passage.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Dichroic glass exhibits moderate thermal resistance, typically with a maximum operating temperature around 600degC, making it suitable for some UV lamp applications but prone to deformation under prolonged high heat exposure. Fused quartz surpasses dichroic glass in thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to approximately 1200degC without significant structural changes, ensuring reliable performance under intense UV lamp conditions. The superior thermal resistance of fused quartz reduces the risk of thermal stress and extends the lifespan of UV lamps operating at elevated temperatures.
Durability and Longevity
Dichroic glass used in UV lamps offers excellent durability with high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, ensuring extended operational lifespan under intense UV exposure. Fused quartz, known for superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion, excels in longevity by maintaining optical clarity and structural integrity even under prolonged high-temperature UV irradiation. Both materials provide strong durability, but fused quartz typically outperforms dichroic glass in longevity due to its exceptional resistance to UV-induced degradation and mechanical stress.
Cost Analysis
Dichroic glass UV lamps typically incur higher upfront costs due to specialized coating processes that enhance UV light filtering and durability, making them a premium choice for precision applications. Fused quartz lamps, while generally more affordable, offer excellent UV transmission and thermal resistance, resulting in lower replacement and maintenance expenses. Assessing total cost of ownership depends on balancing initial investment against longevity and performance efficiency in specific UV lamp uses.
Application Suitability
Dichroic glass offers precise wavelength filtering and high reflectivity, making it ideal for UV lamps requiring targeted UV radiation control in applications like sterilization and curing. Fused quartz provides superior UV transmission and thermal stability, suited for high-intensity UV exposure in industrial and scientific settings where durability and broad-spectrum UV output are essential. Selecting between dichroic glass and fused quartz depends on specific application needs for wavelength specificity versus overall UV throughput and thermal performance.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Dichroic glass used in UV lamps requires careful handling during maintenance to avoid damaging its thin-film coatings, which can degrade performance if scratched or cleaned improperly, necessitating the use of non-abrasive, specialized cleaning agents. Fused quartz exhibits higher durability and chemical resistance, allowing for more robust cleaning methods including alcohol or mild detergents without compromising UV transmission or structural integrity. Maintaining dichroic glass often involves more frequent inspections to preserve its selective wavelength filtering properties, whereas fused quartz demands less frequent cleaning due to its resistance to deposits and environmental factors.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material
Dichroic glass offers excellent UV filtering and heat reflection, making it ideal for applications requiring precise wavelength control and thermal management in UV lamps. Fused quartz provides superior UV transmission, high thermal stability, and resistance to harsh environmental conditions, which is essential for high-intensity UV lamps and extended operating life. Selecting the best material depends on the specific UV lamp application: dichroic glass is preferred for wavelength-specific filtering and heat dissipation, while fused quartz excels in durability and maximum UV output.
Infographic: Dichroic glass vs Fused quartz for UV lamp
 azmater.com
azmater.com