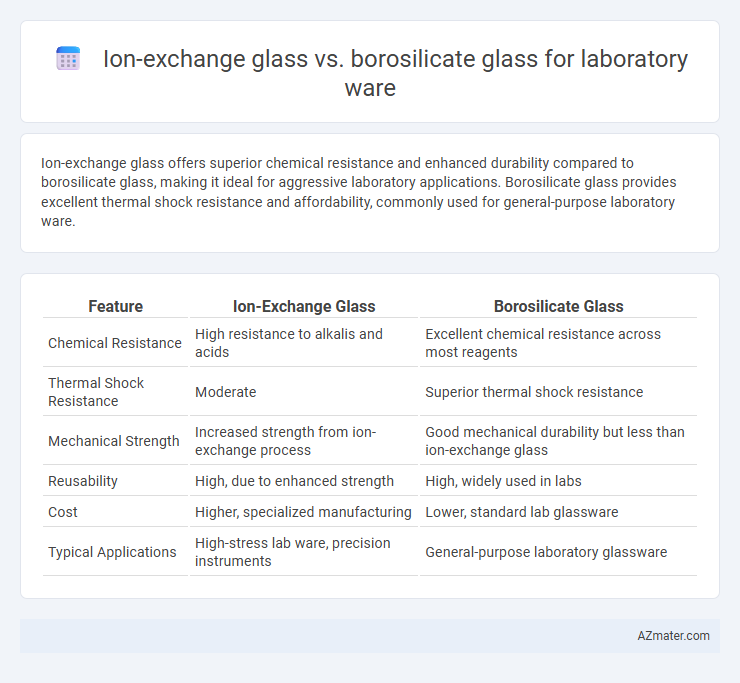
Ion-exchange glass offers superior chemical resistance and enhanced durability compared to borosilicate glass, making it ideal for aggressive laboratory applications. Borosilicate glass provides excellent thermal shock resistance and affordability, commonly used for general-purpose laboratory ware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ion-Exchange Glass | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to alkalis and acids | Excellent chemical resistance across most reagents |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | Superior thermal shock resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Increased strength from ion-exchange process | Good mechanical durability but less than ion-exchange glass |
| Reusability | High, due to enhanced strength | High, widely used in labs |
| Cost | Higher, specialized manufacturing | Lower, standard lab glassware |
| Typical Applications | High-stress lab ware, precision instruments | General-purpose laboratory glassware |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware Materials
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced chemical durability and resistance to alkali attack compared to borosilicate glass, making it suitable for handling highly reactive substances in laboratory settings. Borosilicate glass is prized for its excellent thermal resistance and low thermal expansion coefficient, ideal for general-purpose laboratory ware exposed to thermal cycling. The choice between ion-exchange glass and borosilicate glass depends on the required chemical resistance and thermal stability needed for specific laboratory applications.
What is Ion-Exchange Glass?
Ion-exchange glass is a type of laboratory glassware treated through a chemical process that replaces smaller alkali ions in the glass surface with larger ones, enhancing its strength and chemical resistance. This process results in improved durability compared to standard borosilicate glass, making ion-exchange glass ideal for applications requiring enhanced thermal shock resistance and mechanical stress endurance. Ion-exchange glass maintains superior dimensional stability and resistance to alkali attack, which is crucial for precise and reliable laboratory measurements.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of laboratory glass known for its exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability, composed mainly of silica and boron trioxide. It withstands rapid temperature changes and aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for scientific experiments and laboratory ware such as beakers and flasks. In contrast to ion-exchange glass, which undergoes surface modification to enhance strength, borosilicate glass relies on its inherent low thermal expansion and robust composition for durability.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Ion-exchange glass demonstrates superior chemical resistance to alkaline solutions compared to borosilicate glass, making it highly suitable for handling strong bases in laboratory settings. Borosilicate glass provides balanced resistance against acids, organic solvents, and thermal stress, whereas ion-exchange glass is more vulnerable to hydrofluoric acid and strong acids. The enhanced surface properties of ion-exchange glass offer improved durability and lower alkali leaching, promoting longer lifespan in specific chemical environments.
Thermal Stability and Shock Resistance
Ion-exchange glass demonstrates superior thermal stability compared to borosilicate glass due to its enhanced ion exchange process, which strengthens the glass surface and increases resistance to thermal stress. Borosilicate glass, while renowned for its excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion coefficient (~3.3 x 10-6 /degC), is more susceptible to surface damage and cracking under rapid temperature changes than ion-exchange glass. Laboratories requiring high durability under fluctuating thermal conditions often prefer ion-exchange glass for its improved resistance to thermal shock and prolonged lifespan.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ion-exchange glass offers superior mechanical strength compared to borosilicate glass due to its enhanced surface compression layer, making it highly resistant to scratches and impacts in laboratory applications. Borosilicate glass, while chemically durable and resistant to thermal shock, tends to be more brittle and prone to fracture under mechanical stress. The enhanced durability of ion-exchange glass extends its lifespan in lab environments where frequent handling and mechanical wear are common.
Cost and Availability
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced chemical durability and resistance to surface damage compared to borosilicate glass, but it comes at a significantly higher cost due to the complex manufacturing process. Borosilicate glass remains widely available and affordable, making it the standard choice for most laboratory glassware applications. The broader market presence and lower production expenses of borosilicate glass ensure easier procurement and budget-friendly options for laboratories.
Common Laboratory Applications
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for handling highly acidic or basic solutions in laboratory ware. Borosilicate glass is favored for general-purpose applications due to its excellent thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, suitable for heating and mixing reagents. Both materials are widely used in beakers, flasks, and pipettes, with ion-exchange glass preferred in aggressive chemical environments and borosilicate glass common in routine laboratory settings.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced thermal and chemical resistance compared to borosilicate glass, reducing breakage risks and waste generation in laboratory environments. Borosilicate glass, while more prone to surface degradation, is recyclable and generally easier to handle during high-temperature applications. Safety protocols should consider the specific chemical durability and fracture toughness of each glass type to minimize hazardous exposure and environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Glassware for Your Lab
Ion-exchange glass offers superior alkali resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for handling highly corrosive chemicals in laboratory settings. Borosilicate glass provides excellent thermal resistance and chemical durability, preferred for general-purpose labware requiring high temperature tolerance. Selecting the right glassware involves assessing chemical compatibility, thermal resistance, and mechanical durability specific to experimental needs to maximize safety and performance.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Borosilicate glass for Laboratory ware
 azmater.com
azmater.com