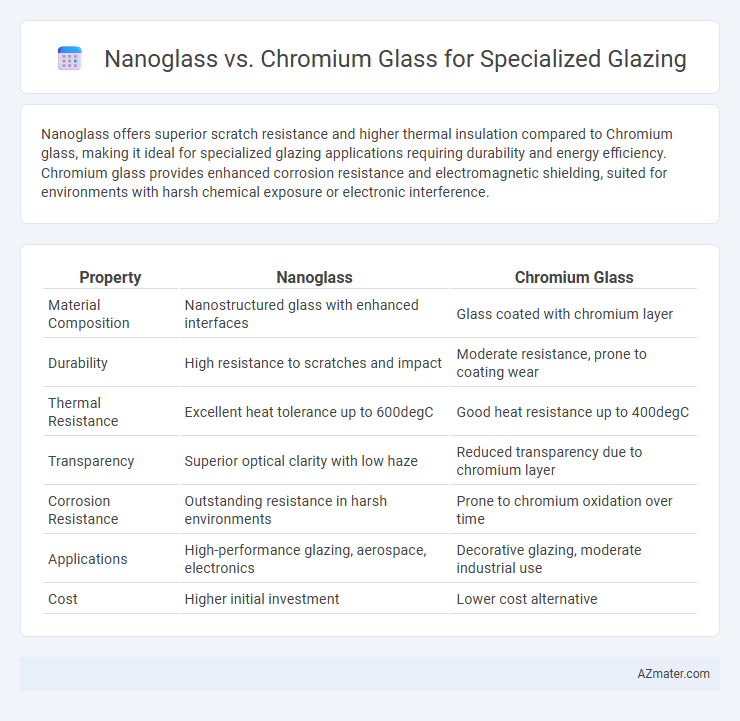
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and higher thermal insulation compared to Chromium glass, making it ideal for specialized glazing applications requiring durability and energy efficiency. Chromium glass provides enhanced corrosion resistance and electromagnetic shielding, suited for environments with harsh chemical exposure or electronic interference.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanoglass | Chromium Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Nanostructured glass with enhanced interfaces | Glass coated with chromium layer |
| Durability | High resistance to scratches and impact | Moderate resistance, prone to coating wear |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent heat tolerance up to 600degC | Good heat resistance up to 400degC |
| Transparency | Superior optical clarity with low haze | Reduced transparency due to chromium layer |
| Corrosion Resistance | Outstanding resistance in harsh environments | Prone to chromium oxidation over time |
| Applications | High-performance glazing, aerospace, electronics | Decorative glazing, moderate industrial use |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost alternative |
Introduction to Specialized Glazing Technologies
Nanoglass offers advanced optical clarity and scratch resistance, making it ideal for high-performance specialized glazing applications requiring durability and minimal distortion. Chromium glass provides exceptional hardness and chemical stability, suited for industrial environments where contamination resistance and long-term strength are critical. Both technologies enhance the functionality of specialized glazing by addressing unique performance requirements in automotive, architectural, and electronic displays.
What is Nanoglass?
Nanoglass is an advanced glazing material composed of nanoscale glass particles designed to enhance strength, clarity, and scratch resistance compared to traditional glazing like chromium glass. Nanoglass features superior thermal insulation and ultraviolet light filtering properties, making it ideal for specialized architectural and automotive applications. Its nanoscale structure provides improved durability and lightweight performance, surpassing the mechanical and optical qualities of chromium glass.
Understanding Chromium Glass
Chromium glass offers exceptional durability and high resistance to scratches and chemical corrosion, making it a preferred choice for specialized glazing applications requiring long-term performance. Its unique optical properties, including enhanced infrared filtering and improved heat resistance, provide significant energy efficiency benefits in architectural and automotive glazing. Compared to Nanoglass, Chromium glass excels in robustness but may have limitations in flexibility and weight, influencing its suitability depending on specific project demands.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Nanoglass features a matrix of nanoscale silica particles embedded in a polymer resin, providing enhanced strength and transparency compared to traditional glass. Chromium glass integrates chromium oxide as a dopant, altering optical properties and improving scratch resistance through a controlled melting and cooling process. Manufacturing nanoglass involves sol-gel techniques for precise nanoparticle dispersion, while chromium glass relies on high-temperature refining to achieve uniform chromium distribution.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Nanoglass exhibits superior strength and durability compared to Chromium glass due to its nanoscale reinforcement, which significantly enhances resistance to impact and scratching. Chromium glass offers moderate strength with good scratch resistance but falls short under high-stress conditions where Nanoglass maintains structural integrity. Specialized glazing applications benefit from Nanoglass's enhanced toughness and longer lifespan, making it a preferred choice for environments demanding exceptional durability.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Nanoglass exhibits superior optical clarity compared to chromium glass, with minimal light distortion and high transparency levels exceeding 90% visible light transmission. Chromium glass, while durable and resistant to scratches, typically allows less light transmission, generally around 70-80%, due to its metallic oxide layer. The enhanced light transmission and reduced haze in nanoglass make it ideal for specialized glazing applications demanding precise visual clarity and maximum daylight penetration.
Scratch and Stain Resistance
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance due to its advanced nanostructured coating that effectively minimizes surface abrasions, making it ideal for high-traffic environments requiring durable specialized glazing. Chromium glass exhibits excellent stain resistance, attributed to its chemical stability and smooth surface, which prevents the adherence of contaminants and eases cleaning processes. Both materials enhance specialized glazing performance, with nanoglass excelling in scratch durability and chromium glass providing enhanced protection against staining and corrosion.
Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
Nanoglass offers superior thermal insulation with significantly lower U-values compared to traditional chromium glass, reducing heat transfer and enhancing building energy efficiency. Chromium glass provides moderate solar control but falls short in minimizing heat loss during colder months, leading to higher HVAC energy consumption. Specialized glazing systems incorporating nanoglass improve overall thermal performance, resulting in lower energy bills and better indoor climate regulation.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Nanoglass typically offers higher energy efficiency and durability but comes with a premium price compared to chromium glass, making initial costs significantly higher. Chromium glass, while less expensive, provides moderate performance and is more widely available in the specialized glazing market due to established manufacturing processes. Market availability favors chromium glass as it enjoys broader distribution channels and quicker lead times compared to the more niche and emerging nanoglass technology.
Best Applications for Nanoglass vs Chromium Glass
Nanoglass excels in specialized glazing applications requiring superior scratch resistance and enhanced optical clarity, making it ideal for high-performance architectural facades and automotive windshields. Chromium glass offers exceptional durability and thermal stability, suited for industrial environments and high-temperature settings like laboratory equipment and protective barriers. Choosing nanoglass benefits projects demanding lightweight, high-transparency materials, while chromium glass is preferred where enhanced toughness and heat resistance are critical.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Chromium glass for Specialized glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com