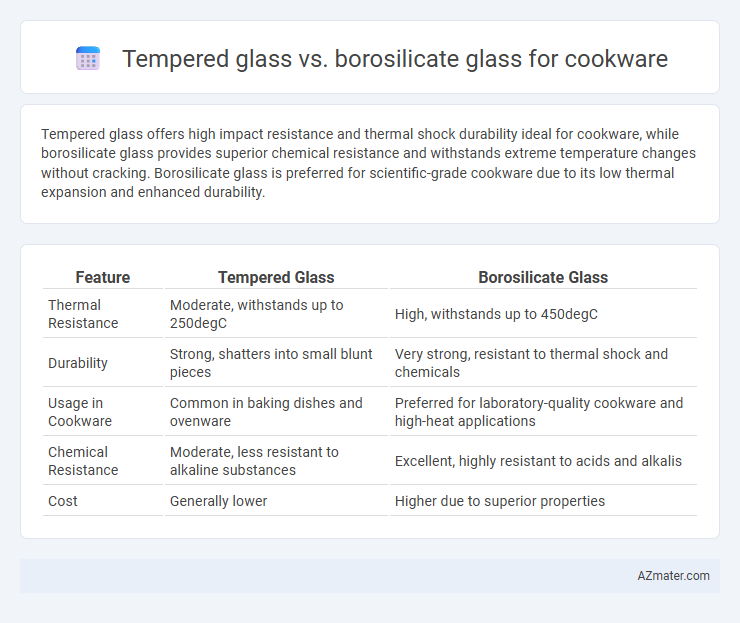
Tempered glass offers high impact resistance and thermal shock durability ideal for cookware, while borosilicate glass provides superior chemical resistance and withstands extreme temperature changes without cracking. Borosilicate glass is preferred for scientific-grade cookware due to its low thermal expansion and enhanced durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, withstands up to 250degC | High, withstands up to 450degC |
| Durability | Strong, shatters into small blunt pieces | Very strong, resistant to thermal shock and chemicals |
| Usage in Cookware | Common in baking dishes and ovenware | Preferred for laboratory-quality cookware and high-heat applications |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, less resistant to alkaline substances | Excellent, highly resistant to acids and alkalis |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to superior properties |
Introduction: Tempered Glass vs Borosilicate Glass for Cookware
Tempered glass for cookware is heat-resistant and designed to withstand sudden temperature changes but may shatter into small pieces upon impact. Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability due to its low thermal expansion, making it ideal for direct stovetop use and oven cooking. Understanding the differences in composition and performance helps in selecting the optimal cookware for safe and efficient kitchen use.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Tempered glass cookware is made by rapidly cooling annealed glass, creating surface compression that enhances strength, typically composed of soda-lime glass with added elements for durability. Borosilicate glass combines silica and boron trioxide, offering superior thermal resistance due to its low thermal expansion coefficient, and is produced through a controlled melting process at high temperatures. The manufacturing of borosilicate glass involves precise mixing and slow cooling to maintain its chemical stability, contrasting with the fast cooling technique used for tempered glass.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Borosilicate glass outperforms tempered glass in thermal shock resistance, with a coefficient of thermal expansion around 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC, compared to tempered glass's higher expansion rate, making it less prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Borosilicate's superior durability allows it to withstand sudden shifts from oven to cold counter or vice versa without damage, a critical advantage in cookware performance. Tempered glass is stronger mechanically but designed more for impact resistance than thermal stability, rendering borosilicate the preferred choice for cookware exposed to frequent thermal stress.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Tempered glass offers high impact resistance and shatterproof qualities due to its rapid cooling process, making it suitable for everyday cookware use. Borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand extreme temperature changes without cracking, enhancing its durability in both stovetop and oven applications. While tempered glass is stronger against mechanical impacts, borosilicate glass excels in heat tolerance and long-term thermal stability.
Heat Tolerance and Oven Safety
Tempered glass cookware typically withstands temperatures up to 400degF (204degC) and offers excellent resistance to thermal shock, making it safe for most oven uses. Borosilicate glass endures higher temperatures, often up to 450degF (232degC) or more, with superior thermal tolerance due to its low expansion coefficient, reducing the risk of breakage under rapid temperature changes. For oven safety, borosilicate glass is preferred in professional and high-heat cooking environments, while tempered glass suits everyday baking and reheating tasks.
Weight and Aesthetic Differences
Tempered glass cookware is generally heavier due to its dense manufacturing process, offering a robust and solid feel, while borosilicate glass is lighter and thinner, enhancing ease of handling and storage. Aesthetically, tempered glass often has a smooth, glossy finish with a slightly thicker appearance, whereas borosilicate glass boasts a clear, sleek look with greater transparency and minimal distortion. These weight and visual distinctions influence both user experience and kitchen design preferences.
Chemical Resistance and Food Safety
Borosilicate glass offers superior chemical resistance compared to tempered glass, making it less likely to react with acidic or alkaline foods during cooking. Tempered glass, while strong and heat-resistant, may be more prone to leaching trace elements when exposed to harsh chemicals or extreme temperature changes. For food safety, borosilicate glass is preferred as it maintains purity and durability without releasing harmful substances, ensuring safer cookware performance.
Maintenance and Cleaning Tips
Tempered glass cookware requires regular gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges to prevent scratches and maintain its clarity, while avoiding sudden temperature changes to reduce the risk of breakage. Borosilicate glass, known for its thermal shock resistance, tolerates high heat and rapid cooling, making it dishwasher safe and easier to clean without compromising durability. Both types benefit from avoiding harsh chemicals and soaking to preserve their longevity and performance in the kitchen.
Cost and Availability
Tempered glass cookware typically costs less than borosilicate glass due to its widespread production and simpler manufacturing process. Borosilicate glass, known for its superior thermal shock resistance, is often pricier and less widely available in retail markets. Availability of tempered glass is higher in general cookware sections, while borosilicate is commonly found in specialty or premium kitchenware stores.
Which Glass Cookware is Best for You?
Tempered glass cookware offers high impact resistance and thermal shock durability, making it ideal for everyday cooking and baking tasks requiring quick temperature changes. Borosilicate glass cookware boasts superior chemical resistance and exceptional heat tolerance up to 450degF, suitable for stovetop use and slow cooking without risk of cracking. Choosing between tempered and borosilicate glass depends on your cooking style: tempered glass suits high-impact, versatile kitchen use, while borosilicate glass excels in precision cooking and thermal stability.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Borosilicate glass for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com