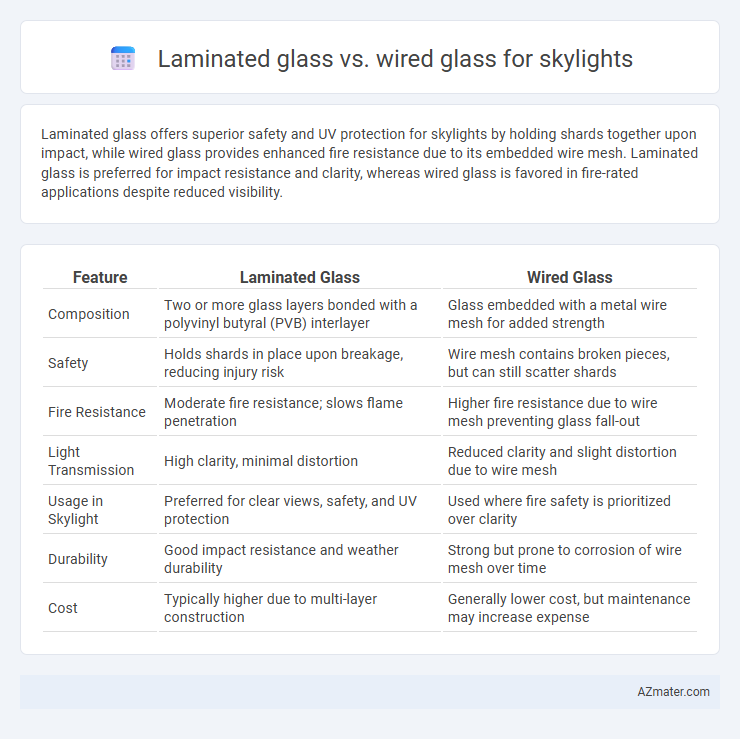
Laminated glass offers superior safety and UV protection for skylights by holding shards together upon impact, while wired glass provides enhanced fire resistance due to its embedded wire mesh. Laminated glass is preferred for impact resistance and clarity, whereas wired glass is favored in fire-rated applications despite reduced visibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer | Glass embedded with a metal wire mesh for added strength |
| Safety | Holds shards in place upon breakage, reducing injury risk | Wire mesh contains broken pieces, but can still scatter shards |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire resistance; slows flame penetration | Higher fire resistance due to wire mesh preventing glass fall-out |
| Light Transmission | High clarity, minimal distortion | Reduced clarity and slight distortion due to wire mesh |
| Usage in Skylight | Preferred for clear views, safety, and UV protection | Used where fire safety is prioritized over clarity |
| Durability | Good impact resistance and weather durability | Strong but prone to corrosion of wire mesh over time |
| Cost | Typically higher due to multi-layer construction | Generally lower cost, but maintenance may increase expense |
Introduction to Skylight Glazing Options
Laminated glass for skylights offers enhanced safety and noise reduction with its durable interlayer that holds shards together upon impact. Wired glass incorporates embedded metal mesh, providing fire resistance and preventing glass from shattering dangerously during thermal stress. Both glazing options balance transparency and strength, but laminated glass emphasizes impact resistance while wired glass prioritizes fire safety and structural integrity.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, providing high safety and impact resistance for skylights. It prevents shattering by holding glass fragments in place, reducing injury risks and improving durability in extreme weather conditions. Compared to wired glass, laminated glass offers better clarity and UV protection while maintaining structural integrity.
What is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of safety glass that contains an embedded metal wire mesh within the glass layers, designed to provide added fire resistance and prevent glass shattering during breakage. This wire mesh reinforces the glass, making it a preferred option for skylights in fire-rated applications where structural integrity under heat is critical. Although laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and sound insulation, wired glass remains a key safety solution for skylight installations requiring compliance with fire codes.
Strength and Safety Comparison
Laminated glass offers superior strength and safety for skylights due to its multiple glass layers bonded with a resilient interlayer that holds shards in place upon impact, reducing the risk of injury. Wired glass, while providing fire resistance through embedded wire mesh, is more prone to shattering into sharp pieces under impact, making it less ideal for skylight applications where safety and durability are critical. Laminated glass also provides enhanced resistance to weather and UV damage, ensuring long-term structural integrity and occupant protection.
Impact Resistance: Laminated vs Wired Glass
Laminated glass offers superior impact resistance for skylights due to its interlayer that holds glass fragments together upon breakage, reducing the risk of injury and maintaining structural integrity. Wired glass, while providing some fire resistance, is more prone to shattering into large, sharp pieces during impact, compromising safety. For enhanced durability and safety in skylight applications, laminated glass is the preferred choice over wired glass.
Fire Protection Capabilities
Laminated glass offers superior fire protection for skylights by maintaining structural integrity under high heat, preventing glass fragmentation, and limiting the spread of flames and smoke. Wired glass contains embedded wire mesh that holds the glass pieces together during a fire but may crack under thermal stress, compromising safety. Fire-rated laminated glass typically achieves higher fire resistance ratings, making it the preferred choice for skylights requiring stringent fire protection standards.
Sound Insulation Performance
Laminated glass offers superior sound insulation performance for skylights due to its interlayer that dampens noise transmission, reducing external sounds like traffic and rain significantly. Wired glass, while providing safety benefits with embedded wire mesh, typically allows more sound to pass through because it lacks a specialized acoustic barrier. Choosing laminated glass enhances acoustic comfort in interior spaces beneath skylights by minimizing ambient noise intrusion.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Laminated glass for skylights offers superior UV protection by blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing interior fading and damage while enhancing energy efficiency through better insulation properties. Wired glass, although primarily valued for safety and fire resistance, provides minimal UV blocking and inferior thermal insulation, leading to higher energy loss. Choosing laminated glass optimizes skylight energy performance and prolongs interior material lifespan due to its advanced UV filtering capabilities.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Laminated glass offers superior aesthetic appeal for skylights with its clear, seamless appearance and customizable tint options, enhancing natural light while maintaining safety. Wired glass, often characterized by embedded wire mesh, provides a more industrial look that can limit design flexibility and reduce transparency. Designers favor laminated glass for modern skylight applications due to its versatility in shapes, sizes, and finishes, allowing for innovative architectural expressions.
Cost Considerations and Long-term Value
Laminated glass for skylights typically incurs higher upfront costs due to its multiple layers and specialized interlayers, offering superior impact resistance and UV protection. Wired glass, while generally less expensive initially, may have higher long-term maintenance costs because it is more prone to breakage and offers lower energy efficiency. Considering long-term value, laminated glass provides enhanced durability, safety, and energy savings, making it a cost-effective investment over the lifespan of the skylight.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Wired glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com