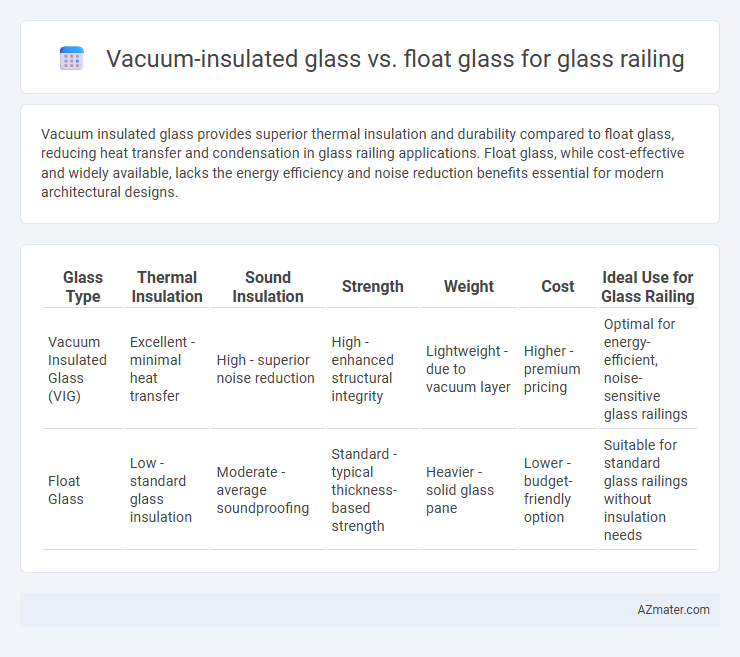
Vacuum insulated glass provides superior thermal insulation and durability compared to float glass, reducing heat transfer and condensation in glass railing applications. Float glass, while cost-effective and widely available, lacks the energy efficiency and noise reduction benefits essential for modern architectural designs.
Table of Comparison
| Glass Type | Thermal Insulation | Sound Insulation | Strength | Weight | Cost | Ideal Use for Glass Railing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Excellent - minimal heat transfer | High - superior noise reduction | High - enhanced structural integrity | Lightweight - due to vacuum layer | Higher - premium pricing | Optimal for energy-efficient, noise-sensitive glass railings |
| Float Glass | Low - standard glass insulation | Moderate - average soundproofing | Standard - typical thickness-based strength | Heavier - solid glass pane | Lower - budget-friendly option | Suitable for standard glass railings without insulation needs |
Introduction: Importance of Glass Selection in Railing Systems
Selecting the appropriate glass is crucial for glass railing systems to ensure safety, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and condensation resistance compared to traditional float glass, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort in outdoor or semi-enclosed spaces. Float glass, while more cost-effective, lacks the insulating properties of vacuum insulated glass and may require additional treatments to meet safety and performance standards in railing applications.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum space that drastically reduces heat transfer, making it highly energy-efficient compared to float glass. In glass railing applications, VIG offers superior thermal insulation and condensation resistance, enhancing comfort and durability in various climates. Unlike traditional float glass, VIG's vacuum layer minimizes sound transmission and improves the overall structural performance of glass railings.
Understanding Float Glass
Float glass is the most common type of glass used in glass railings due to its affordability, clarity, and ease of fabrication. It is manufactured by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, resulting in a uniform thickness and smooth surface that enhances safety and aesthetics in railing applications. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, float glass offers no thermal insulation but is highly durable and suitable for structural components where thermal performance is not a primary concern.
Key Structural Differences Between the Two Glass Types
Vacuum insulated glass features two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer, significantly reducing heat transfer and enhancing thermal insulation compared to float glass, which is a single, solid pane. Structurally, vacuum insulated glass offers higher rigidity and resistance to temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for durable glass railings in outdoor or extreme environments. Float glass, being less structurally robust, is prone to thermal stress and requires additional treatments or laminations for enhanced strength and safety in railing applications.
Thermal Performance: Vacuum Insulated Glass vs Float Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) significantly outperforms float glass in thermal insulation, offering U-values as low as 0.5 W/m2K compared to float glass's typical U-value around 5.7 W/m2K. The vacuum layer in VIG almost entirely eliminates conductive and convective heat transfer, drastically reducing heat loss and enhancing energy efficiency in glass railings. Float glass lacks this vacuum barrier, resulting in higher thermal conductivity and inferior insulation properties for temperature-sensitive environments.
Safety and Strength Considerations
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior strength and thermal performance compared to traditional float glass, making it highly suitable for glass railings where safety is paramount. The vacuum layer in VIG enhances impact resistance and reduces the risk of breakage under stress, providing increased structural integrity and occupant protection. Float glass, while cost-effective, lacks the durability and energy efficiency of VIG, making it less ideal for safety-critical applications in architectural railing systems.
Acoustic Insulation Properties Compared
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior acoustic insulation properties compared to float glass due to its airless cavity, which significantly reduces sound transmission and enhances noise reduction in glass railing applications. Float glass, being a single pane without any specialized insulation, provides minimal soundproofing and allows more external noise to penetrate. For glass railings requiring effective noise control, vacuum insulated glass is the preferred choice, delivering quieter environments in both residential and commercial settings.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior clarity and a slimmer profile compared to float glass, enhancing the sleek and modern aesthetic of glass railings. Its reduced thickness and minimal frame requirements allow for greater design flexibility, enabling architects to create uninterrupted, clean lines and expansive views. Float glass, while more affordable, often necessitates thicker panes and bulkier framing, limiting creative design possibilities and compromising the overall visual appeal.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal performance and durability for glass railings compared to traditional float glass, resulting in reduced energy costs and enhanced structural integrity over time. While the initial purchase and installation costs of VIG are higher, its long-term value is justified through decreased maintenance expenses and improved energy efficiency, making it a cost-effective investment for sustainable building projects. Float glass, despite lower upfront costs, often incurs higher replacement and maintenance fees due to its lower insulation properties and susceptibility to damage.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Railing
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and soundproofing, making it ideal for glass railings in environments with extreme weather or noise concerns, such as high-rise balconies and urban settings. Float glass provides a cost-effective solution with ample strength for indoor or low-exposure railings where insulation is less critical. Choosing the right glass depends on balancing factors like energy efficiency, durability, and budget to ensure safety and comfort in your railing application.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Float glass for Glass railing
 azmater.com
azmater.com