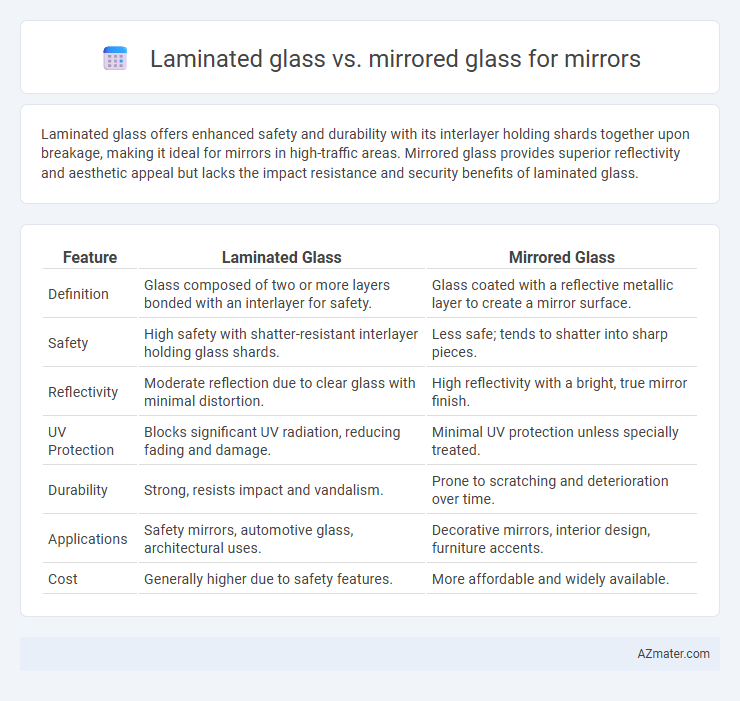
Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and durability with its interlayer holding shards together upon breakage, making it ideal for mirrors in high-traffic areas. Mirrored glass provides superior reflectivity and aesthetic appeal but lacks the impact resistance and security benefits of laminated glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Mirrored Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass composed of two or more layers bonded with an interlayer for safety. | Glass coated with a reflective metallic layer to create a mirror surface. |
| Safety | High safety with shatter-resistant interlayer holding glass shards. | Less safe; tends to shatter into sharp pieces. |
| Reflectivity | Moderate reflection due to clear glass with minimal distortion. | High reflectivity with a bright, true mirror finish. |
| UV Protection | Blocks significant UV radiation, reducing fading and damage. | Minimal UV protection unless specially treated. |
| Durability | Strong, resists impact and vandalism. | Prone to scratching and deterioration over time. |
| Applications | Safety mirrors, automotive glass, architectural uses. | Decorative mirrors, interior design, furniture accents. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to safety features. | More affordable and widely available. |
Introduction: Laminated Glass vs Mirrored Glass for Mirrors
Laminated glass consists of multiple layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, offering enhanced safety and durability ideal for mirrors in high-traffic or impact-prone areas. Mirrored glass features a reflective coating on one side, providing a clear, crisp reflection but typically lacks the added strength and shatter resistance of laminated glass. Choosing between laminated and mirrored glass depends on the balance of safety requirements versus optical clarity in mirror applications.
Key Differences Between Laminated and Mirrored Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, offering enhanced safety and sound insulation, while mirrored glass features a reflective coating that creates a one-way mirror effect for privacy and aesthetic appeal. Laminated glass excels in impact resistance and shatter retention, making it ideal for security applications, whereas mirrored glass primarily serves decorative purposes and controls light reflection. The choice between laminated and mirrored glass hinges on specific needs such as safety, visibility, and design preference.
Safety Features: Which Glass is More Secure?
Laminated glass provides superior safety features due to its construction, which includes a plastic interlayer that holds the glass shards together upon impact, reducing the risk of injury from shattered glass. Mirrored glass, while offering reflective properties, typically lacks this interlayer and can break into sharp, hazardous pieces, making it less secure in high-risk environments. For applications requiring enhanced safety, laminated glass is the preferred choice as it combines structural integrity with impact resistance.
Durability: Longevity Comparison
Laminated glass offers superior durability and longevity due to its multi-layer construction with a plastic interlayer that holds the glass together even when shattered, providing enhanced safety and resistance to impact. Mirrored glass, while aesthetically appealing, is more prone to scratches, delamination, and damage over time, especially in high-humidity environments, reducing its lifespan. Laminated glass mirrors typically maintain structural integrity and clarity longer, making them a preferred choice for durability and long-term use.
Visual Clarity and Reflection Quality
Laminated glass offers superior visual clarity due to its clear interlayer, minimizing distortion and enhancing true-to-life reflection quality. Mirrored glass, coated with reflective metal layers, provides high reflectivity but may exhibit slight color shifts or reduced transparency under specific lighting. Choosing laminated glass ensures safer, sharper reflections, whereas mirrored glass delivers intense, vibrant visuals ideal for decorative uses.
Installation Requirements and Maintenance
Laminated glass requires careful handling during installation due to its layered structure, ensuring proper sealing to maintain its safety features and prevent delamination. Mirrored glass installation demands precision alignment and robust support to accommodate its reflective coating, which is sensitive to scratches and pressure. Maintenance of laminated glass involves regular cleaning with non-abrasive materials to preserve clarity and integrity, while mirrored glass requires gentle cleaning agents to avoid damaging the reflective surface and frequent inspection for signs of tarnishing or damage.
Cost Analysis: Laminated vs Mirrored Glass
Laminated glass typically costs more than mirrored glass due to its multi-layer construction, which includes a PVB interlayer enhancing safety and durability. Mirrored glass is generally less expensive but may require additional maintenance or replacement over time because it is more prone to scratching and damage. When budgeting for mirrors, consider laminated glass for long-term investment despite higher upfront costs, while mirrored glass suits projects with tighter initial budgets.
Design Flexibility and Customization Options
Laminated glass offers superior design flexibility with the ability to incorporate various interlayers, colors, and patterns, enabling customized aesthetics and enhanced safety for mirrors. Mirrored glass provides a sleek, reflective surface but is typically limited in customization options, mainly focusing on tint variations and coatings. Choosing laminated glass allows for tailored design solutions that combine durability and unique visual effects, while mirrored glass excels in delivering high reflectivity and straightforward style.
Ideal Applications: Where to Use Each Type
Laminated glass is ideal for safety-critical applications such as storefronts, skylights, and vehicle windshields due to its shatter-resistant properties that hold glass fragments in place upon impact. Mirrored glass, commonly used in interior design, decorative elements, and privacy-enhancing partitions, provides high reflectivity and aesthetic appeal but lacks the structural safety features of laminated glass. Choosing between laminated and mirrored glass depends on balancing safety requirements with visual and functional needs in architectural and automotive projects.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Mirror Needs
Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and durability, making it ideal for high-traffic areas or homes with children, while mirrored glass excels in providing a clear, reflective surface with aesthetic appeal. Consider laminated glass for impact resistance and sound reduction, and opt for mirrored glass when clarity and design are the primary priorities. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing functional needs with visual preferences to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Mirrored glass for Mirror
 azmater.com
azmater.com