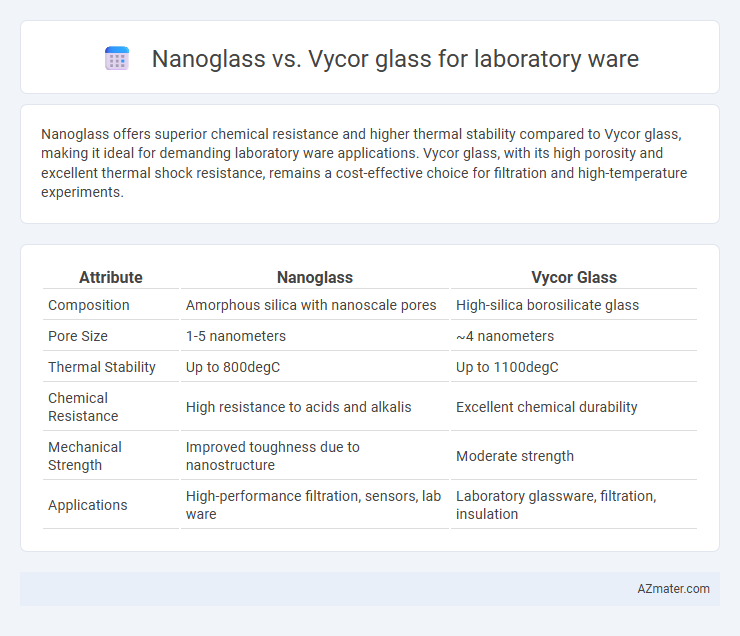
Nanoglass offers superior chemical resistance and higher thermal stability compared to Vycor glass, making it ideal for demanding laboratory ware applications. Vycor glass, with its high porosity and excellent thermal shock resistance, remains a cost-effective choice for filtration and high-temperature experiments.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Nanoglass | Vycor Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Amorphous silica with nanoscale pores | High-silica borosilicate glass |
| Pore Size | 1-5 nanometers | ~4 nanometers |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 800degC | Up to 1100degC |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent chemical durability |
| Mechanical Strength | Improved toughness due to nanostructure | Moderate strength |
| Applications | High-performance filtration, sensors, lab ware | Laboratory glassware, filtration, insulation |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware Materials
Nanoglass and Vycor glass each offer distinct advantages for laboratory ware, with Nanoglass providing enhanced strength and chemical resistance due to its nanostructured composition. Vycor glass is a high-silica, borosilicate glass known for thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for heating and chemical reactions. Selecting between these materials depends on specific laboratory needs such as durability, thermal shock resistance, and chemical inertness.
Overview of Nanoglass: Composition and Properties
Nanoglass, composed primarily of amorphous silica nanoparticles with controlled porosity, offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Vycor glass, which contains porous borosilicate silica. The unique nanoscale structure of nanoglass enhances mechanical strength, reduces weight, and improves surface area, making it ideal for specialized laboratory ware applications requiring high durability and inertness. These properties enable nanoglass to outperform Vycor in environments involving extreme temperature fluctuations and aggressive chemical exposure.
Understanding Vycor Glass: Features and Characteristics
Vycor glass, composed primarily of high-silica content, offers exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for laboratory ware exposed to high temperatures and corrosive substances. Its porous structure allows for enhanced thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, ensuring stability during rapid temperature changes. This combination of features makes Vycor glass superior in applications requiring precise thermal control and chemical inertness compared to conventional glasses like Nanoglass.
Chemical Resistance: Nanoglass vs Vycor Glass
Nanoglass exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to Vycor glass due to its enhanced purity and densely packed amorphous structure, which minimizes reactive sites and prevents corrosion by aggressive chemicals. Vycor glass, while resilient to thermal shock and moderately resistant to chemical attack, tends to show limited durability when exposed to strong alkalis or hydrofluoric acid. Laboratories requiring high chemical resistance for handling corrosive reagents often prefer nanoglass because of its exceptional inertness and long-term stability under harsh conditions.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Nanoglass demonstrates superior thermal stability compared to Vycor glass, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 600degC due to its amorphous nanoporous structure. Vycor glass, composed primarily of high-purity silica, withstands thermal shock up to approximately 500degC but shows increased risk of cracking under rapid temperature changes. The enhanced thermal durability of Nanoglass makes it preferable for laboratory ware applications requiring consistent performance in high-temperature reactions and thermal cycling.
Mechanical Strength: Durability and Breakage
Nanoglass exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to Vycor glass, offering enhanced durability and resistance to breakage in laboratory ware applications. The nanostructured morphology of Nanoglass significantly increases its fracture toughness, making it less prone to cracking under thermal or mechanical stress. Vycor glass, while resistant to thermal shock due to its high silica content, tends to be more brittle and susceptible to breakage during rough handling in laboratory environments.
Transparency and Optical Properties
Nanoglass exhibits superior transparency with enhanced optical clarity compared to Vycor glass, making it ideal for precise laboratory measurements and visual observations. Vycor glass, while highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, demonstrates slightly lower light transmittance due to its porous structure. The advanced nano-scale uniformity of Nanoglass results in reduced light scattering, providing clearer and more consistent optical properties essential for scientific instrumentation.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Nanoglass laboratory ware often comes at a higher cost due to advanced manufacturing techniques and limited production scale, whereas Vycor glass is typically more affordable and widely available because of its established industrial fabrication. Vycor's cost-effectiveness makes it a preferred choice for routine laboratory applications requiring thermal resistance and chemical durability. Nanoglass offers superior mechanical strength and clarity but may face availability constraints and premium pricing in comparison to the more accessible Vycor glass.
Typical Laboratory Applications: Nanoglass vs Vycor Glass
Nanoglass exhibits superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-precision analytical instruments and microfluidic devices. Vycor glass is favored in typical laboratory applications requiring high porosity and silica content, such as filtration, catalyst supports, and humidity sensors. The choice between Nanoglass and Vycor depends on whether the application demands enhanced durability and nanoscale uniformity or porosity and thermal shock resistance.
Choosing the Right Glassware: Practical Recommendations
Nanoglass offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to Vycor glass, making it ideal for laboratories handling aggressive reagents or high-temperature processes. Vycor glass provides excellent thermal shock resistance and is preferable for standard heating applications requiring durability and cost-effectiveness. Selecting the right glassware depends on specific experimental conditions such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Vycor glass for Laboratory ware
 azmater.com
azmater.com