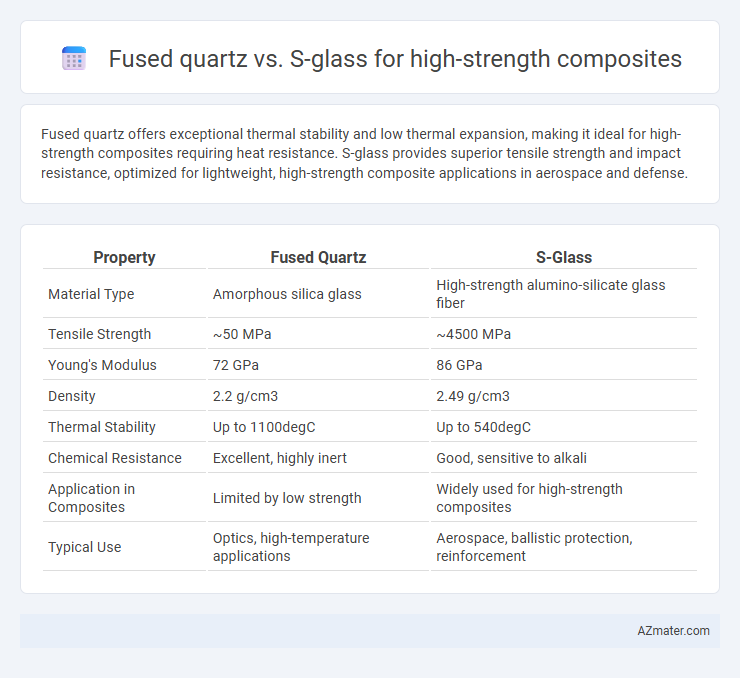
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-strength composites requiring heat resistance. S-glass provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance, optimized for lightweight, high-strength composite applications in aerospace and defense.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | S-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Amorphous silica glass | High-strength alumino-silicate glass fiber |
| Tensile Strength | ~50 MPa | ~4500 MPa |
| Young's Modulus | 72 GPa | 86 GPa |
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 | 2.49 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1100degC | Up to 540degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, highly inert | Good, sensitive to alkali |
| Application in Composites | Limited by low strength | Widely used for high-strength composites |
| Typical Use | Optics, high-temperature applications | Aerospace, ballistic protection, reinforcement |
Introduction to High-Strength Composites
High-strength composites commonly incorporate materials like fused quartz and S-glass due to their superior mechanical properties and thermal stability. Fused quartz exhibits exceptional thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for applications requiring dimensional stability under extreme conditions. S-glass offers higher tensile strength and improved impact resistance, which enhances the overall structural performance of composites used in aerospace and defense industries.
Overview of Fused Quartz in Composites
Fused quartz is a high-purity silicon dioxide material characterized by exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-strength composite applications. Its amorphous structure provides superior mechanical strength and optical clarity compared to S-glass, while maintaining resistance to thermal shock and environmental degradation. The integration of fused quartz fibers into composites enhances tensile strength and stiffness, supporting advanced aerospace and electronics industries where reliable performance under extreme conditions is critical.
S-Glass: Properties and Applications
S-Glass fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, with values reaching up to 4.9 GPa, significantly outperforming fused quartz in high-strength composite applications due to its superior toughness and elasticity. Its excellent thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 540degC, alongside low density (~2.48 g/cm3), makes S-Glass ideal for aerospace, defense, and sporting goods where durability and lightweight properties are critical. The material's high resistance to alkali and chemical corrosion enhances composite longevity in harsh environments, positioning S-Glass as a preferred reinforcement in advanced structural components.
Mechanical Performance Comparison
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional tensile strength and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-strength composites that require precise dimensional stability under stress. S-glass offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to E-glass, with enhanced fatigue resistance and higher elastic modulus, resulting in improved mechanical performance for structural applications. While fused quartz excels in environments requiring thermal stability and low creep, S-glass provides a balanced combination of strength, toughness, and flexibility ideal for dynamic loading conditions.
Thermal Stability and Resistance
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional thermal stability with a melting point around 1,650degC and very low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-strength composites exposed to extreme temperatures. S-glass, a high-strength fiberglass variant, offers good mechanical strength but lower thermal resistance, typically up to 540degC, limiting its use in high-heat applications. The superior thermal stability and resistance of fused quartz ensure better performance and durability in composite materials subjected to thermal cycling and high-temperature environments.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Fused quartz offers exceptional durability with its outstanding thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for high-strength composites exposed to extreme heat. S-glass provides superior environmental resistance, particularly against moisture and chemical corrosion, enhancing composite longevity in harsh conditions. Both materials deliver high tensile strength, but fused quartz excels in thermal durability, while S-glass is preferred for environments demanding enhanced chemical and moisture resistance.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Fused quartz requires high-temperature melting and precise thermal shock management during manufacturing, whereas S-glass production involves controlled fiber drawing from molten glass at lower temperatures, enabling mass production of continuous fibers. Fused quartz composites demand extensive processing time due to slow cooling and shaping, while S-glass fibers allow faster lay-up and curing in composite fabrication. The difference in thermal properties and viscosity between fused quartz and S-glass impacts corresponding resin compatibility and processing parameters in high-strength composite manufacturing.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-strength composites, but its high production cost limits cost efficiency compared to S-glass. S-glass provides a balanced combination of tensile strength and affordability, widely available in global markets, enhancing cost-efficiency for large-scale composite manufacturing. Availability of S-glass fibers supports consistent supply chains, while fused quartz's niche production restricts accessibility and drives prices higher.
Application Suitability: Fused Quartz vs S-Glass
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-strength composite applications requiring extreme heat tolerance and minimal thermal expansion, such as aerospace and optical components. S-glass provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance, making it more suitable for structural composites in automotive, marine, and sports equipment where mechanical durability and lightweight performance are critical. The choice between fused quartz and S-glass depends on application-specific requirements like temperature resistance versus mechanical toughness.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Reinforcement
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature, high-strength composites. S-glass provides exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, favoring applications requiring enhanced mechanical performance. Selecting the optimal reinforcement depends on balancing thermal requirements with mechanical strength, where fused quartz suits thermal-critical environments and S-glass excels in structural durability.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs S-glass for High-strength composite
 azmater.com
azmater.com