Silica glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability for lamps, while opal glass provides better light diffusion and a softer glow. Choosing silica glass enhances heat tolerance and longevity, whereas opal glass optimizes aesthetic lighting effects.
Table of Comparison
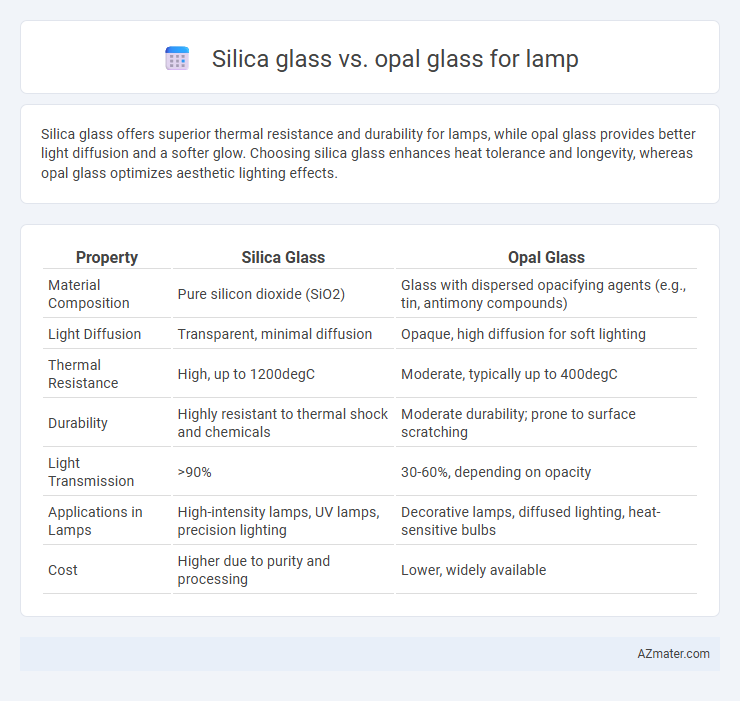
| Property | Silica Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Glass with dispersed opacifying agents (e.g., tin, antimony compounds) |
| Light Diffusion | Transparent, minimal diffusion | Opaque, high diffusion for soft lighting |
| Thermal Resistance | High, up to 1200degC | Moderate, typically up to 400degC |
| Durability | Highly resistant to thermal shock and chemicals | Moderate durability; prone to surface scratching |
| Light Transmission | >90% | 30-60%, depending on opacity |
| Applications in Lamps | High-intensity lamps, UV lamps, precision lighting | Decorative lamps, diffused lighting, heat-sensitive bulbs |
| Cost | Higher due to purity and processing | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Silica Glass and Opal Glass
Silica glass, also known as fused quartz, is a highly transparent material with exceptional thermal and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature lamp applications. Opal glass, characterized by its milky white, diffused appearance, is designed to evenly disperse light and reduce glare in lighting fixtures. Both materials serve distinct purposes in lamps, with silica glass offering clarity and durability, while opal glass enhances aesthetic diffusion and comfort.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Silica glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with minimal impurities, is manufactured through high-temperature melting processes, resulting in superior thermal resistance and optical clarity ideal for lamps requiring high heat tolerance. Opal glass contains a mixture of silica and opacifying agents such as phosphates or fluorides, created by adding these substances during melting to produce a diffused, frosted appearance that softens light emission. The difference in composition and manufacturing techniques directly impacts the mechanical strength, translucency, and heat resistance, making silica glass preferable for performance-focused lamps and opal glass favored in decorative lighting.
Optical Clarity and Light Diffusion
Silica glass offers superior optical clarity with high transparency and minimal light distortion, making it ideal for lamps requiring bright, clear illumination. Opal glass provides excellent light diffusion by scattering light evenly, reducing glare and creating a soft, uniform glow. Choosing between silica and opal glass depends on whether the lamp's design prioritizes sharp light transmission or gentle, diffused lighting ambiance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Silica glass offers exceptional strength and high thermal resistance, making it highly durable for lamp applications exposed to heat and mechanical stress. Opal glass, while aesthetically pleasing with its diffused light quality, has lower tensile strength and is more prone to chipping or cracking under impact. For long-lasting lamps requiring robust structural integrity, silica glass outperforms opal glass in terms of strength and durability.
Aesthetic Appeal for Lamp Design
Silica glass offers a sleek, transparent finish that enhances the minimalistic and modern aesthetic of lamp designs, allowing light to emit with high clarity and brilliance. Opal glass provides a soft, diffused glow with a milky, opaque look that creates a warm and cozy ambiance, making it ideal for designs focused on comfort and subtlety. Choosing between silica and opal glass significantly impacts the lamp's visual appeal and the quality of light it produces, aligning with either sharp elegance or gentle illumination.
Light Transmission Efficiency
Silica glass offers superior light transmission efficiency, typically around 90% or higher, due to its high purity and minimal impurities that reduce scattering and absorption. Opal glass, characterized by its milky, diffused surface, transmits significantly less light, often between 50-70%, as it scatters light to create a softer, more uniform glow. For lamps requiring maximum brightness and clarity, silica glass is the optimal choice, while opal glass excels in applications prioritizing diffused, glare-free illumination.
Heat Resistance and Safety
Silica glass offers superior heat resistance with a melting point above 1700degC, making it ideal for high-temperature lamp applications where durability under thermal stress is crucial. Opal glass, while providing excellent diffusion and aesthetic appeal, has a lower heat tolerance, typically around 600-800degC, limiting its use in high-heat environments. In terms of safety, silica glass reduces thermal shock risks and is less prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes compared to opal glass, ensuring longer lifespan and safer operation in lamps.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Silica glass lamps offer high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making their maintenance straightforward with minimal risk of surface damage during cleaning. Opal glass lamps require gentle cleaning using non-abrasive agents to preserve their matte finish and prevent surface scratches or clouding. Regular maintenance for both involves dust removal and careful handling, but silica glass tolerates more aggressive cleaning methods without compromising clarity.
Cost Considerations for Lamps
Silica glass for lamps offers higher temperature resistance and durability but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to opal glass. Opal glass provides a more affordable option with good light diffusion properties, making it suitable for decorative and residential lighting where budget constraints are important. Cost considerations should balance the longevity and performance benefits of silica glass against the economic efficiency of opal glass in lamp manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Glass for Lamps
Silica glass offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature lamp applications and long-lasting performance. Opal glass provides excellent light diffusion and aesthetic appeal, enhancing visual comfort and lamp design versatility. Selecting silica glass is best for functional durability, while opal glass suits decorative and soft lighting needs.
Infographic: Silica glass vs Opal glass for Lamp
 azmater.com
azmater.com