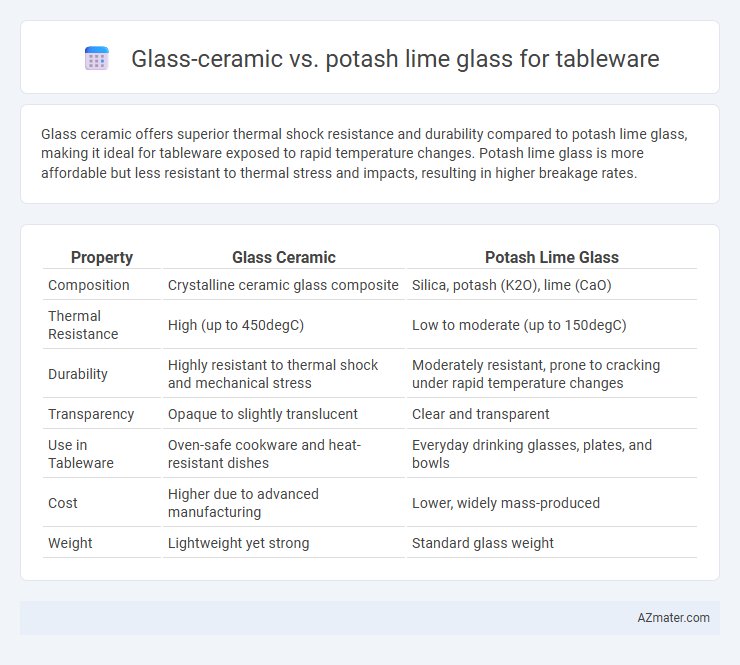
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to potash lime glass, making it ideal for tableware exposed to rapid temperature changes. Potash lime glass is more affordable but less resistant to thermal stress and impacts, resulting in higher breakage rates.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Ceramic | Potash Lime Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Crystalline ceramic glass composite | Silica, potash (K2O), lime (CaO) |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Low to moderate (up to 150degC) |
| Durability | Highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress | Moderately resistant, prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes |
| Transparency | Opaque to slightly translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Use in Tableware | Oven-safe cookware and heat-resistant dishes | Everyday drinking glasses, plates, and bowls |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced manufacturing | Lower, widely mass-produced |
| Weight | Lightweight yet strong | Standard glass weight |
Introduction: Understanding Tableware Glass Types
Glass ceramic and potash lime glass represent two distinct materials used in tableware, each offering unique thermal and mechanical properties. Glass ceramic is prized for its exceptional resistance to thermal shock and durability, making it ideal for cookware and dinnerware exposed to rapid temperature changes. Potash lime glass, a traditional soda-lime variant enriched with potassium oxide, provides affordability and clarity but generally lacks the thermal resilience found in glass ceramic.
Composition of Glass Ceramic
Glass ceramic tableware features a unique composition primarily composed of silica (SiO2), alumina (Al2O3), and lithium oxide (Li2O), which undergoes controlled crystallization to develop a durable, non-porous microstructure. In contrast, potash lime glass consists mainly of silica, potassium oxide (K2O), and calcium oxide (CaO), resulting in a more amorphous and less heat-resistant material. The distinct crystal phases in glass ceramics provide enhanced thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength compared to the relatively softer and more chemically reactive potash lime glass.
Composition of Potash Lime Glass
Potash lime glass used for tableware primarily consists of silica (SiO2), potassium oxide (K2O), and calcium oxide (CaO), which provide durability and heat resistance. This composition differs from glass ceramic, which incorporates crystalline phases within a glassy matrix, enhancing thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength. The higher potassium oxide content in potash lime glass improves its chemical durability compared to soda lime glass, making it suitable for decorative and functional tableware.
Thermal Properties: Resistance and Stability
Glass ceramic tableware offers superior thermal resistance and stability compared to potash lime glass, withstanding rapid temperature changes up to 700degC without cracking. Potash lime glass typically tolerates lower thermal shocks and sudden temperature variations around 120-150degC, making it less durable under extreme heat conditions. This enhanced thermal stability of glass ceramics ensures longer-lasting, safer use in ovens and microwaves, ideal for high-temperature culinary applications.
Mechanical Strength: Durability in Daily Use
Glass ceramic exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to potash lime glass, making it highly resistant to impact and thermal shock in daily use. Its crystalline structure enhances durability, preventing chipping and breaking even under frequent handling. Potash lime glass, while aesthetically pleasing, is more prone to scratches and fractures, reducing its longevity for tableware applications.
Aesthetic Qualities: Clarity and Design Flexibility
Glass ceramic tableware offers superior clarity with a smooth, consistent surface that enhances intricate designs, making it ideal for elegant and modern aesthetics. Potash lime glass exhibits good clarity but tends to have a softer look, limiting design flexibility and often resulting in less vibrant patterns. The higher resistance to thermal shock in glass ceramics also allows for more creative and durable decorative techniques.
Chemical Resistance: Reaction to Foods and Detergents
Glass ceramic exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to potash lime glass, showing minimal reaction to acidic or alkaline foods and harsh detergents, which preserves its surface integrity over time. Potash lime glass is more prone to etching and clouding when exposed to acidic substances and strong cleaning agents, reducing its durability and clarity. This makes glass ceramic a preferred choice for tableware requiring long-term resistance to food acids and detergent chemicals.
Cost Comparison: Manufacturing and Market Prices
Glass ceramic tableware generally incurs higher manufacturing costs due to advanced materials and a complex production process, resulting in greater durability and heat resistance. Potash lime glass is less expensive to produce, benefiting from simpler raw materials and a more established manufacturing infrastructure, leading to lower market prices. The price difference reflects the trade-off between cost efficiency and performance features essential for specific tableware applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass ceramic tableware offers superior thermal stability and durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste compared to potash lime glass. Potash lime glass, while more energy-intensive to produce due to higher melting temperatures, is often more recyclable, promoting circularity in glass waste management. Evaluating environmental impact, glass ceramic's longevity contributes to sustainability by lowering resource consumption over time, whereas potash lime glass benefits from established recycling infrastructure that supports material recovery.
Choosing the Best Glass for Tableware
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to potash lime glass, making it ideal for tableware exposed to rapid temperature changes. Potash lime glass, while more affordable and aesthetically versatile, is more prone to chipping and cracking under stress. Selecting the best glass for tableware depends on prioritizing durability for everyday use or cost-effectiveness for occasional settings.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs Potash lime glass for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com