Lead glass offers superior radiation shielding properties, making it ideal for medical and industrial insulation applications, while fiberglass excels in thermal insulation with high resistance to heat and fire. Fiberglass is lighter and more cost-effective compared to lead glass, which is denser and primarily used where radiation protection is essential.
Table of Comparison
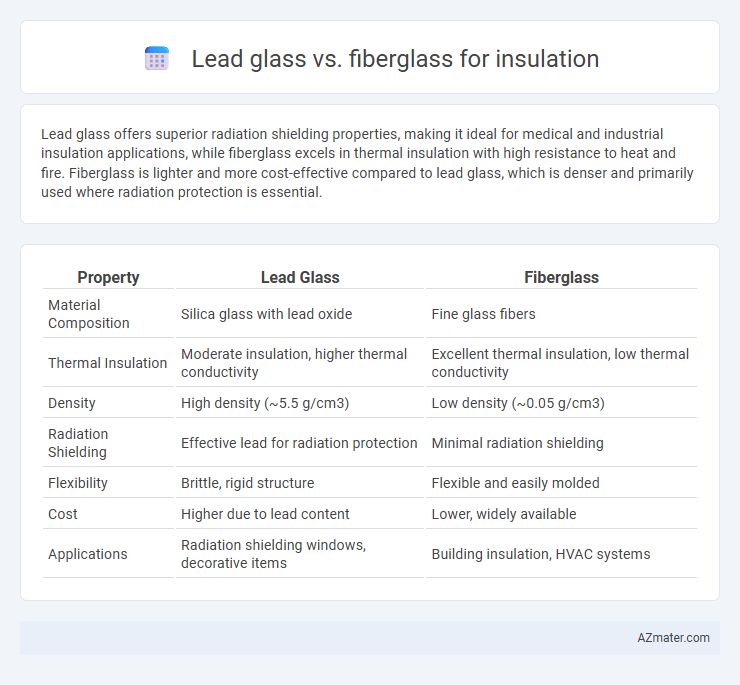
| Property | Lead Glass | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silica glass with lead oxide | Fine glass fibers |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation, higher thermal conductivity | Excellent thermal insulation, low thermal conductivity |
| Density | High density (~5.5 g/cm3) | Low density (~0.05 g/cm3) |
| Radiation Shielding | Effective lead for radiation protection | Minimal radiation shielding |
| Flexibility | Brittle, rigid structure | Flexible and easily molded |
| Cost | Higher due to lead content | Lower, widely available |
| Applications | Radiation shielding windows, decorative items | Building insulation, HVAC systems |
Introduction to Lead Glass and Fiberglass Insulation
Lead glass insulation provides superior radiation shielding due to its high-density lead content, making it ideal for environments requiring protection from X-rays and gamma rays. Fiberglass insulation, composed of fine glass fibers, excels in thermal and acoustic insulation by trapping air and reducing heat transfer and noise. While lead glass prioritizes safety and shielding in specialized settings, fiberglass is widely used for energy efficiency and soundproofing in residential and commercial buildings.
Composition and Material Properties
Lead glass insulation consists primarily of silica, lead oxide, and other metal oxides, offering high density and superior radiation shielding properties. Fiberglass insulation is made from fine glass fibers spun from molten glass, characterized by low density, excellent thermal resistance, and high tensile strength. Lead glass provides enhanced protection against X-rays and gamma rays, while fiberglass excels in thermal insulation and soundproofing due to its porous structure and flexibility.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Lead glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its high density and low thermal conductivity, effectively reducing heat transfer in specialized applications like radiation shielding. Fiberglass insulation excels with an R-value ranging from R-2.2 to R-4 per inch, providing excellent resistance to heat flow in residential and commercial buildings. While lead glass is ideal for environments requiring radiation protection, fiberglass remains the preferred choice for general thermal insulation owing to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation.
Radiation Shielding Capabilities
Lead glass offers superior radiation shielding capabilities compared to fiberglass due to its high density and lead content, effectively blocking gamma rays and X-rays in medical and industrial settings. Fiberglass, while commonly used for thermal insulation, provides minimal protection against radiation because of its low atomic number materials and porous structure. For applications requiring robust radiation shielding, lead glass remains the preferred material due to its proven effectiveness in absorbing ionizing radiation.
Durability and Longevity
Lead glass offers superior durability due to its high density and resistance to radiation, ensuring long-term performance in specialized insulation applications such as X-ray rooms. Fiberglass insulation, while less dense, provides excellent longevity with resistance to moisture, mold, and thermal degradation, making it ideal for general building insulation. Both materials maintain structural integrity over time, but lead glass excels in heavy-duty, radiation-shielding environments, whereas fiberglass is preferred for everyday thermal and acoustic insulation needs.
Safety and Health Considerations
Lead glass poses significant health risks due to lead toxicity, requiring careful handling and disposal to prevent lead exposure and environmental contamination. Fiberglass insulation, while non-toxic, can cause skin irritation and respiratory issues if fibers become airborne during installation, necessitating protective gear and proper ventilation. Both materials demand adherence to safety guidelines to minimize health hazards, but fiberglass is generally considered safer for routine handling and long-term use in insulation applications.
Installation Procedures and Flexibility
Fiberglass insulation is lightweight and flexible, allowing for easy cutting, fitting, and installation around irregular shapes and tight spaces without specialized tools. Lead glass, primarily used in radiation shielding rather than insulation, demands careful handling and professional installation due to its rigidity, weight, and fragility, limiting flexibility during application. The ease of fiberglass installation makes it a preferred choice for residential and commercial insulation projects requiring adaptability and quick setup.
Cost Comparison and Economic Factors
Lead glass insulation tends to have higher material and installation costs due to its density and specialized manufacturing processes, while fiberglass insulation remains more economical with widespread availability and lower production expenses. Fiberglass offers cost-effective thermal performance and simpler installation, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious projects. Economic factors such as long-term energy savings and durability also influence the cost-effectiveness of each material in different insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lead glass insulation poses significant environmental concerns due to the toxicity of lead, which can leach into soil and water, creating long-term contamination risks. Fiberglass insulation offers a more sustainable alternative as it is made primarily from abundant natural silica sand and recycled glass, with lower environmental toxicity and improved energy efficiency. The production and disposal of fiberglass have a reduced ecological footprint compared to lead glass, making fiberglass a preferable choice for eco-friendly construction.
Ideal Applications and Use Cases
Lead glass is ideal for applications requiring radiation shielding, such as in medical imaging rooms and nuclear facilities due to its high density and ability to absorb X-rays and gamma rays. Fiberglass excels in thermal and acoustic insulation for residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, providing efficient energy conservation and noise reduction. Its lightweight, non-toxic properties make fiberglass suitable for HVAC systems, wall cavities, and attic insulation.
Infographic: Lead glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com