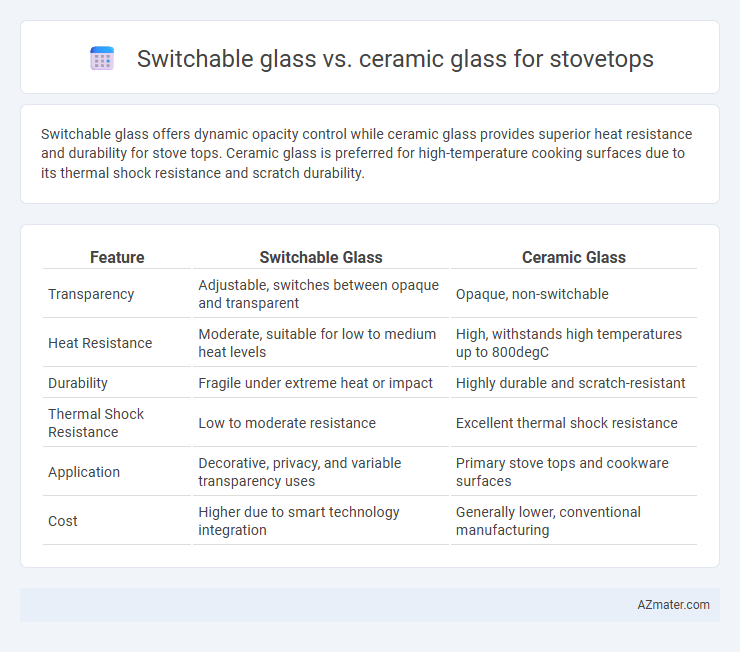
Switchable glass offers dynamic opacity control while ceramic glass provides superior heat resistance and durability for stove tops. Ceramic glass is preferred for high-temperature cooking surfaces due to its thermal shock resistance and scratch durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Switchable Glass | Ceramic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Adjustable, switches between opaque and transparent | Opaque, non-switchable |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, suitable for low to medium heat levels | High, withstands high temperatures up to 800degC |
| Durability | Fragile under extreme heat or impact | Highly durable and scratch-resistant |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low to moderate resistance | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Application | Decorative, privacy, and variable transparency uses | Primary stove tops and cookware surfaces |
| Cost | Higher due to smart technology integration | Generally lower, conventional manufacturing |
Overview of Switchable Glass and Ceramic Glass
Switchable glass for stove tops offers dynamic opacity control, allowing users to transition between transparent and frosted states for enhanced safety and aesthetic appeal. Ceramic glass, commonly used in stove tops, provides superior heat resistance and durability, ensuring reliable performance under high temperatures. While switchable glass emphasizes modern functionality and design flexibility, ceramic glass remains the industry standard for its thermal stability and robustness.
Key Differences Between Switchable Glass and Ceramic Glass
Switchable glass for stove tops offers dynamic opacity control through electrical activation, allowing it to alternate between transparent and opaque states for privacy or aesthetic purposes, whereas ceramic glass provides superior heat resistance and durability essential for direct contact with stove flames and high temperatures. Ceramic glass withstands extreme thermal stress without cracking or warping, making it ideal for cooktops, while switchable glass generally lacks the necessary heat tolerance and is more suited for decorative or partition applications. The key differences lie in their thermal resistance, functional use, and material composition, with ceramic glass engineered for high performance in heat-intensive environments and switchable glass optimized for visual modulation.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Switchable glass for stove tops offers moderate heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 150degC, making it suitable for low to medium heat cooking but less ideal for high-temperature applications. Ceramic glass provides superior thermal performance, enduring temperatures up to 700degC or higher, ensuring exceptional durability and minimal thermal expansion, which prevents cracks and damage during intense heat exposure. This makes ceramic glass the preferred choice for stove tops requiring high heat resistance and consistent thermal performance over time.
Durability and Longevity
Switchable glass and ceramic glass differ significantly in durability and longevity for stove tops, with ceramic glass offering superior heat resistance and scratch durability due to its tempered composition, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking surfaces. Switchable glass, primarily designed for variable opacity, typically lacks the hardness and thermal shock resistance of ceramic glass, which may result in shorter lifespan under constant stove top use. Ceramic glass withstands extreme temperature changes and mechanical stress better, ensuring longer-lasting performance in demanding kitchen environments.
Safety Features and User Protection
Switchable glass for stove tops offers enhanced safety by providing instant opacity to shield users from heat and flames, reducing the risk of burns and accidents. Ceramic glass is highly heat-resistant, preventing cracks and breakage under rapid temperature changes, thus ensuring durable protection during cooking. Both materials improve user safety, with switchable glass adding customizable visibility control and ceramic glass delivering superior thermal stability.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Switchable glass offers moderate energy efficiency for stove tops by controlling heat transmission and reducing heat loss, but ceramic glass excels with superior heat resistance and minimal thermal conductivity, enhancing overall energy conservation. Ceramic glass maintains consistent surface temperature and prevents heat escape more effectively, which lowers energy consumption during cooking. The advanced thermal insulation properties of ceramic glass make it the preferred choice for energy-efficient stove tops compared to switchable glass.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Switchable glass offers dynamic opacity control that enhances kitchen aesthetics by allowing seamless transitions between transparency and privacy, creating a modern and versatile stove top design. Ceramic glass provides a sleek, uniform surface with high heat resistance, supporting minimalist and clean design preferences without compromising functionality. Both materials contribute to design flexibility, but switchable glass introduces interactive elements that elevate visual appeal and customization in contemporary kitchens.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Switchable glass stove tops require gentle cleaning with non-abrasive cloths and mild detergents to maintain their electronic components and smooth finish, avoiding harsh chemicals that can damage the glazing. Ceramic glass stove tops demand regular wiping with specialized ceramic stove cleaners to prevent residue buildup and scratches, ensuring the surface remains heat-resistant and visually clear. Both materials benefit from immediate cleaning after use to avoid stubborn stains, but ceramic glass typically shows fingerprints and smudges more prominently than switchable glass.
Cost Considerations and Value
Switchable glass for stove tops typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced technology that integrates privacy and energy efficiency features, appealing to premium market segments. Ceramic glass, by contrast, offers cost-effective durability and excellent heat resistance, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious consumers seeking reliable performance. Evaluating long-term value, ceramic glass ensures sustained functionality with lower maintenance expenses, while switchable glass may justify its price through added versatility and aesthetic benefits in modern kitchen designs.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Stovetop
Switchable glass offers privacy and versatility, making it ideal for modern kitchen designs where controlling light and visibility is important, but it may be less heat-resistant than ceramic glass. Ceramic glass excels in durability and thermal shock resistance, making it the best choice for stovetops exposed to high temperatures and frequent cooking. Selecting the right glass depends on whether aesthetic flexibility or superior heat performance is the priority for your cooking environment.
Infographic: Switchable glass vs Ceramic glass for Stove top
 azmater.com
azmater.com