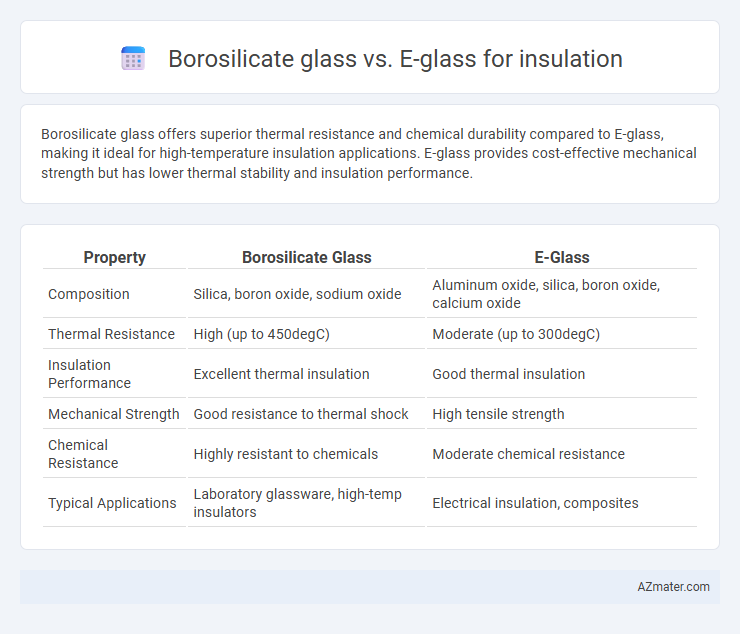
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to E-glass, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. E-glass provides cost-effective mechanical strength but has lower thermal stability and insulation performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, boron oxide, sodium oxide | Aluminum oxide, silica, boron oxide, calcium oxide |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Moderate (up to 300degC) |
| Insulation Performance | Excellent thermal insulation | Good thermal insulation |
| Mechanical Strength | Good resistance to thermal shock | High tensile strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Typical Applications | Laboratory glassware, high-temp insulators | Electrical insulation, composites |
Introduction to Glass Materials for Insulation
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications compared to E-glass, which is primarily used for its electrical insulating properties and mechanical strength. E-glass, composed mainly of silica, alumina, and calcium oxide, provides excellent dielectric strength but lower temperature tolerance compared to borosilicate glass. The choice between borosilicate and E-glass depends on specific insulation requirements such as thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical durability in industrial or electronic environments.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its exceptional thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for insulation applications where high temperature stability is required. Unlike E-glass, which is primarily used for reinforcement in composites and has moderate heat resistance, borosilicate glass withstands sudden temperature changes without cracking due to its unique composition of silica and boron oxide. This characteristic makes borosilicate glass superior for insulating environments exposed to extreme heat and thermal cycling.
What is E-Glass?
E-glass, short for electrical glass, is a type of fiberglass known for its excellent electrical insulation properties and high tensile strength. It is composed primarily of silica, alumina, boron oxide, and calcium oxide, making it a cost-effective option for thermal and electrical insulation applications. Compared to borosilicate glass, E-glass offers superior mechanical strength but lower thermal resistance, making it ideal for insulating electrical components rather than high-temperature environments.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Borosilicate glass consists primarily of silica and boron trioxide, providing excellent thermal and chemical resistance, making it ideal for insulation in high-temperature environments. E-glass, composed mainly of silica, alumina, calcium oxide, and magnesium oxide, offers good mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties but has lower chemical resistance compared to borosilicate glass. The addition of boron in borosilicate glass significantly enhances its thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, differentiating it from the standard composition of E-glass insulation materials.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its low thermal expansion coefficient of approximately 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under rapid temperature changes. E-glass, while more cost-effective, has a higher thermal conductivity ranging from 1.0 to 1.4 W/m*K, resulting in less efficient insulation compared to borosilicate glass, which typically exhibits thermal conductivities around 1.1 W/m*K or lower. The enhanced thermal stability and lower heat transfer of borosilicate glass contribute to its preferred use in high-performance insulation systems, especially in laboratory and industrial environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Borosilicate glass offers superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to E-glass, making it ideal for high-stress insulation applications exposed to rapid temperature changes. E-glass, while less resistant to thermal shock, provides good tensile strength and is more cost-effective for general insulation purposes. The durability of borosilicate glass in corrosive and high-temperature environments significantly outperforms E-glass, enhancing its lifespan in demanding insulation scenarios.
Resistance to Chemical Corrosion
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior resistance to chemical corrosion compared to E-glass due to its low alkali content and high silica composition, making it ideal for environments exposed to acids and alkalis. E-glass, primarily composed of alumina and silica but with higher alkali levels, is more prone to chemical degradation under harsh conditions. This chemical resistance makes borosilicate glass preferred for advanced insulation applications in laboratory, chemical processing, and high-performance industrial settings.
Cost and Availability
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability but comes at a higher cost compared to E-glass, making it less economically feasible for large-scale insulation projects. E-glass is more widely available and cost-effective, commonly used in insulation due to its balanced performance and affordability. The choice between borosilicate glass and E-glass for insulation primarily depends on budget constraints and the specific thermal requirements of the application.
Applications in Insulation Industries
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications in industries such as aerospace and chemical processing. E-glass provides excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength while being cost-effective, widely used in building insulation, electrical components, and fiberglass reinforcement. Both materials serve critical roles in insulation industries, with borosilicate preferred for extreme temperature stability and E-glass favored for general electrical insulation and structural applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Insulation Needs
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications, while E-glass provides excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness for general insulation purposes. For environments requiring chemical durability and thermal shock resistance, borosilicate glass insulation outperforms E-glass by maintaining integrity under extreme conditions. Selecting the right glass depends on specific insulation demands such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and budget constraints, with borosilicate suited for specialized, high-performance insulation and E-glass for standard, cost-sensitive projects.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs E-glass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com