Ion-exchange glass offers superior chemical durability and scratch resistance compared to lead glass, making it ideal for high-performance optical lenses. Lead glass provides higher refractive indices and excellent light dispersion, enhancing image clarity but with lower durability than ion-exchange alternatives.
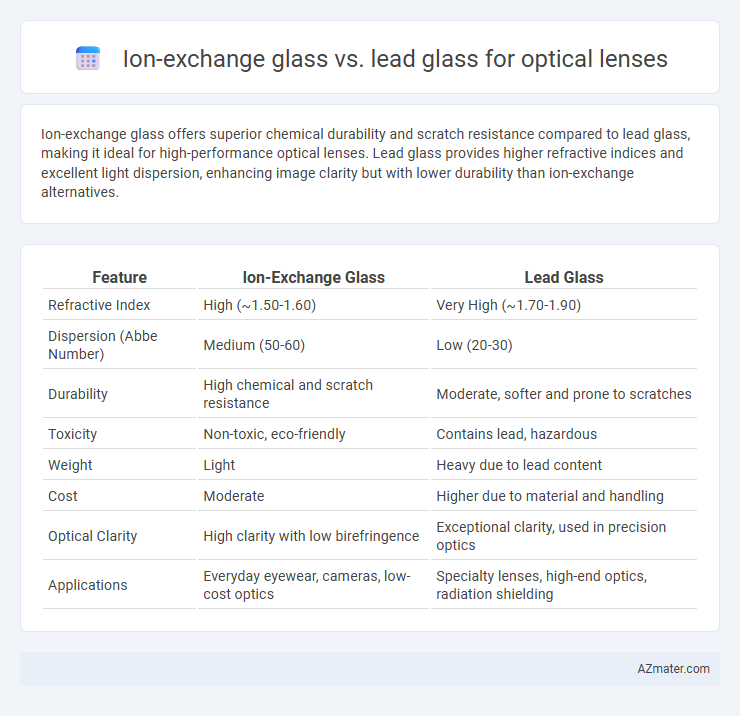
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ion-Exchange Glass | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Refractive Index | High (~1.50-1.60) | Very High (~1.70-1.90) |
| Dispersion (Abbe Number) | Medium (50-60) | Low (20-30) |
| Durability | High chemical and scratch resistance | Moderate, softer and prone to scratches |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | Contains lead, hazardous |
| Weight | Light | Heavy due to lead content |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to material and handling |
| Optical Clarity | High clarity with low birefringence | Exceptional clarity, used in precision optics |
| Applications | Everyday eyewear, cameras, low-cost optics | Specialty lenses, high-end optics, radiation shielding |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced surface strength and improved chemical durability compared to lead glass, making it a preferred choice for high-performance optical lenses. Lead glass provides superior refractive index and excellent light dispersion, beneficial for applications requiring precise image clarity and color correction. Both materials balance optical properties and mechanical resilience, with ion-exchange glass excelling in durability and lead glass optimizing optical precision.
Overview of Ion-Exchange Glass
Ion-exchange glass is an advanced optical material characterized by enhanced strength and chemical durability due to the ion-exchange process, where smaller sodium ions are replaced by larger potassium ions in the glass matrix. This treatment improves its resistance to scratches and mechanical stress, making it ideal for precision optical lenses in smartphones, cameras, and eyewear. Compared to lead glass, ion-exchange glass offers superior environmental safety and better performance in impact resistance, while maintaining excellent optical clarity and refractive properties.
Properties of Lead Glass
Lead glass exhibits high refractive index and excellent dispersion properties, enhancing image clarity and color correction in optical lenses. Its increased density and atomic weight contribute to superior brilliance and contrast compared to ion-exchange glass. However, the higher lead content results in lower chemical durability and increased weight, requiring careful handling in lens manufacturing.
Optical Performance Comparison
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior optical performance over lead glass due to its lower refractive index variation and enhanced resistance to stress-induced birefringence, resulting in clearer, more precise image quality. The higher Abbe number of ion-exchange glass reduces chromatic aberration, improving color fidelity and sharpness in optical lenses. Lead glass, while offering high density and excellent light dispersion, often suffers from increased weight and potential environmental toxicity, limiting its use in high-performance optical applications.
Durability and Mechanical Strength
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to lead glass, due to its chemically strengthened surface formed by ion-exchange processes that introduce compressive stress layers. Lead glass, while offering high refractive index and clarity, tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical stress, making it less suitable for high-impact or high-wear optical applications. The increased toughness and resistance to surface damage in ion-exchange glass make it preferable for optical lenses requiring long-term durability and structural integrity.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Ion-exchange glass offers significant environmental and health advantages over lead glass, as it eliminates the toxic lead content that poses severe risks during manufacturing and disposal. Lead glass can leach hazardous substances, contaminating ecosystems and posing health hazards to workers and end-users. Choosing ion-exchange glass reduces environmental pollution and enhances workplace safety, aligning with stringent regulatory standards on harmful materials.
Cost and Manufacturing Differences
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced surface strength through a chemical tempering process, which raises production costs compared to lead glass. Lead glass contains high levels of lead oxide, making it denser and easier to mold, resulting in lower manufacturing expenses but posing environmental and health concerns. The cost efficiency of lead glass stems from simpler melting and shaping processes, while ion-exchange glass requires additional chemical treatment steps that increase overall manufacturing complexity and expense.
Applications in Modern Optics
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for high-precision optical lenses in smartphones, cameras, and wearable devices. Lead glass provides superior refractive index and dispersion control, crucial for high-performance lenses used in microscopes, binoculars, and advanced imaging systems. Modern optics increasingly favor ion-exchange glass for everyday applications due to its toughness, while lead glass remains preferred for specialized, high-resolution optical instruments.
Advances and Innovations
Ion-exchange glass for optical lenses offers enhanced durability and resistance to mechanical stress compared to traditional lead glass, enabling thinner, lighter lenses with improved optical clarity. Recent advances in ion-exchange technology have optimized the surface compression layer, resulting in higher scratch resistance and prolonged lens lifespan. Innovations in lead glass formulations focus on reducing lead content while maintaining high refractive indices, but ion-exchange glass remains superior for applications demanding robust performance and weight reduction.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Optical Lenses
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced surface strength and resistance to scratches, making it ideal for durable optical lenses in high-impact environments. Lead glass provides superior optical clarity and higher refractive index, which is beneficial for applications requiring precise light manipulation and minimal distortion. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing mechanical durability with optical performance based on specific lens requirements.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Lead glass for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com