Antimicrobial glass for facades inhibits bacterial growth and enhances hygiene, making it ideal for healthcare and public buildings. Solar control glass reduces heat gain and glare, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort in commercial and residential facades.
Table of Comparison
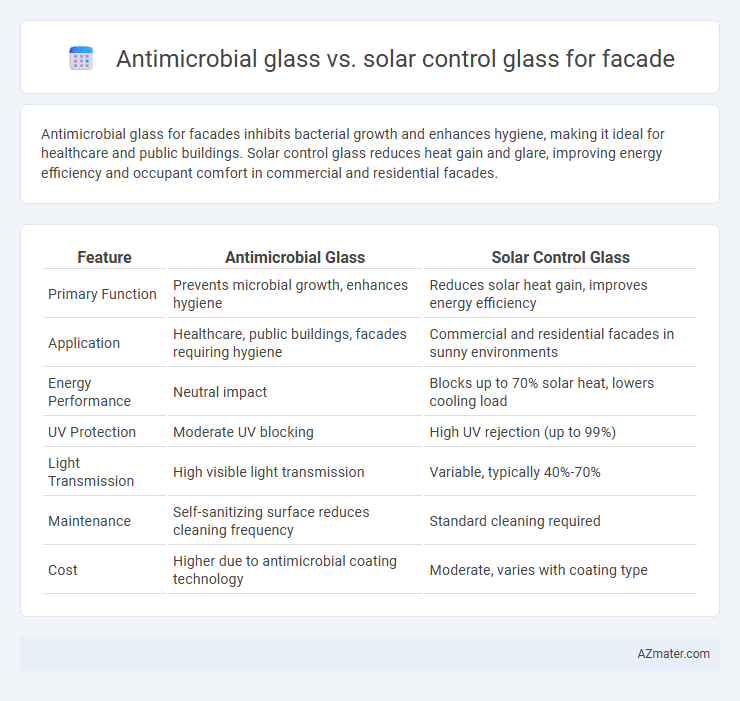
| Feature | Antimicrobial Glass | Solar Control Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevents microbial growth, enhances hygiene | Reduces solar heat gain, improves energy efficiency |
| Application | Healthcare, public buildings, facades requiring hygiene | Commercial and residential facades in sunny environments |
| Energy Performance | Neutral impact | Blocks up to 70% solar heat, lowers cooling load |
| UV Protection | Moderate UV blocking | High UV rejection (up to 99%) |
| Light Transmission | High visible light transmission | Variable, typically 40%-70% |
| Maintenance | Self-sanitizing surface reduces cleaning frequency | Standard cleaning required |
| Cost | Higher due to antimicrobial coating technology | Moderate, varies with coating type |
Introduction to Facade Glass Technologies
Antimicrobial glass for facades incorporates surface coatings that actively inhibit the growth of bacteria and viruses, enhancing hygiene in public and healthcare buildings. Solar control glass features specialized coatings or tints designed to reduce solar heat gain and glare while maintaining natural daylighting and visibility. Both technologies address distinct performance criteria in facade design--antimicrobial glass optimizes surface cleanliness and occupant health, whereas solar control glass improves energy efficiency and indoor thermal comfort.
What is Antimicrobial Glass?
Antimicrobial glass is a specialized glass embedded with ions such as silver or copper that inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi on its surface, making it ideal for hygienic environments. Unlike solar control glass, which primarily reduces heat gain and UV radiation through coatings, antimicrobial glass enhances surface cleanliness and reduces microbial contamination risks. This technology is especially beneficial for facade applications in hospitals, schools, and public buildings where maintaining a sterile environment is critical.
What is Solar Control Glass?
Solar control glass is engineered to reduce heat gain by reflecting and absorbing a significant portion of solar radiation, thereby enhancing energy efficiency in building facades. It features coatings or tints that block ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) rays while maintaining high visible light transmission for natural daylight. Unlike antimicrobial glass, which inhibits microbial growth on surfaces, solar control glass primarily optimizes thermal performance and glare reduction to improve indoor comfort and reduce cooling costs.
Key Features of Antimicrobial Glass
Antimicrobial glass features an engineered surface infused with copper or silver ions that actively inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, promoting a cleaner and safer environment. Unlike solar control glass, which primarily reduces heat gain and UV radiation through coatings that reflect or absorb solar energy, antimicrobial glass enhances hygiene by continuously reducing microbial contamination. Its key benefits include improved indoor air quality, reduced surface transmission of pathogens, and suitability for high-traffic facades in healthcare, commercial, and public buildings.
Key Features of Solar Control Glass
Solar control glass for facades offers high solar heat rejection, reducing cooling loads and enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. It features special coatings that filter ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) rays while maintaining optimal visible light transmission. This glass type improves occupant comfort by minimizing glare and preventing excessive heat buildup, making it ideal for architectural applications requiring both natural light and thermal regulation.
Performance Comparison: Health and Hygiene
Antimicrobial glass incorporates advanced coatings that inhibit microbial growth, promoting superior health and hygiene in facade applications by reducing surface contamination and the spread of pathogens. Solar control glass, while primarily designed to manage solar heat gain and improve energy efficiency, does not provide inherent antimicrobial properties, making it less effective in controlling microbial presence on facade surfaces. For environments where hygiene is paramount, such as healthcare or public buildings, antimicrobial glass offers enhanced protection compared to solar control glass, contributing to healthier indoor environments.
Performance Comparison: Energy Efficiency
Antimicrobial glass offers surface protection without significantly impacting thermal insulation, while solar control glass is engineered with low-emissivity coatings to reduce solar heat gain and enhance energy efficiency in building facades. Solar control glass can decrease cooling loads by blocking up to 80% of solar infrared radiation, directly lowering air conditioning energy consumption. In contrast, antimicrobial glass primarily targets hygiene and does not contribute to reducing HVAC energy demands.
Application Scenarios for Antimicrobial Glass
Antimicrobial glass is ideal for high-contact facade areas in healthcare facilities, schools, and public transportation hubs, where it reduces pathogen transmission and enhances hygiene. Solar control glass is primarily used in commercial or residential facades to improve energy efficiency by minimizing solar heat gain and glare. In environments demanding both health safety and energy performance, integrating antimicrobial glass with solar control properties offers a dual-function solution.
Application Scenarios for Solar Control Glass
Solar control glass is ideal for facades in commercial buildings located in hot climates, significantly reducing energy consumption by minimizing solar heat gain and glare while maintaining natural daylight. This glass type enhances occupant comfort and decreases reliance on air conditioning systems in office complexes, shopping centers, and residential high-rises. Unlike antimicrobial glass, which focuses on hygiene by inhibiting microbial growth, solar control glass primarily addresses thermal performance and energy efficiency in facade applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Facade
Antimicrobial glass incorporates a surface treatment that inhibits microbial growth, making it ideal for facades in healthcare facilities and high-traffic buildings where hygiene is critical. Solar control glass enhances energy efficiency by reflecting solar radiation, reducing heat gain, and improving indoor comfort in commercial and residential facades exposed to intense sunlight. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing hygiene needs with energy performance requirements, considering factors such as building location, usage, and environmental impact.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs Solar control glass for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com