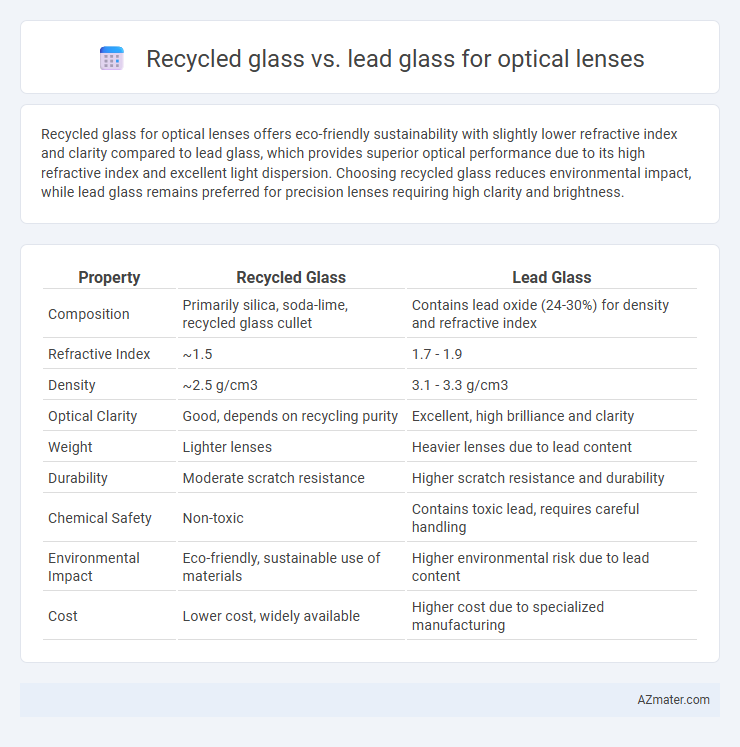
Recycled glass for optical lenses offers eco-friendly sustainability with slightly lower refractive index and clarity compared to lead glass, which provides superior optical performance due to its high refractive index and excellent light dispersion. Choosing recycled glass reduces environmental impact, while lead glass remains preferred for precision lenses requiring high clarity and brightness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Glass | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Primarily silica, soda-lime, recycled glass cullet | Contains lead oxide (24-30%) for density and refractive index |
| Refractive Index | ~1.5 | 1.7 - 1.9 |
| Density | ~2.5 g/cm3 | 3.1 - 3.3 g/cm3 |
| Optical Clarity | Good, depends on recycling purity | Excellent, high brilliance and clarity |
| Weight | Lighter lenses | Heavier lenses due to lead content |
| Durability | Moderate scratch resistance | Higher scratch resistance and durability |
| Chemical Safety | Non-toxic | Contains toxic lead, requires careful handling |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable use of materials | Higher environmental risk due to lead content |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to specialized manufacturing |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Recycled glass and lead glass serve distinct roles in optical lens manufacturing, with recycled glass offering an eco-friendly option that reduces raw material consumption while maintaining acceptable optical clarity for certain applications. Lead glass, characterized by its high refractive index and excellent light dispersion, remains preferred for precision lenses requiring superior optical performance such as in microscopes and high-end cameras. Optical lens materials are selected based on factors like refractive index, Abbe number, and environmental impact, where recycled glass provides sustainability benefits and lead glass offers unmatched optical quality.
Overview of Recycled Glass in Optics
Recycled glass in optics offers a sustainable alternative to traditional materials by repurposing waste glass into high-quality lenses with comparable clarity and durability. Its reduced environmental footprint aligns with green manufacturing practices while maintaining essential optical properties like refractive index and light transmission. Advances in purification and processing techniques enhance the performance of recycled glass lenses, making them increasingly viable for both consumer and industrial optical applications.
Properties of Lead Glass for Optical Applications
Lead glass exhibits a high refractive index and exceptional clarity, making it ideal for precision optical lenses. Its density and high dispersion enhance light refraction and minimize chromatic aberration, crucial for applications requiring sharp imaging. The material's durability and resistance to chemical degradation ensure long-lasting performance in demanding optical environments.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Lead Glass
Recycled glass lenses significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and raw material extraction compared to lead glass production, which involves toxic lead compounds harmful to ecosystems. The recycling process minimizes landfill waste and decreases CO2 emissions, while lead glass manufacturing poses hazardous waste disposal challenges and potential soil and water contamination. Choosing recycled glass not only supports sustainable resource use but also mitigates long-term ecological risks linked to lead toxicity in optical lens production.
Optical Performance Comparison
Recycled glass lenses exhibit slightly lower refractive indices and higher chromatic aberration compared to lead glass, which offers superior optical clarity and brightness due to its high lead oxide content. Lead glass lenses provide enhanced light dispersion and reduced optical distortions, making them ideal for precision optical applications requiring high resolution and color accuracy. However, recycled glass lenses contribute to environmental sustainability with acceptable performance trade-offs for general optical uses.
Durability and Lifespan
Recycled glass lenses offer moderate durability but typically have a shorter lifespan compared to lead glass lenses, which are renowned for their superior hardness and resistance to scratches. Lead glass's higher density and refractive index enhance optical performance while providing enhanced structural integrity, making it more suitable for long-term use in optical applications. However, recycled glass can be more environmentally friendly but may require additional treatments to approach the durability standards of lead glass in lenses.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Recycled glass for optical lenses offers significant cost advantages due to lower raw material expenses and reduced environmental impact, making it a sustainable choice in lens manufacturing. Lead glass, while more expensive because of the high lead content and complex refining processes, provides superior optical properties such as higher refractive index and better clarity. Manufacturing with recycled glass generally involves less energy-intensive processing, whereas lead glass production demands stringent safety protocols and specialized equipment due to toxicity concerns.
Safety and Health Concerns
Recycled glass used in optical lenses often contains fewer hazardous substances compared to lead glass, reducing the risk of lead exposure and associated health issues such as neurological damage. Lead glass, characterized by its high refractive index and clarity, poses significant safety concerns during manufacturing and disposal due to lead's toxicity and potential for environmental contamination. Choosing recycled glass for optical lenses enhances safety by minimizing lead-related health hazards while supporting sustainable material reuse practices.
Market Trends and Industry Preferences
The optical lens market is witnessing a growing preference for recycled glass due to increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products, with recycled glass offering comparable optical clarity and reduced production costs. Lead glass remains favored in high-precision optical applications for its superior refractive index and brilliance, despite rising concerns over lead toxicity and stricter safety standards. Industry trends indicate a gradual shift towards eco-friendly materials such as recycled glass, driven by advancements in purification technologies and regulatory pressures limiting lead content in consumer optics.
Future Developments in Optical Lens Materials
Recycled glass in optical lenses offers sustainable advantages by reducing environmental impact and conserving raw materials, but challenges remain in achieving the high refractive index and clarity of lead glass. Future developments focus on enhancing recycled glass purity and developing composite materials that combine recycled elements with advanced polymers to match or exceed lead glass optical performance. Innovations in nanotechnology and material engineering are expected to drive breakthroughs in lens durability, weight reduction, and optical precision, positioning recycled glass as a viable alternative in next-generation optical lenses.
Infographic: Recycled glass vs Lead glass for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com